Cell Organization
Category : 11th Class
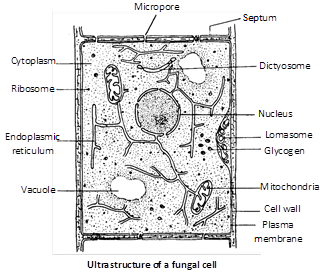
The cell wall of fungi is mainly made up of chitin and cellulose. While chitin is a polymer of N-acetyl glucosamine, the celulose is polymer of d-glucose. Precisely, the cell wall may be made up of cellulose-glucan (oomycetes), chitin-chitosan (Zygomycetes), mannan-glucan (Ascomycetes), chitin-mannan (Basidiomycetes) and chitin-glucan (some Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes). Besides, the cell wall may be made up of cellulose-glycogen, cellulose-chitin or polygalactosamine-galactan.
The cell wall is closely associated with the inner layer, the plasma membrane. In fungi, plasma membrane bears coiled membranes outgrowth called lomasomes (Moore and McAlear, 1961).
Fungi cells are eukaryotic. They possess all eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria, E.R., ribosomes, microbodies, lysosomes, vacuoles and reserve food particles (glycogen, lipid etc.). Golgi body or dictyosome are also not typical. In many cases they are unicisternal. The cells lack chloroplast. However, a reddish pigment, neocercosporin has been isolated from the fungus Cercospora kikuchii. The vacuoles are bound by tonoplast. The genetic material is DNA.
Near the hyphal tip the cytoplasm contains small vesicular structure called chitosomes (Barker et.al, 1974). They contain cell wall material.
Fungi possess true nucleus having definite nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope persists during nuclear division. It has called karyochorisis by Moore (1965). The nuclear spindle is formed within the nuclear envelope in both mitosis and meiosis. The spindle poles either contain centrioles are spindle pole bodies (SPB) but lack microtubular organization.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
