LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson - will help you to:-
- appreciate the cultural diversity in food.
- study about food derived from plants and animals.
- learn about various fuels and vessels used in cooking.
- learn about various techniques of preparing food.
- study about food for animals.
Real Life Examples
- Many food such as rice, idlis, momos etc are cooked by the process of steaming.
- According to the age, the diet of a person also varies. For ex. A small child takes only milk and liquid food but adults and young persons have the capacity to eat and digest various foods.
Amazing Facts
- The first soup was made of hippopotamus.
- There are more than 10,000 varieties of tomatoes.
- Watermelons are 97% water, lettuce 97%, tomatoes 95%, carrots 90%, and bread 30%.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
- Like water, food is also essential for the survival.
- Every living organism needs food.
CULTURAL DIVERSITY IN FOOD
- Like everything, food also varies from culture to culture.
- Across the world, different foods are prepared using different traditional vessels, cooking methods and ingredients which are popular in their culture.
- The foods we eat help to understand and connect us to different worlds and to different times.
For example. The English are associated with fish and chips; Americans with hamburgers and chewing gum and Italians with pizza and parmesan cheese.
- In India, different cultures persist and accordingly there are various food items.
For example. Kashmiri food, Gujarati food, Punjabi food, South-Indian food etc are all examples of how different cultures live on the same land.
FOOD FROM PLANTS
- Plants are the major source of food.
- Plants prepare food by the process of photosynthesis using water, sunlight and carbon-dioxide.
- Plants give us fruits and vegetables.
- Several spices and herbs are also obtained from plants.
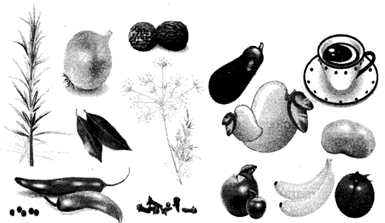
PARTS OF PLANTS THAT ARE EATEN
Almost every part of a plant is eaten. But there is hardly any plant that is eaten whole.
Different parts of a plant that are eaten are- roots (carrot, radish, turnip etc), stems (celery, lotus-stem etc), leaves (cabbage, spinach, coriander etc), seeds (ex. peas), fruit (cherry, mango, apple, pear etc), flower (ex. Rose, saffron etc).
FOOD FROM ANIMALS
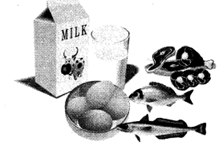
- The food from animals includes milk, meat, eggs, etc.
- The products from milk are called dairy products. For example: curd, cream, cheese etc.
- Poultry products are those which we obtain from poultry animals such as hen. For example: Eggs and chicken.
- Sea-foods are those food items that we obtain from sea-animals. For example: Fish, shrimps, prawns etc.
- Food from animals is called non-vegetarian food.
Historical Preview
- The early man derived its first food from the water in the from of sea animals. And later on only he discovered various fruits and vegetables in the jungle.
- Earlier food was cooked by burning the wood, coal or cowdung.
- In the middle Ages, sugar was a treasured luxury costing 9 times as much as milk.
Misconcept/ Concept
Misconcept: Meat is the best source of protein
Concept: Many vegetarian food also contain high protein like chickpeas, lentils, paneer, nuts etc.
Misconcept: Coffee beans are beans.
Concept: coffee beans are not beans. They are seeds.
Misconcept: Frozen fruits and vege-tables are less nutritious than fresh ones.
Concept: It’s true only if you eat them right out of the garden. All nutrient levels drop somewhat during shipping and storage. Most frozen fruits and vegetables are picked ripe and immediately frozen, so actually retain most of their nutrients.
FOOD THAT CAN BE EATEN RAW
- Some food items can be eaten raw without cooking. For example: fruits like apple, banana, grapes, watermelons, oranges etc.
- Most of the food items need to be cooked before they can be eaten. For example: vegetable, meat, fish, chapatis etc.
- Cooking makes the food tasty, healthy and digestible.
Shortcut to Problem Solving
- Dry fruits are the fruits that are dried. Ex. Raisins are dried grapes. They are dried to remove the Moisture from them so that the can be eaten for a long time. Dry fruits contain all the nutrients of a fresh fruit.
- Frozen fruits are those which are immediately frozen after plucking so as to keep them fresh and to retain their moisture content.
Ex. Frozen berries.
FUELS USED IN COOKING
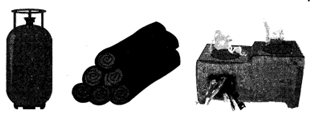
- Since many years, different fuels are being used to cook food. For example: Coal, wood, cow-dung, kerosene, LP6. LPG is used in modern households nowadays.
DIFFERENT VESSELS AND CONTAINERS IN WHICH FOOD ARE MADE
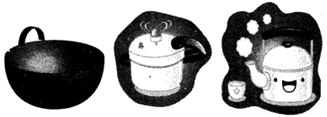
- Vessels and containers of different shapes and sizes are available for cooking.
- Vessels are made of different metals. Most commonly used metals that are used for making vessels and containers for cooking are iron, steel, aluminum, etc.
- Ceramics and glass are also used for making different utensils.
- Pans, bowls, flat-pans, pressure-cookers, kettles, pots, boilers etc are all used in cooking.
WHAT DO DOMESTIC AND WILD ANIMALS EAT?
- Food eaten by domestic and wild animals differ considerably.
- Domestic animals such as cats, dogs, rabbits, birds etc eat food provided by their masters.
- Wild animals that live in jungles eat just about anything from flesh of other animals to wild fruits and vegetables.
- Nowadays, different food products are available in the market especially for domestic animals.
VARIOUS METHODS OF COOKING
- Various cooking methods include boiling, simmering, steaming, baking, roasting and frying.
FOOD HABITS ACCORDING TO GENDER AND AGE
- Small kids drink only milk and liquids.
- Males have more diet than females.
- Food habit depends on your culture, your family and also your friends.
- Since early time, women have been associated with cooking.
- Our lifestyle determines our food habits.




