Plants
Category : 3rd Class
Amazing Facts
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to: -
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
What are plants?
Plants are living things. They occur in many different shapes and sizes. Plants grow in soil or water. They make their own food and store their food in roots, stems, leaves, fruits or flowers. Plants produce flowers of different colours, shapes and sizes.

PARTS OF PLANTS
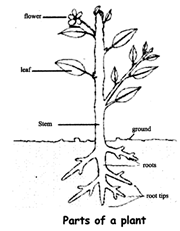
5. Fruits have seeds or they may be seedless. Seeds can give rise to a new plant of the same kind. 
TYPES OF PLANTS
1. Trees are the large plants with a tall, strong and woody stem.
(a) Some stems are thick, strong and woody. They are covered with bark. For example: A stem of Neem.
(b) Some stems are thick but they are soft. For example: A banana stem.

2. Climbers and Creepers grow along the ground or up the sides of walls or trees. These have a weak stem. These cannot grow erect without support. For example: Money Plant, Watermelon.
3. Grass is of many kinds. They can be short or tall, brown, yellow or green.

4. Shrubs are small plants. They have many separate stems which grow from near the ground. The stems are hard and do not bend easily. 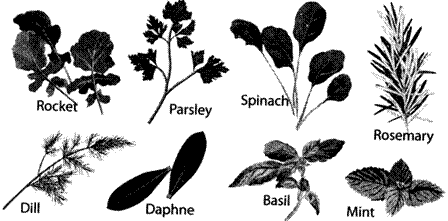
5. Herbs are plants that are valued for flavour, scent, medicinal or other qualities. Weeds are also herbs. Weeds are unwanted plants that grow where we don't want them to grow! They can grow almost everywhere

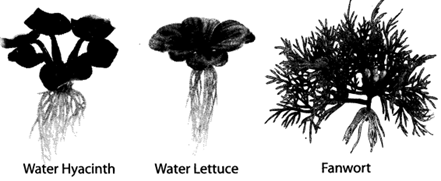
6. Aquatic plants grow in water or in wet soil under water.
TYPES OF LEAVES
Leaves are made to catch light and have openings to allow water and air to come and go. The outer surface of the leaf has a waxy coating called a cuticle which protects the leaf. Veins carry water and nutrients within the leaf.
Leaf has a flat and broad part called leaf blade which has tiny holes. These holes are called stomata. Plants breathe air in and out through these stomata. Leaves contain a substance called chlorophyll. It helps making food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight the process by which plants make their food from air, water and sunlight is called photosynthesis.
Historical preview

DIFFERENT PATTERNS OF LEAVES

CHANGING PLANTS
Plants can be seasonal or evergreen/perennial. Evergreen/ perennial plants are those which grow throughout the year and do not shed their leaves in a particular season. For example: Garden asparagus and peepal. Seasonal plants are those which grow during a particular season and shed their leaves in a particular season. For example: Sal and Oak. Some plants grow fruits and vegetables only in winters whereas some other plants grow fruits and vegetables only in summers. Some winter fruits and Vegetables are orange and peas. Some summer fruits and Vegetables are cucumber and mango. During dry season of summer or winter when there is a shortage of water, trees shed their leaves to save water. In deserts, we find plants like cactus and babul whose leaves are in the form of spines. In these plants stems store water instead of eaves.
Sowing of Seeds: There are two methods of sowing seeds:
(A) Direct method and (B) Indirect method. In (A) direct method, seeds of crop plants like wheat, maize, gram, beans etc. are scattered and sown directly in the field. In (B) indirect method, seeds of crops like rice are grown first in small seedbeds. When the seedlings are few inches high, they are taken out and planted in the fields. This method is also called as transplanting.
USES OF PLANTS
1. Plants clean the air - Plants make the air clean by converting atmospheric carbon-dioxide into useful oxygen. Which we use for breathing.
2. Plants give us food- We eat fruits, vegetables, nuts, berries, grains, roots, stems, leaves and seeds of some plants. For example leaves of spinach, coriander, mint, lettuce and tea are used in our daily lives. our daily lives.+
3. Plants decorate our surroundings. Plants make garden look beautiful. We use flowers and leaves from plants for decoration.
4. Plants provide homes - Some birds and animals make their homes in plants. They also get their food from plants.
5. Plants give us fibers - We use cotton fibers to make thread and cloth. Jute fibre is used to make sacks bags, mats and ropes etc.
6. Trees give us wood - We use wood to make pencil, ladder, box, chair, paper, boat, furniture etc.
7. Plants give us other useful items like rubber, oil, perfume, medicines, manure etc. For example leaves of neem, aloevera and tulsi are used as medicines. used as medicines.

Misconcept/ Concept Misconcept:
Leaves are always green. Concept: Leaves can be of different colours. The colour we see actually comes from the green colour of chlorophyll and deep red or yellow colours from pigments of various chemicals. Misconcept: Leaves take in water. Concept: water is taken in through the roots.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
