Plant
Category : 8th Class
Cells are the structural and functional unit of life. All the living organisms are made up of the cells. It comprises of various cell organelles, which performs the function within the cell. The basic structure of a plant cell is given below:
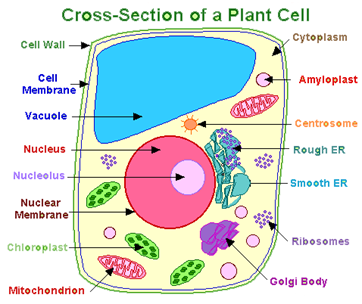
![]() The Various Cell Organelles of the Plant Cell are Given Below
The Various Cell Organelles of the Plant Cell are Given Below
![]() Amyloplast
Amyloplast
An organelle, found in some plant cells that stores starch. Amyloplasts is found in starchy plants, like tubers and fruits.
![]() ATP
ATP
ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. It is a high-energy molecule used for energy storage by organisms. In plant cell ATP is produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
![]() Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
The thin layer of protein and fats that surrounds the cell from inside the cell wall, is called the cell membrane. It is selectively semipermeable and allows only some selective substances to pass into the cell through it, blocking others.
![]() Cell Wall
Cell Wall
It is a thick and rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. It is made up of cellulose fiber, which gives the cell most rigidity and support to the structure. The cell wall also helps to connect with other cell wall, to form the structure of the plant.
![]() Centrosome
Centrosome
They are the small bodies located near the nucleus. It consists of a dense center containing radiating tubules. The centrosomes are made up of microtubules. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosomes divides into two parts, which move to the opposite sides of the dividing cell. Unlike the centrosomes in animal cells, the plant cell centrosomes do not have centrioles.
![]() Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is the molecules that can use light energy from sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide gas into sugar and oxygen, during the process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is magnesium based and is usually green, which provides green colour to the plants.
![]() Chloroplast
Chloroplast
It is an elongated or disc-shaped organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis in plants takes place in the chloroplasts.
![]() Christae
Christae
It is the multiple-folded inner membrane of a cell organelle. In mitochondria, it is a finger-like projections. The cell produces energy (ATP) on the walls of the cristae.
![]() Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
It is the jelly like material outside the nucleus. It contains the cell organelles.
![]() Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus
They are also known as golgi complex. They are flattened, layered and sac-like organelle and look like a stack of books. They are located near the nucleus. The golgi body packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles to transport it from one part of the body to another part.
![]() Granum
Granum
It is a stack of thylakoid disk inside the chloroplast.
![]() Mitochondria
Mitochondria
It is a special cell organelles, which is spherical or rod-shaped with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections called cristae. Its outer layer gives it the required shape. The mitochondria converts the energy stored in cell from glucose into ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) for the use of cell. This energy is used by cell to perform all the basic functions within the body.
![]() Nuclear Membrane
Nuclear Membrane
It is the membrane that bounds the nucleus and separates it from the rest of the cell.
![]() Nucleolus
Nucleolus
The organelles within the nucleus, where ribosomal RNA is produced, is called nucleolus.
![]() Nucleus
Nucleus
It is the spherical body containing many organelles. It controls the functions of the cell by controlling protein synthesis. It contains DNA in chromosomes. It is surrounded by the nuclear membrane.
![]() Ribosome
Ribosome
These are the small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules. It is a site of protein synthesis. It is of two types:
(i) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): It is a vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks, that are located in the cytoplasm. RER contains ribosomes, which gives it a rough appearance. It transports materials through the cell and helps in protein synthesis.
(ii) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): It is a vast system of interconnected/ membranous, infolded tubes, which are located in the cytoplasm. The space within the SER is called the SER lumen. It transports materials through the cell and contains enzymes that produce and digest lipids (fats) and membrane proteins. SER develops from RER and transports the newly-made proteins and lipids to the golgi body.
![]() Stroma
Stroma
It is a part of the chloroplast in plant cell. It is located within the inner membrane ofchloroplasts.
![]() Thylakoid Disk
Thylakoid Disk
They are the disk-shaped membrane structures in the chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll. It is made up of stacks ofthylakoid disks, which are called granum. Photosynthesis takes place in thylakoid disks.
![]() Vacuole
Vacuole
It is a large membrane-bound space within a cell. It is filled with fluid. Most plant cells have single vacuole that occupies much of the cell. It helps to maintain the shape of the cell and provide turgidity and rigidity to the cell.

![]() As we prepare our food in our kitchen, cell also has kitchen to prepare their food. Name the organ, which is also called the kitchen of the cell.
As we prepare our food in our kitchen, cell also has kitchen to prepare their food. Name the organ, which is also called the kitchen of the cell.
(a) Vacuoles
(b) Stroma
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Ribosomes
(e) None of these
Answer: (c)
Explanation
The kitchen of the cell, where the energy is produced is mitochondria.
![]() The cell have different organelles to perform different functions, right from the preparation of food to digestion of food. It also the transports the food from one part of the cell to another part. The organelles which helps in protein synthesis within the cell is:
The cell have different organelles to perform different functions, right from the preparation of food to digestion of food. It also the transports the food from one part of the cell to another part. The organelles which helps in protein synthesis within the cell is:
(a) RER
(b) SER
(c) Granum
(d) Thylakoid
(e) None of these
Answer: (a)
Explanation
The ribosome helps in protein synthesis in the cell and it lies on the endoplasmic reticulum. Hence it is known as RER.
![]() Cell Diversity
Cell Diversity
A group of cell, having similar shape and performing similar functions, are called tissues. There are four main types of plant tissues, namely dermal tissue, ground tissue, vascular tissue and meristernatic tissue. The shape and structure of the cell depends on their location and function within the organism.
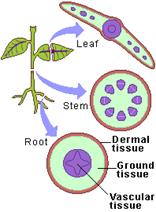
Cell Diversity

![]() Plant absorbs nutrient and water from the soil for its growth and development. Maria kept a potted plant on her terrace. She provided sufficient amount of sunlight and water and observed that the plant was absorbing water from the soil. The tissue which is responsible for absorption of water from the soil is ______.
Plant absorbs nutrient and water from the soil for its growth and development. Maria kept a potted plant on her terrace. She provided sufficient amount of sunlight and water and observed that the plant was absorbing water from the soil. The tissue which is responsible for absorption of water from the soil is ______.
(a) Phloem tissue
(b) Xylem tissue
(c) Cortex tissue
(d) Dermal tissue
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
Explanation
The tissue responsible for absorptions of water and mineral from the soil is xylem tissue.
![]() Thomas cuts a cross section of stem and observes that, there are different concentric layers on the cross section. On touching, he finds that the central part is very soft and droplets of water is coming out of it. The central part is made up of which tissues?
Thomas cuts a cross section of stem and observes that, there are different concentric layers on the cross section. On touching, he finds that the central part is very soft and droplets of water is coming out of it. The central part is made up of which tissues?
(a) Dermal tissue
(b) Ground tissue
(c) Vascular tissue
(d) Conducting tissue
(e) None of these
Answer: (c)
Explanation
The tissue which helps in transmission of nutrient from bottom to the top of the plant is vascular tissue..
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
