Xylenes (Dimethyl benzene) \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}\]
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
The molecular formula, \[{{C}_{8}}{{H}_{10}}\] represents four isomers.
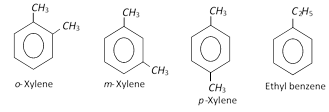
These are produced along with benzene, toluene and ethylbenzene when aromatisation of \[{{C}_{6}}-{{C}_{8}}\] fraction of petroleum naphtha is done. The xylenes are isolated from the resulting mixture (BTX) by fractional distillation.
These can be prepared by Wurtz ? Fittig reaction. A mixture of bromotoluene and methylbromide is treated with sodium in dry ethereal solution to form the desired xylene.
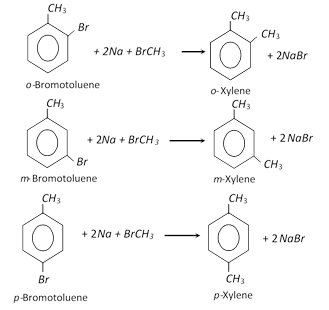
These can also be obtained by Friedel – craft's synthesis,
m-Xylene can be obtained from mesitylene.
Xylenes are colourless liquids having characteristic odour. The boiling points of three isomers are,
o-Xylene=144°C; m-Xylene=139°C; p-Xylene=138°C.
Xylenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions in the same manner as toluene. Upon oxidation with \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\] or \[{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}\], Xylenes form corresponding dicarboxylic acids.
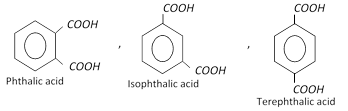
Xylenes are used in the manufacture of lacquers and as solvent for rubber. o-Xylene is used for the manufacture of phthalic anhydride.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
