Analog and Digital Signals
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
In communication system, a signal means a time varying electrical signal containing informations.
(1) Analog signals : It is a continuous wave form which changes smoothly over time.
(i) Such signals can be easily generated from the source of information by using an appropriate transducer e.g. pressure variations in the sound waves can be converted into corresponding current or voltage pulses with the help of a microphone.
(ii) A simple analog signal is represented by a sine wave
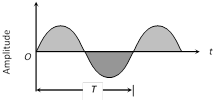
(iii) The frequency of analog signals associated with speed or music varies over a range between 20 Hz to 20 KHz. (iv) The range over which the frequencies of a signal vary is called band width.
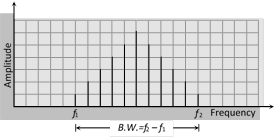
(v) The term base band designates the band of frequencies representing the signal supplied by the source of information.
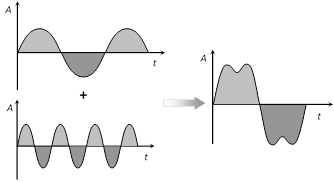
(vi) A signal consist of two or more waves of different frequencies is known as a complex analog signal.
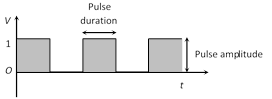
(2) Digital signals : A digital signal is a discontinuous function of time. It has only two voltage level i.e. either low (0) or high (1).
Either of 0 and 1 is known as bit. A group of bit is called byte. A byte comprising of 2 bits can give on the four code combination i.e. 00, 01, 10 and 11.
The number of code combination increase with number of bits in a byte is given by \[N={{2}^{x}}\], where x = number of bits in a byte.
The number of binary digits (bits) per second, which describe a digital signal is called it's bit rate. Bit rate is expressed in bits per second (bps).
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
