Principle of Laser
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
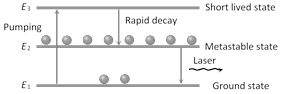
Atoms from the ground state \[{{E}_{1}}\] are 'pumped' up to an excited state \[{{E}_{3}}\]. From \[{{E}_{3}}\] the atom decay rapidly to state of energy \[{{E}_{2}}\]. For lasing (lasing means laser action) to occur, this state must be metastable. If conditions are right, state \[{{E}_{2}}\] can then become more heavily populated than state \[{{E}_{1}}\], thus providing the needed population inversion.
When photon of energy \[h\nu ={{E}_{2}}-{{E}_{1}}\] is incident on one of the atoms present in the metastable state, the atom will drop to lower energy state \[{{E}_{1}}\], emitting a photon of same energy as that of the incident photon, which is in phase with it and is emitted in the same direction. The two photons, then interact with two more atoms present in metastable state and so on. This process is called amplification of light.
For smooth process two conditions are necessary
(1) The metastable state should all the time have larger number of atoms than the number of atoms in lower energy state.
(It is achieved by pumping)
(2) The photons emitted due to stimulated emission should stimulate other atoms to multiply the photons inside the system.
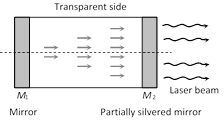
(It is achieved by two mirrors are fixed at the ends of the system containing lasing material. The mirrors reflect the photons back and forth to keep them inside the region for a long time.)
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
