Positive Rays
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
When potential difference is applied across the electrodes of a discharge tube (\[{{10}^{-3}}\,mm\] of Hg), electrons are emitted from the perforated cathode. As they move towards anode, they gain energy. These energetic electrons when collide with the atoms of the gas in the discharge tube, they ionize the atoms. The positive ions so formed at various places between cathode and anode, travel towards the cathode. Since during their motion, the positive ions when reach the cathode, some pass through the holes in the cathode and a faint luminous glow comes out from each hole on the backside of the cathode. It is called positive rays, which are coming out from the holes.
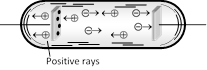
(1) Positive rays are positive ions having same mass if the experimental gas does not have isotopes. However if the gas has isotopes then positive rays are group of positive ions having different masses.
(2) They travel in straight lines and cast shadows of objects placed in their path. But the speed of the positive rays is much smaller than that of cathode rays.
(3) They are deflected by electric and magnetic fields but the deflections are small as compared to that for cathode rays.
(4) They show a spectrum of velocities. Different positive ions move with different velocities. Being heavy, their velocity is much less than that of cathode rays.
(5) q /m ratio of these rays depends on the nature of the gas in the tube (while in case of the cathode rays q/m is constant and doesn't depend on the nature of gas in the tube). q/m for hydrogen is maximum.
(6) They carry energy and momentum. The kinetic energy of positive rays is more than that of cathode rays.
(7) The value of charge on positive rays is an integral multiple of electronic charge. (8) They cause ionisation (which is much more than that produced by cathode rays).
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
