Heat Engine
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
Heat engine is a device which converts heat into work continuously through a cyclic process.
The essential parts of a heat engine are
(1) Source : It is a reservoir of heat at high temperature and infinite thermal capacity. Any amount of heat can be extracted from it.
(2) Working substance : Steam, petrol etc.
(3) Sink : It is a reservoir of heat at low temperature and infinite thermal capacity. Any amount of heat can be given to the sink.
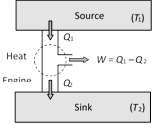
The working substance absorbs heat \[{{Q}_{1}}\] from the source, does an amount of work W, returns the remaining amount of heat to the sink and comes back to its original state and there occurs no change in its internal energy.
By repeating the same cycle over and over again, work is continuously obtained.
The performance of heat engine is expressed by means of ?efficiency? \[\eta \] which is defined as the ratio of useful work obtained from the engine to the heat supplied to it.
\[\eta =\frac{\text{Work done}}{\text{Heat input}}=\frac{W}{{{Q}_{1}}}\]
For cyclic process \[\Delta U=0\] hence from FLOT \[\Delta Q=\Delta W\]
So \[W={{Q}_{1}}-{{Q}_{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[\eta =\frac{{{Q}_{1}}-{{Q}_{2}}}{{{Q}_{1}}}=1-\frac{{{Q}_{2}}}{{{Q}_{1}}}\]
A perfect heat engine is one which converts all heat into work i.e. \[W={{Q}_{1}}\] so that \[{{Q}_{2}}=0\] and hence\[\eta =1\].
But practically efficiency of an engine is always less than 1.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
