Isobaric Process
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
When a thermodynamic system undergoes a physical change in such a way that its pressure remains constant, then the change is known as isobaric process.
(1) Equation of state : In this process V and T changes but P remains constant. Hence Charle?s law is obeyed in this process.
Hence if pressure remains constant \[V\propto T\Rightarrow \frac{{{V}_{1}}}{{{T}_{1}}}=\frac{{{V}_{2}}}{{{T}_{2}}}\]
(2) Indicator diagram : Graph 1 represent isobaric expansion, graph 2 represent isobaric compression.
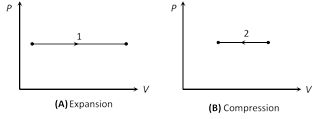
Slope =\[\frac{dP}{dV}=0\] Slope = \[\frac{dP}{dV}=0\]
(i) In isobaric expansion (Heating)
Temperature \[\xrightarrow{\,\,\,\,}\] increases so \[\Delta U\] is positive
Volume \[\xrightarrow{\,\,\,\,}\] increases so \[\Delta W\] is positive
Heat \[\xrightarrow{\,\,\,\,}\] flows into the system so \[\Delta Q\] is positive
(ii) In isobaric compression (Cooling)
Temperature \[\xrightarrow{\,\,\,\,}\] decreases so \[\Delta U\] is negative
Volume \[\xrightarrow{\,\,\,\,}\] decreases so \[\Delta W\] is negative
Heat \[\xrightarrow{\,\,\,\,}\] flows out from the system so \[\Delta Q\] is negative
(3) Specific heat : Specific heat of gas during isobaric process \[{{C}_{P}}=\left( \frac{f}{2}+1 \right)R\]
(4) Bulk modulus of elasticity : \[K=\frac{\Delta P}{\frac{-\Delta V}{V}}=0\] [As \[\Delta P=0\]]
(5) Work done in isobaric process
\[\Delta W=\int_{{{V}_{i}}}^{{{V}_{f}}}{P\,dV}=P\int_{{{V}_{i}}}^{{{V}_{f}}}{dV}=P[{{V}_{f}}-{{V}_{i}}]\] [As P = constant]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\Delta W=P({{V}_{f}}-{{V}_{i}})=\mu R[{{T}_{f}}-{{T}_{i}}]=\mu R\,\Delta T\]
(6) FLOT in isobaric process : From \[\Delta Q=\Delta U+\Delta W\]
\[\because \] \[\Delta U=\mu \,{{C}_{V}}\,\Delta T\]\[=\mu \frac{R}{(\gamma -1)}\Delta T\] and \[\Delta W=\mu R\,\Delta T\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[{{(\Delta Q)}_{P}}=\mu \frac{R}{(\gamma -1)}\Delta T+\mu R\,\Delta T\]\[=\mu \left( \frac{\gamma }{\gamma -1} \right)R\,\Delta T\]\[=\mu \,{{C}_{P}}\,\Delta T\]
(7) Examples of isobaric process : All state changes occurs at constant temperature and pressure.
Boiling of water
(i) Water \[\xrightarrow{\,}\] vapours
(ii) Temperature \[\xrightarrow{{}}\] constant
(iii) Volume \[\xrightarrow{\,}\]increases
(iv) A part of heat supplied is used to change volume (expansion) against external pressure and remaining part is used to increase it's potential energy (kinetic energy remains constant)
(v) From FLOT \[\Delta Q=\Delta U+\Delta W\Rightarrow mL=\Delta U+P({{V}_{f}}-{{V}_{i}})\]
Freezing of water
(i) Water \[\xrightarrow{\,}\] ice
(ii) Temperature \[\xrightarrow{\,}\] constant
(iii) Volume \[\xrightarrow{\,}\]increases
(iv) Heat is given by water it self. It is used to do work against external atmospheric pressure and to decreases the internal potential energy.
(v) From FLOT \[\Delta Q=\Delta U+\Delta W\Rightarrow -mL=\Delta U+P({{V}_{f}}{{V}_{i}})\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
