Doppler's Effect
Category : JEE Main & Advanced

Whenever there is a relative motion between a source of sound and the observer (listener), the frequency of sound heard by the observer is different from the actual frequency of sound emitted by the source.
The frequency observed by the observer is called the apparent frequency. It may be less than or greater than the actual frequency emitted by the sound source. The difference depends on the relative motion between the source and observer.
(1) When observer and source are stationary
(i) Sound waves propagate in the form of spherical wavefronts (shown as circles)
(ii) The distance between two successive circles is equal to wavelength \[\lambda \].
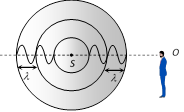
(iii) Number of waves crossing the observer = Number of waves emitted by the source (iv) Thus apparent frequency \[(n')=\] actual frequency \[(n)\].
(2) When source is moving but observer is at rest
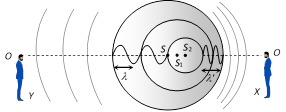
(i) \[{{S}_{1}},\,{{S}_{2}},\,{{S}_{3}}\] are the positions of the source at three different positions.
(ii) Waves are represented by non-concentric circles, they appear compressed in the forward direction and spread out in backward direction.
(iii) For observer (X)
Apparent wavelength \[\lambda '<\] Actual wavelength \[\lambda \]
\[\Rightarrow \] Apparent frequency \[n'>\] Actual frequency \[n\]
For observer (Y) : \[\lambda '>\lambda \]\[\Rightarrow n'<n\]
(3) When source is stationary but observer is moving
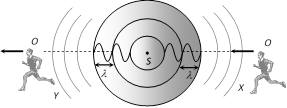
(i) Waves are again represented by concentric circles.
(ii) No change in wavelength received by either observer X or Y.
(iii) Observer X (moving towards) receives wave fronts at shorter interval thus \[n'>n.\]
(iv) Observer Y receives wavelengths at longer interval thus \[n'<n.\]
(4) General expression for apparent frequency : Suppose observed (O) and source (S) are moving in the same direction along a line with velocities \[{{v}_{O}}\] and \[{{v}_{S}}\] respectively. Velocity of sound is v and velocity of medium is \[{{v}_{m}}\] then apparent frequency observed by observer is given by \[n'=\left[ \frac{(v+{{v}_{m}})-{{v}_{0}}}{(v+{{v}_{m}})-{{v}_{S}}} \right]n\]
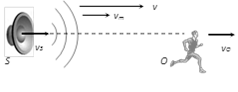
If medium is stationary i.e. \[{{v}_{m}}=0\] then \[n'=n\,\left( \frac{v-{{v}_{O}}}{v-{{v}_{S}}} \right)\]
Sign convection for different situation
(i) The direction of v is always taken from source to observer.
(ii) All the velocities in the direction of v are taken positive.
(iii) All the velocities in the opposite direction of v are taken negative.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
