Kundt's Tube
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
The apparatus consists of a long glass tube about 5 cm in diameter, fixed horizontally. A metal rod R clamped firmly at the centre is mounted so that its one end carrying a light disc \[{{P}_{1}}\] (of cork or card board) projects some distance into the glass tube. The other end of the glass tube is closed with a moveable piston \[{{P}_{2}}\]. Any desired length of the air or gas can be enclosed in between the two discs \[{{P}_{1}}\] and \[{{P}_{2}}\]. A small amount of dry lycopodium powder or cork dust is spread along base of the entire length of the tube.
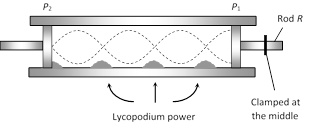
The free end of the metal rod R is rubbed (stroked) along the length with resined cloth. The rod begins to vibrate longitudinally and emits a very high pitched shrill note. These vibrations are impressed upon the air column in the tube through disc \[{{P}_{1}}\]. Let disc \[{{P}_{2}}\] is so adjusted, that the stationary waves are formed in the air (gas) column in the tube. At antinodes powder is set into oscillations vigorously while it remains uneffected at nodes. Heaps of power are formed at nodes.
Let n is the frequency of vibration of the rod then, this is also the frequency of sound wave in the air column in the tube.
For rod : \[\frac{{{\lambda }_{rod}}}{2}={{l}_{rod}}\], For air : \[\frac{{{\lambda }_{air}}}{2}={{l}_{air}}\]
where \[{{l}_{air}}\] is the distance between two heaps of power in the tube (i.e. distance between two nodes). If \[{{v}_{air}}\] and \[{{v}_{rod}}\] are velocity of sound waves in the air and rod respectively, then
\[n=\frac{{{v}_{air}}}{{{\lambda }_{air}}}=\frac{{{v}_{rod}}}{{{\lambda }_{rod}}}\]. Therefore \[\frac{{{v}_{air}}}{{{v}_{rod}}}=\frac{{{\lambda }_{air}}}{{{\lambda }_{rod}}}\]\[=\frac{{{\lambda }_{air}}}{{{\lambda }_{rod}}}\]
Thus knowledge of \[{{v}_{rod}},\] determiens \[{{v}_{air}}\]
Kundt's tube may be used for
(i) Comparison of velocities of sound in different gases.
(ii) Comparison of velocities of sound in different solids
(iii) Comparison of velocities of sound in a solid and in a gas.
(iv) Comparison of density of two gases.
(v) Determination of \[\gamma \] of a gas.
(vi) Determination of velocity of sound in a liquid.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
