Diffraction Due to a Circular Disc
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
When a disc is placed in the path of a light beam, then diffraction pattern is formed on the screen.
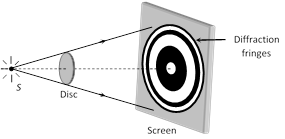
(1) At the centre of the circular shadow of disc, there occurs a bright spot. This spot is called Fresnel's spot or Poisson's spot.
(2) The intensity of bright spot decreases, when the size of the disc is increased or when the screen is moved towards the disc.
(3) Circular alternate bright and dark fringes are formed around the bright spot with fringe width in decreasing order.
(4) Let r be the radius of the disc, d is the distance between screen and the disc and \[\lambda \] is the wavelength of light used.
If n HPZ are covered by disc then \[nd\lambda =\pi {{r}^{2}}\Rightarrow n=\frac{{{r}^{2}}}{d\lambda }\]
(5) If the disc obstruct only first HPZ, the resultant amplitude at the central point\[R=-{{R}_{2}}+{{R}_{3}}+.........\approx -\frac{{{R}_{2}}}{2}\]
So intensity is \[\frac{kR_{2}^{2}}{4}\]which is slightly less than the intensity \[\frac{k\,R_{1}^{2}}{4}\] due to whole wave front, when no obstacle is placed.
(6) The intensity at bright spot is given by \[I=k{{\left[ \frac{{{R}_{n+1}}}{2} \right]}^{2}}\]
where n = Number of obstructed HPZ's
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
