Toluene, methyl benzene or phenyl methane
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
Toluene is the simplest homolouge of benzene. It was first obtained by dry distillation of tolubalsam and hence named toluene. It is commercially known as tolual.
(1) Methods of preparation
(i) From benzene [Friedel-craft's reaction] :

\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}+\underset{n-\text{Propyl}\,\text{chloride}}{\mathop{ClC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}}}\,\xrightarrow{AlC{{l}_{3}}}\underset{\text{(Cumene)}}{\mathop{\underset{\text{Isopropyl}\,\text{benzene}\,\text{(65}-\text{70 }\!\!%\!\!\text{ )}}{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CH/\backslash \ \ \\\begin{matrix}C{{H}_{3}} \\C{{H}_{3}} \\\end{matrix}}}\,+HCl}}\,\]
\[AlC{{l}_{3}}\] are, ![]() \[AlC{{l}_{3}}>SbC{{l}_{3}}>SnC{{l}_{4}}>B{{F}_{3}}>ZnC{{l}_{2}}>HgC{{l}_{2}}\]
\[AlC{{l}_{3}}>SbC{{l}_{3}}>SnC{{l}_{4}}>B{{F}_{3}}>ZnC{{l}_{2}}>HgC{{l}_{2}}\]
(ii) Wurtz fitting reaction :
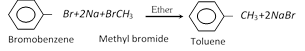
(iii) Decarboxylation :
\[\underset{\text{Sodium}\,\text{toluate}}{\mathop{\underset{\text{(}o-,m-\,\text{or}\,p-)}{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}\begin{matrix}C{{H}_{3}} \\\,\,\,\,\,\,COONa \\\end{matrix}}}\,}}\,+NaOH\xrightarrow{\text{Soda}\,\text{lime}}\underset{\text{Toluene}}{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{3}}}}\,+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\]
(iv) From cresol :

(v) From toluene sulphonic acid :

(vi) From toluidine :
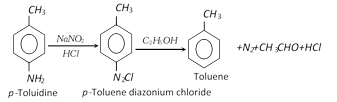
(vii) From grignard reagent :
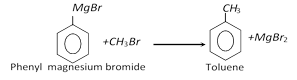
(viii) Commercial preparation
From coal tar :
The main source of commercial production of toluene is the light oil fraction of coal-tar. The light oil fraction is washed with conc. \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\] to remove the bases, then with \[NaOH\]to remove acidic substances and finally with water. It is subjected to fractional distillation. The vapours collected between \[80-110{}^\circ C\] is 90% benzol which contains \[70-80%\] benzene and \[14-24%\] toluene. 90% benzol is again distilled and the portion distilling between \[108-110{}^\circ C\] is collected as toluene.
(ix) From n- heptane and methyl cyclohexane
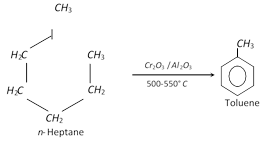
(2) Physical properties
(i) It is a colourless mobile liquid having characteristic aromatic odour.
(ii) It is lighter than water (sp. gr. 0.867 at \[{{20}^{o}}C\]).
(iii) It is insoluble in water but miscible with alcohol and ether in all proportions.
(iv) Its vapours are inflammable. It boils at \[{{110}^{o}}C\] and freezes at \[-{{96}^{o}}C\].
(v) It is a good solvent for many organic compounds.
(vi) It is a weak polar compound having dipole moment 0.4D.
(3) Chemical properties : Toluene shows the behaviour of both an alipatic and an aromatic compound.
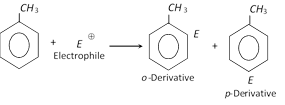
(i) Electrophilic substitution reactions : Aromatic character (More reactive than benzene) due to electron releasing nature of methyl group.
(ii) Reactions of side chain
(a) Side chain halogenation :

\[\underset{\text{(Benzylchloride)}}{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl}}\,+NaOH\xrightarrow{{}}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}OH+NaCl\]
\[\underset{\text{(Benzalchloride)}}{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CHC{{l}_{2}}}}\,+2NaOH\xrightarrow{{}}\underset{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CHO+{{H}_{2}}O\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{\underset{\downarrow }{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CH{{(OH)}_{2}}}}\,+2NaCl}}\,\]
\[\underset{\text{(Benzotrichloride)}}{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CC{{l}_{3}}}}\,+3NaOH\xrightarrow{{}}\underset{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH+{{H}_{2}}O\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{\underset{\downarrow }{\mathop{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{(OH)}_{3}}}}\,+3NaCl}}\,\]
(b) Oxidation :


(c) Hydrogenation :

(d) Combustion : \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{3}}+9{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{{}}7C{{O}_{2}}+4{{H}_{2}}O\]
(e) Ozonolysis : .


(4) Uses
(i) In the manufacture of benzyl chloride, benzal chloride, benzyl alcohol, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid, saccharin, etc.
(ii) In the manufacture of trinitrotoluene (TNT), a highly explosive substance.
(iii) As an industrial solvent and in drycleaning.
(iv) As a petrol substitute.
(v) In the manufacture of certain dyes and drugs.
T.N.T. (Tri-nitro toluene)
Preparation :


Properties : It is pale yellow crystalline solid (M.P. \[={{81}^{o}}C\]).
Uses :
T.N.B. (Tri-nitro benzene)
Preparation :


Properties and uses: It is colourless solid (M.P. \[={{122}^{o}}C\]). It is more explosive than T.N.T. and used for making explosive.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
