Electric Field
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
A positive charge or a negative charge is said to create its field around itself. Thus space around a charge in which another charged particle experiences a force is said to have electrical field in it.
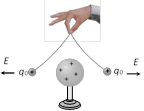
(1) Electric field intensity \[(\vec{E})\]: The electric field intensity at any point is defined as the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. \[\vec{E}= \frac{{\vec{F}}}{{{q}_{0}}}\]
Where \[{{q}_{0}}\to 0\] so that presence of this charge may not affect the source charge Q and its electric field is not changed, therefore expression for electric field intensity can be better written as \[\vec{E}=\underset{{{q}_{0}}\to 0}{\mathop{\text{Lim}}}\,\,\,\,\frac{{\vec{F}}}{{{q}_{\mathbf{0}}}}\]
(2) Unit and Dimensional formula
It's S.I. unit \[\frac{Newton}{coulomb}=\frac{volt}{meter}=\frac{Joule}{coulomb\times meter}\]
and C.G.S. unit - dyne/stat coulomb.
Dimension :\[[E]=[ML{{T}^{-3}}{{A}^{-1}}]\]
(3) Direction of electric field : Electric field (intensity) \[\vec{E}\] is a vector quantity. Electric field due to a positive charge is always away from the charge and that due to a negative charge is always towards the charge.
(4) Relation between electric force and electric field : In an electric field \[\vec{E}\] a charge (Q) experiences a force \[\overrightarrow{F}=Q\overrightarrow{E}\]. If charge is positive then force is directed in the direction of field while if charge is negative force acts on it in the opposite direction of field
![]()
(5) Super position of electric field (electric field at a point due to various charges) : The resultant electric field at any point is equal to the vector sum of electric fields at that point due to various charges i.e. \[\vec{E}={{\vec{E}}_{1}}+{{\vec{E}}_{2}}+{{\vec{E}}_{3}}+...\]
(6) Electric field due to continuous distribution of charge : A system of closely spaced electric charges forms a continuous charge distribution. To find the field of a continuous charge distribution, we divide the charge into infinitesimal charge elements. Each infinitesimal charge element is then considered, as a point charge and electric field \[\overrightarrow{dE}\] is determined due to this charge at given point. The Net field at the given point is the summation of fields of all the elements. i.e., \[\overrightarrow{E\,}=\int{\overrightarrow{dE}}\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
