Lorentz Force
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
When the moving charged particle is subjected simultaneously to both electric field \[\overrightarrow{E}\] and magnetic field \[\overrightarrow{B}\], the moving charged particle will experience electric force \[\overrightarrow{{{F}_{e}}}=q\overrightarrow{E}\] and magnetic force \[\overrightarrow{{{F}_{m}}}=q(\overrightarrow{v}\times \overrightarrow{B})\]; so the net force on it will be \[\overrightarrow{F}=q\mathbf{[}\overrightarrow{E}+\mathbf{(}\overrightarrow{v\,}\times \overrightarrow{B}\mathbf{)]}\]. Which is the famous 'Lorentz-force equation'.
Depending on the directions of \[\overrightarrow{v},\,E\] and \[\overrightarrow{B}\] following situations are possible
(i) When \[\overrightarrow{v},\,\overrightarrow{E}\] and \[\overrightarrow{B}\] all the three are collinear : In this situation the magnetic force on it will be zero and only electric force will act and so \[\vec{a}=\frac{{\vec{F}}}{m}=\frac{q\vec{E}}{m}\]
(ii) The particle will pass through the field following a straight-line path (parallel field) with change in its speed. So in this situation speed, velocity, momentum and kinetic energy all will change without change in direction of motion as shown
![]()
(iii) \[\overrightarrow{v\,},\,\overrightarrow{E}\] and \[\overrightarrow{B}\] are mutually perpendicular : In this situation if \[\overrightarrow{E}\] and \[\overrightarrow{B}\] are such that \[\overrightarrow{F}=\overrightarrow{{{F}_{e}}}+\overrightarrow{{{F}_{m}}}=0\] i.e., \[\overrightarrow{a}=(\overrightarrow{F}/m)=0\]
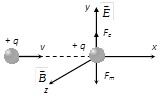
as shown in figure, the particle will pass through the field with same velocity, without any deviation in path.
And in this situation, as \[{{F}_{e}}={{F}_{m}}\] i.e., \[qE=qvB\] \[v=E/B\]
This principle is used in 'velocity-selector' to get a charged beam having a specific velocity.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
