Newton's Rings
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) If we place a plano-convex lens on a plane glass surface, a thin film of air is formed between the curved surface of the lens and plane glass plate.
(2) If we allow monochomatic light to fall normally on the surface of lens, then circular interference fringes of radius r can be seen in the reflected light. This circular fringes are called Newton rings.
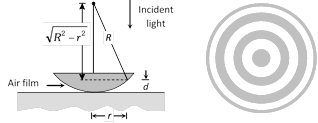
(3) The central fringe is a dark spot then there are alternate bright and dark fringes (Ring shape).
(4) Radius of nth dark ring \[{{r}_{m}}\tilde{}\,\sqrt{\lambda R}\]
n = 0, 1, 2, ....., R = Radius of convex surface
(5) Radius of nth bright ring \[{{r}_{n}}=\sqrt{\left( n+\frac{1}{2} \right)\lambda R}\]
(6) If a liquid of ref index m is introduced between the lens and glass plate, the radii of dark ring would be \[{{r}_{n}}=\sqrt{\frac{n\lambda R}{\mu }}\]
(7) Newton's ring arrangement is used of determining the wavelength of monochromatic light. For this the diameter of nth dark ring \[({{D}_{n}})\] and \[{{(n+p)}^{th}}\] dark ring \[({{D}_{n+p}})\] are measured then
\[D_{(n+p)}^{2}=4(n+p)\lambda R\] and \[D_{n}^{2}=4n\lambda R\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[\lambda =\frac{D_{n+p}^{2}-D_{n}^{2}}{4pR}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
