Answer:
According to Nernst equation:
\[{{E}_{\text{(electrode)}}}={{E}^{o}}_{\text{(electrode)}}+\frac{0.0591}{n}\,\log
\,[{{M}^{n+}}\,(aq)]\]
This means that the reduction
potential of the electrode is directly proportional to the concentration of the
metal ions or cations in solution.
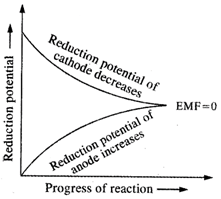
In an electrochemical cell, to
start with the reduction potential of the cathode is more than that of the
anode. As the redox reaction progresses in the cell, the concentration of the
metal ions in the reduction half cell decreases and it increases in the
oxidation half cell. Thus, the reduction potential of the anode gradually
increases while that of the cathode decreases. This keeps on till the two
become equal. At this stage, the cell stops working because its EMF will be
zero. This has been shown graphically in the adjacent figure.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
