A) \[3-\frac{1}{2}i\]or \[1-\frac{3}{2}i\]
B) \[\frac{3}{2}-i\]or \[\frac{1}{2}-3i\]
C) \[\frac{1}{2}-i\]or \[1-\frac{1}{2}i\]
D) None of these
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
\[BD=2AC\Rightarrow 2DM=2(2AM)\] or \[DM=2AM\]or \[D{{M}^{2}}=4A{{M}^{2}}\] or \[5=4[{{(x-2)}^{2}}+{{(y+1)}^{2}}]\] .....(i) Again slope of \[DM=-2\] and slope of \[AM\]is \[\frac{y+1}{x-2}\] AM is perpendicular to DM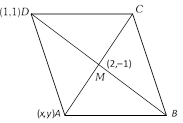 \[\therefore \,\,\,-2\left( \frac{y+1}{x-2} \right)=-1\Rightarrow x-2=2(y+1)\] .....(ii) Hence from (i) and (ii), we get \[\therefore \,\,y=-\frac{1}{2},-\frac{3}{2}\]and \[x=3,1\]
\[\therefore \,\,\,-2\left( \frac{y+1}{x-2} \right)=-1\Rightarrow x-2=2(y+1)\] .....(ii) Hence from (i) and (ii), we get \[\therefore \,\,y=-\frac{1}{2},-\frac{3}{2}\]and \[x=3,1\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
