A) \[2\sqrt{5}\]
B) \[6\sqrt{2}\]
C) \[4\sqrt{5}\]
D) \[6\sqrt{5}\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
Let the vertices be \[{{z}_{0}},{{z}_{1}},.....,{{z}_{5}}\,\,w.r.t\] centre O at origin and \[|{{z}_{0}}|\,=\sqrt{5}\].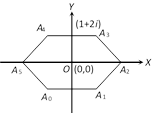 \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{A}_{0}}{{A}_{1}}\]= \[|{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{0}}|\,=\,|{{z}_{0}}{{e}^{i\,\theta }}-{{z}_{o}}|\] = \[|{{z}_{0}}||\cos \theta +i\sin \theta -1|\] = \[\sqrt{5}\,\sqrt{{{(\cos \theta -1)}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }\] = \[\sqrt{5}\,\sqrt{2\,(1-\cos \theta )}\]=\[\sqrt{5}\,\,2\sin (\theta /2)\] Þ\[{{A}_{0}}{{A}_{1}}\]=\[\sqrt{5}\,.\,2\sin \,\left( \frac{\pi }{6} \right)\]=\[\sqrt{5}\] \[\left( \because \,\,\theta =\frac{2\pi }{6}=\frac{\pi }{3} \right)\] ....(i) Similarly, \[{{A}_{1}}{{A}_{2}}={{A}_{2}}{{A}_{3}}={{A}_{3}}{{A}_{4}}={{A}_{4}}{{A}_{5}}={{A}_{5}}{{A}_{0}}=\sqrt{5}\]. Hence the perimeter of, regular polygon is \[={{A}_{o}}{{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{1}}{{A}_{2}}+{{A}_{2}}{{A}_{3}}+{{A}_{3}}{{A}_{4}}+{{A}_{4}}{{A}_{5}}+{{A}_{5}}{{A}_{0}}\]\[=\,\,6\sqrt{5}\].
\[\Rightarrow \] \[{{A}_{0}}{{A}_{1}}\]= \[|{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{0}}|\,=\,|{{z}_{0}}{{e}^{i\,\theta }}-{{z}_{o}}|\] = \[|{{z}_{0}}||\cos \theta +i\sin \theta -1|\] = \[\sqrt{5}\,\sqrt{{{(\cos \theta -1)}^{2}}+{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }\] = \[\sqrt{5}\,\sqrt{2\,(1-\cos \theta )}\]=\[\sqrt{5}\,\,2\sin (\theta /2)\] Þ\[{{A}_{0}}{{A}_{1}}\]=\[\sqrt{5}\,.\,2\sin \,\left( \frac{\pi }{6} \right)\]=\[\sqrt{5}\] \[\left( \because \,\,\theta =\frac{2\pi }{6}=\frac{\pi }{3} \right)\] ....(i) Similarly, \[{{A}_{1}}{{A}_{2}}={{A}_{2}}{{A}_{3}}={{A}_{3}}{{A}_{4}}={{A}_{4}}{{A}_{5}}={{A}_{5}}{{A}_{0}}=\sqrt{5}\]. Hence the perimeter of, regular polygon is \[={{A}_{o}}{{A}_{1}}+{{A}_{1}}{{A}_{2}}+{{A}_{2}}{{A}_{3}}+{{A}_{3}}{{A}_{4}}+{{A}_{4}}{{A}_{5}}+{{A}_{5}}{{A}_{0}}\]\[=\,\,6\sqrt{5}\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
