A) \[\underset{H}{\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-\underset{|}{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}}\,-C{{H}_{2}}}}}\,OC{{H}_{3}}\]
B) \[C{{H}_{3}}\underset{\,\,\,\,\,OC{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{-\underset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,H-}}\,C{{H}_{2}}\ C{{H}_{3}}\]
C) \[\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,=C{{H}_{2}}}}\,\]
D) \[\underset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,OC{{H}_{3}}}{\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-\underset{|}{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}}\,-C{{H}_{3}}}}}\,\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
\[\underset{\underset{H\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}}\,}{\mathop{\overset{\overset{C{{H}_{3}}\,\,}{\mathop{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}}\,}{\mathop{{{H}_{3}}C-C-C{{H}_{2}}-Br}}\,}}\,\underset{C{{H}_{3}}OH}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{C{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{-}}}}}\,A\]? Alkyl halide is 1°. Keep in mind 1° halide give product by SN 2 / E - 2 mechanism and 1° halide always gives substitution reaction except when strongly hindered base is used. ex.: With \[\underset{\underset{\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\,|}}\,}{\mathop{\overset{\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\,\,|}}\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-C-{{O}^{(-)}}}}\,}}\,\] it gives mainly elimination. The reaction involves carbocation intermediate. i.e. \[\underset{\text{(primary carbocation)}}{\mathop{\underset{\underset{H}{\mathop{|}}\,}{\mathop{\overset{\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{|}}\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-C-C{{\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{H}}\,}_{2}}}}\,}}\,}}\,\] but as it is a primary carbocation it will rearrange to give a tertiary carbocation, which completes the reaction \[\underset{\text{teritiary carbocation}}{\mathop{\underset{\underset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|}}\,}{\mathop{\overset{\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,C{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,|}}\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{3}}-{{C}^{\oplus }}}}\,}}\,}}\,\] Stability of carbocation: \[3{}^\circ >2{}^\circ >1{}^\circ >\]\[\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,{{H}_{3}}\] It is because the stability of a charged system is increased by dispersal of the charge. The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed. N.B. - Rearrangement can be done in two ways.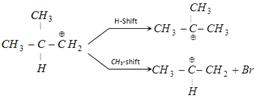 Therefore,
Therefore, 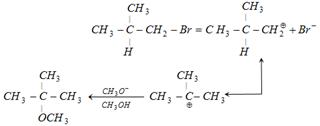
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
