Answer:
(i) Peptisation Peptisation involves conversion of
a freshly formed precipitate (such as AgCl, Fe(OH)3, Al (OH)3) into
a sol by the addition of a small amount of a suitable electrolyte. An
electrolyte having an ion in common with the material to be dispersed is required
for sol formation. The peptisation action is due to preferential adsoprtion of
the common ion of the electrolyte and the precipitate to be dispersed.
As a result of
preferential adsorption of the common ion, particles acquire a positive or
negative charge depending on the charge on the ion adsorbed.
Because of
the presence of the same type of charge, the particles of the precipitate are
pushed apart and get dispersed forming a stable colloidal sol.
Agl is
peptised by addition of ![]()
![]() as
common ion)
or KI (
as
common ion)
or KI (![]() as
common ion).
as
common ion).
![]() (
(![]() is
adsorbed)
is
adsorbed)![]() (
(![]() is
adsorbed
Ferric
hydroxide sol is formed by the addition of
is
adsorbed
Ferric
hydroxide sol is formed by the addition of![]() solution
to the freshly formed precipitate of
solution
to the freshly formed precipitate of ![]() which
adsorbs
which
adsorbs ![]() and thus
stable sol is formed.
and thus
stable sol is formed.
![]() Similariy,
an aluminium hydroxide sol is formed when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to
freshly precipitated aluminium hydroxide. This is due to adsorption of
Similariy,
an aluminium hydroxide sol is formed when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to
freshly precipitated aluminium hydroxide. This is due to adsorption of ![]() on
on ![]() is formed
first by action of
is formed
first by action of ![]() on
on
![]() [1]
[1]
![]()
![]() (ii)
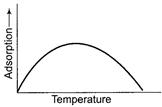
Effect of temperature on chemisorptions Adsorption is a
spontaneous change
(ii)
Effect of temperature on chemisorptions Adsorption is a
spontaneous change ![]() taking
place with decrease in entropy.
taking
place with decrease in entropy.![]() and to
make
and to
make ![]() should
be negative. Thus adsorption is exothermic change. By Le-Chatelaine principle,
increase in temperature should decrease extent of adsorption, but in chemisorptions,
there is first increase and then decrease in adsorption.
should
be negative. Thus adsorption is exothermic change. By Le-Chatelaine principle,
increase in temperature should decrease extent of adsorption, but in chemisorptions,
there is first increase and then decrease in adsorption.
 (iii)
Associated colloids There are certain colloids which behave as normal
strong electrolytes at low concentrations but exhibit colloidal properties at higher
concentrations due to formation of aggregated particles. These are called
associated colloids (micelles).
(iii)
Associated colloids There are certain colloids which behave as normal
strong electrolytes at low concentrations but exhibit colloidal properties at higher
concentrations due to formation of aggregated particles. These are called
associated colloids (micelles).
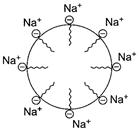 Examples
Surface active agents like soap, detergents.
Soap is
Examples
Surface active agents like soap, detergents.
Soap is ![]() In
aqueous solution ,there is formation of
In
aqueous solution ,there is formation of ![]() and
and ![]() . In oily
matter (say grease) washing with detergent soap/
. In oily
matter (say grease) washing with detergent soap/![]() (R-hydrophobic)
goes into oil and forms associated colloids, [1]
(R-hydrophobic)
goes into oil and forms associated colloids, [1]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
