 Choose the correct statement from the following?
Choose the correct statement from the following?
A) \[f=f,\,f=f\]
B) \[f=2f,\,f=2f\]
C) \[f=f,\,f=2f\]
D) \[f=2f,\,f=f\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
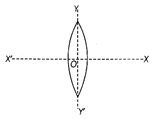
The focal length of equiconvex lens \[\frac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \frac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\frac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)\] ?. (i) For equiconvex lens, \[{{R}_{1}}={{R}_{2}}=R\] \[\frac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \frac{1}{R}-\frac{1}{-R} \right)=\frac{2\,(\mu -1)}{R}\] Case I When the lens is cut along XOX, then each half is given equiconvex with \[{{R}_{1}}=+R,\,\,{{R}_{2}}=-R\] \[\therefore \] \[\frac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left[ \frac{1}{R}-\left( \frac{1}{-R} \right) \right]\Rightarrow \frac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\] \[\left( \frac{1}{R}+\frac{1}{R} \right)\] \[=(\mu -1)\frac{2}{R}=\frac{1}{f}\Rightarrow \,\,f=f\] Case II When lens is cut along YOY, then each half becomes plano-convexd with \[{{R}_{1}}=+R,\,\,{{R}_{2}}=\infty \] \[\therefore \] \[\frac{1}{f}=(\mu -1)\left( \frac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\frac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)\] \[=(\mu -1)\left( \frac{1}{R}-\frac{1}{\infty } \right)=\left( \frac{\mu -1}{R} \right)=\frac{1}{2f}\Rightarrow f=2f\]You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
