A) \[0.25\,\,A\]
B) \[0.8\,\,A\]
C) \[0.2\,\,A\]
D) \[0.5\,\,A\]
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
Key Idea: Potential difference across galvanometer should be equal to potential difference across shunt. The shunt and galvanometer are connected as shown in figure.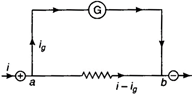 Let total current through the parallel combination is \[i\], the current through the galvanometer is \[{{i}_{g}}\] and the current through the shunt\[i-{{i}_{g}}\]. The potential difference \[{{V}_{ab}}(={{V}_{a}}-{{V}_{b}})\] is the same for both paths, so \[{{i}_{g}}G=(i-{{i}_{g}})S\] or \[{{i}_{g}}(G+S)=i\,\,S\] or \[\frac{{{i}_{g}}}{i}=\frac{S}{S+G}\] The fraction of current passing through shunt \[=\frac{i-{{i}_{g}}}{i}=1-\frac{{{i}_{g}}}{i}\] \[=1-\frac{S}{S+G}=\frac{G}{S+G}\] \[=\frac{8}{2+8}=\frac{8}{10}\] \[=0.8\,\,A\]
Let total current through the parallel combination is \[i\], the current through the galvanometer is \[{{i}_{g}}\] and the current through the shunt\[i-{{i}_{g}}\]. The potential difference \[{{V}_{ab}}(={{V}_{a}}-{{V}_{b}})\] is the same for both paths, so \[{{i}_{g}}G=(i-{{i}_{g}})S\] or \[{{i}_{g}}(G+S)=i\,\,S\] or \[\frac{{{i}_{g}}}{i}=\frac{S}{S+G}\] The fraction of current passing through shunt \[=\frac{i-{{i}_{g}}}{i}=1-\frac{{{i}_{g}}}{i}\] \[=1-\frac{S}{S+G}=\frac{G}{S+G}\] \[=\frac{8}{2+8}=\frac{8}{10}\] \[=0.8\,\,A\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
