A) \[4\sqrt{2}\]
B) \[2\sqrt{2}\]
C) \[\sqrt{2}\]
D) \[\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
The slope of the line\[x-y+1=0\]is 1. So, it makes an angle of\[{{45}^{o}}\]with\[x-\]axis. The equation of a line passing through (2, 3) and making an angle of\[{{45}^{o}}\] \[\frac{x-2}{\cos {{45}^{o}}}=\frac{y-3}{\sin {{45}^{o}}}=r\] Coordinates of any point on this line are \[(2+r\cos {{45}^{o}},\,\,3+r\sin {{45}^{o}})\] or \[\left( 2+\frac{r}{\sqrt{2}},\,\,3+\frac{r}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] If this point lies on the line\[2x-3y+9=0\], then\[4+\sqrt{2}r-9-\frac{3r}{\sqrt{2}}+9=0\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[r=4\sqrt{2}\] Alternate Method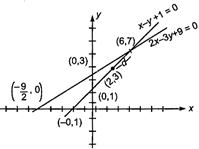 Since the point\[(2,\,\,3)\]lies on the line\[x-y+1=0\]. Therefore the distance from\[(2,\,\,3)\]to the line\[2x-3y+9=0\]along the line \[x-y+1=0\]is equal to the distance between the points\[(2,\,\,3)\]and intersection point of\[2x-3y+9=0\]and\[x-y+1=0\]ie, (6, 7). Hence required distance \[d=\sqrt{{{(6-2)}^{2}}+{{(7-3)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{32}\] \[d=4\sqrt{2}\]
Since the point\[(2,\,\,3)\]lies on the line\[x-y+1=0\]. Therefore the distance from\[(2,\,\,3)\]to the line\[2x-3y+9=0\]along the line \[x-y+1=0\]is equal to the distance between the points\[(2,\,\,3)\]and intersection point of\[2x-3y+9=0\]and\[x-y+1=0\]ie, (6, 7). Hence required distance \[d=\sqrt{{{(6-2)}^{2}}+{{(7-3)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{32}\] \[d=4\sqrt{2}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
