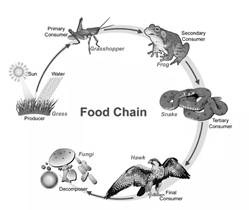
 Food Chain
Land animals take oxygen directly from air
Land animals take oxygen directly from air and utilize it to get energy.
Land animals produce sound
Most of the land animals produce sound. For example, cat mews, dog barks, etc.
Land animals reproduce
Land animals reproduce by laying eggs or by giving birth to young ones.
Land animals have tail
Most of the land animals have tail that help them in their movement. Tail also help them to maintain the body balance. For example, lion, elephant, dog, cat, etc.
Classification of Land Animals
Land animals are divided into:
(i) Domestic animals
(ii) Wild animals
Domestic Animals
Animals that live with us are called domestic animals. For example, dog, cat, etc.
Wild Animals
Animals that live in the forest are called wild animals, .or example, lion, tiger etc.
Land animals are classified also:
(i) Milk giving animals
(ii) Draught animals
Milk Giving Animals
Animals that give us milk are called milk giving animals. For example, cow, buffalo, etc.
Draught Animals
Animal that work and carry load for us are called draught animals. For example, ox, horse, etc.
In the third category, the land animals are classified as.
(i) Herbivorous animals
(ii) Carnivorous animals
(iii) Omnivorous animals
Herbivorous Animals
Animals that eat plants are called herbivorous animals.
Carnivorous Animals
Animals that eat flesh are called carnivorous animals.
Omnivorous Animals
Animals that eat both plants and flesh are called omnivorous animals.
Mammals
Animals which give birth to babies are called mammals. For example, human being, dog, whale, dolphin, etc.
Aquatic Animals
Aquatic animals live in water. For example, fish, dolphin, whale, etc. Aquatic animals also live in lakes, oceans and rivers. Some animals like tortoise, frog, etc. live both on land and in water and are called amphibians.
Classification of Aquatic Animals
Aquatic animals can be classified on the basis of:
(i) Their habitat (the kind of water they live in)
(ii) Food (the type of food they take in)
Classification on the basis of habitat:
Fresh water animals
They are the animals that live in rivers, more...
Food Chain
Land animals take oxygen directly from air
Land animals take oxygen directly from air and utilize it to get energy.
Land animals produce sound
Most of the land animals produce sound. For example, cat mews, dog barks, etc.
Land animals reproduce
Land animals reproduce by laying eggs or by giving birth to young ones.
Land animals have tail
Most of the land animals have tail that help them in their movement. Tail also help them to maintain the body balance. For example, lion, elephant, dog, cat, etc.
Classification of Land Animals
Land animals are divided into:
(i) Domestic animals
(ii) Wild animals
Domestic Animals
Animals that live with us are called domestic animals. For example, dog, cat, etc.
Wild Animals
Animals that live in the forest are called wild animals, .or example, lion, tiger etc.
Land animals are classified also:
(i) Milk giving animals
(ii) Draught animals
Milk Giving Animals
Animals that give us milk are called milk giving animals. For example, cow, buffalo, etc.
Draught Animals
Animal that work and carry load for us are called draught animals. For example, ox, horse, etc.
In the third category, the land animals are classified as.
(i) Herbivorous animals
(ii) Carnivorous animals
(iii) Omnivorous animals
Herbivorous Animals
Animals that eat plants are called herbivorous animals.
Carnivorous Animals
Animals that eat flesh are called carnivorous animals.
Omnivorous Animals
Animals that eat both plants and flesh are called omnivorous animals.
Mammals
Animals which give birth to babies are called mammals. For example, human being, dog, whale, dolphin, etc.
Aquatic Animals
Aquatic animals live in water. For example, fish, dolphin, whale, etc. Aquatic animals also live in lakes, oceans and rivers. Some animals like tortoise, frog, etc. live both on land and in water and are called amphibians.
Classification of Aquatic Animals
Aquatic animals can be classified on the basis of:
(i) Their habitat (the kind of water they live in)
(ii) Food (the type of food they take in)
Classification on the basis of habitat:
Fresh water animals
They are the animals that live in rivers, more... 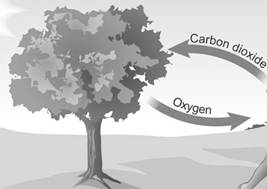 Tree
Characteristics of Plants
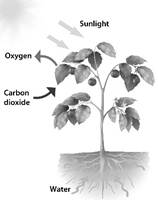
Plants Make their Own Food
Green plants are autotrophs. They make their own food in the presence of carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. Green plants have a pigment called chlorophyll that helps them to make food.
Tree
Characteristics of Plants
Plants Make their Own Food
Green plants are autotrophs. They make their own food in the presence of carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. Green plants have a pigment called chlorophyll that helps them to make food.
 Plants have Roots and Shoots
Root grows under the ground and shoot grows above the ground.
Plants have Roots and Shoots
Root grows under the ground and shoot grows above the ground.
 Plant
Many Plants bear Fruits
Many plants bear fruits that are very nutritious and delicious.
Plant
Many Plants bear Fruits
Many plants bear fruits that are very nutritious and delicious.
 Mango Tree
Plants Reproduce
Plants reproduce to continue their existence. They reproduce with the help of seeds, stems and roots.
Plants Grow throughout their Life Cycle
Most of the plants grow throughout their life cycle. They attain maximum height.
Few Plants have Thorns
For example, rose, cactus, etc.
Leaves of a Plant
Plants make food in the leaves. Therefore, leaf is called the kitchen of the plant. Plants get energy from this food.
There is a small opening in the leaf. It is called stomata. Plants breathe through this opening.
Plant's leaves can be of different shapes. For example, leaves can be round, long or triangular.
Mango Tree
Plants Reproduce
Plants reproduce to continue their existence. They reproduce with the help of seeds, stems and roots.
Plants Grow throughout their Life Cycle
Most of the plants grow throughout their life cycle. They attain maximum height.
Few Plants have Thorns
For example, rose, cactus, etc.
Leaves of a Plant
Plants make food in the leaves. Therefore, leaf is called the kitchen of the plant. Plants get energy from this food.
There is a small opening in the leaf. It is called stomata. Plants breathe through this opening.
Plant's leaves can be of different shapes. For example, leaves can be round, long or triangular.


 Long leave Round leave Triangular leave
(Mango) (Lotus) (Peepal)
Leaves of many plants are used to cure diseases. For example, neem's leaves cure skin problem.
Classification of Plants
Plants are classified into three types:
Trees
Plants having tall and hard trunks are called trees. Trees have thick and woody branches.
For example, mango tree. Banyan tree, etc.
Herbs
Plants having weak and soft stem are called herbs. For example, tulsi, mint, etc.
Shrubs
Scrubs are taller than herbs and have multiple woody stems. For example, rose plant sunflower, etc.
Long leave Round leave Triangular leave
(Mango) (Lotus) (Peepal)
Leaves of many plants are used to cure diseases. For example, neem's leaves cure skin problem.
Classification of Plants
Plants are classified into three types:
Trees
Plants having tall and hard trunks are called trees. Trees have thick and woody branches.
For example, mango tree. Banyan tree, etc.
Herbs
Plants having weak and soft stem are called herbs. For example, tulsi, mint, etc.
Shrubs
Scrubs are taller than herbs and have multiple woody stems. For example, rose plant sunflower, etc.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
