Category : 5th Class
Categories of Computers
Introduction
Computers are categorized on the basis of types of input signal processed by its peripherals, purpose of their use, physical structure, speed and reliability. Two types of signal are usually processed by the computer, these are digital and analog signal. Some types of computer processes both analog and digital signal. Therefore, depending on the types of input signal processed by computer, they are categorized into three groups.
v Digital computers work on digital signal.
v Analog computers work on analog signal.
v Hybrid computers work on both digital and analog signal.
In this chapter we will study more about these classification.
Digital Computer
A digital computer is a computer that stores data in terms of binary digits (digital) and proceeds in discrete steps from one state to the next. The word 'digital' stands for discrete (step-by-step) and hence, digital computers can take only discrete values. A digital computer gives accurate information than an analog computer.
Types of Digital Computer
Types of Digital computer are based on their size and performance, purpose of their use, etc.
Depending upon the size and performance, digital computers are categorized into five tvpes. They are the followings.
Embedded Computer
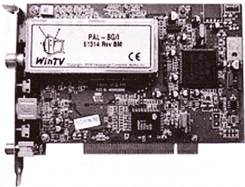
An Embedded computer is one that has computer hardware with software embedded in it as one its important components. Smallest Embedded computers are equipped within the circuit and they are programmed for performing the specific task. An example of embedded computer is soldered on the television circuit which performs the task during the tuning to a particular television frequency.
Look at the following picture of Embedded computers as a TV tuner card:
Microcomputer
A Microcomputer contain a microprocessor which works as a CPU. It accepts input, stores large quantities of data, execute complex instructions which direct it to perform mathematical and logical operations and outputs the answer in a human readable form. The microcomputers are basically used in educational training, playing games, etc. The microcomputer are further divided into Desktop computer, workstation and PDAs.
Minicomputers
A Minicomputer is midsized computer. A multi-user computer capable of supporting from 10 to 100 of users simultaneously. In terms of size and power, minicomputers lie between microcomputer and mainframe. They have capability to connected more input and output devices than microcomputer and also known as multiuser computer.
Mainframe Computers
A Mainframe computers are large-sized, powerful multi-user computers that can support concurrent programs. It can be used by as many as hundreds or thousands of users at the same time. Large organisations may use a mainframe computer to execute large-scale processes such as processing the organisation's payroll. It is designed to handle large volume of data and information and also has great processing speed as compare to the minicomputer. It is multiuser and multiprocessor computer.
Super Computer
Super computers consist of many processor working together hence they process data faster than mini, micro and mainframe computers. The benefits and uses of supercomputers are used in many different fields. The supercomputers are used for weather forecasting, mathematical calculations, seismic activity (earthquakes), nuclear energy research, fluid dynamic calculations, pattern matching, graph analysis, cryptology (the science of breaking codes) and researching anything on the internet.
Analog Computer
An analog computer is an electronic system which recognizes data as continuous measurements of a physical quantity, such as pressure, voltage or temperatures along a continuous scale. The devices that measure such quantities are analog devices, e.g., Voltmeter, ammeter, speedometer in your car etc. The output of an analog computer is usually in the form of dial gauge readings or graphs. The term 'analog' means continuous.
An example of analog computer system is the processor attached to the petrol pump which converts the fuel flow measurements in digital output and displays the quantity and price.
Uses of Analog Computers:
v Analog computers are used for paper making and in chemical industry.
v It is widely used for certain specialized engineering and scientific applications.

Hybrid Computers
A computer which performs operations based on both analog and digital principles is known as a hybrid computer. A hybrid computer displays capabilities, behavior, functions and principles of operation of both the analog and digital computer.
A gas pump is actually a hybrid computer. Although it processes measured data, such as the amount of fluid passing through the gas hose, the data displayed to you, the amount of gas and the amount you owe is displayed in a digital format.
In general, analog computers are extraordinarily fast, but the precision of analog computers is not good. Digital computers have an almost unlimited level of precision, but are slow compared to analog computers. In most cases, hybrid computers are substantially faster than a digital computer, and can supply a far more specific computation than an analog computer.
Look at the following picture of a Hybrid computer:

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
