Category : 5th Class
Human Body and Nutrition
Human Body
The organs of our body work together to perform various functions for the body. A group of organs doing some particular jobs for the body form an organ system.
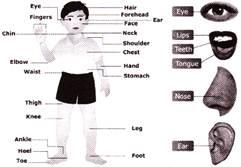
Human body has the following systems performing certain functions:
Skeletal System
It is the framework of bones which gives support to human body. Adult human skeleton has 206 bones. Different parts of the human skeleton are:
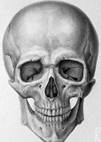
Skull
Skull consists of 22 bones which protects the brain. All bones of skull are immovable except the lower jaw. With the help of movable lower jaw, we can talk and eat. In lower and upper jaw, we have teeth for cutting and chewing food.
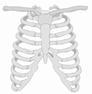
Rib Cage
Ribs make a cage of bones around the chest which is called rib cage. It protects our internal organs. Generally adults have 12 pairs of ribs. There is a long bone at the centre of the chest, which holds the ribs in place, called sternum. Ribs are attached to the backbone. Last two ribs are not attached to the sternum and are known as floating ribs. These floating ribs are attached to the backbone.
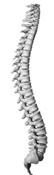
Backbone
It is made up of 33-ring shaped small bones called vertebrae. Backbone is also called as vertebral column. It is a hollow tube through which spinal cord runs.
Limbs
All human beings have two pairs of limbs: the forelimbs (arms) and hindlimbs (legs). Both forelimb and hindlimb is made up of 30 bones each. Thigh bone or femur is the longest bone in the body.
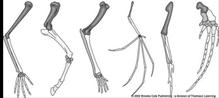
Note: The smallest bone of the body called stapes is present in the ear.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system has the following functions:
(i) The skull protects the brain.
(ii) The rib cage protects the heart and the lungs.
(iii) The backbone protects the spinal cord.
Joints
A joint is the place where two bones meet. Most joints are movable. There are five kinds of free movable joints in our body.
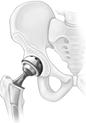
Ball and Socket Joint
This type of joint allows movement in many directions. The shoulder joint and the hip joint are the examples of ball and socket joint.
Hinge Joint
This type of joint works like the hinges in the door. This kind of joint only allows back and forth movement. Bones in the knee, elbow, fingers, and toes have this type of joint.
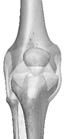
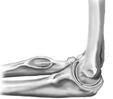
Knee joint Elbow joint
Pivot Joint
This type of joint is found between the first two vertebrae of our backbone. It allows us to move our head up, down, and sideways.
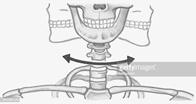
Gliding Joint
This type of joint is found in the bones of the wrist and the ankle. It allows these bones to slide against each other in a gliding motion.
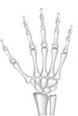
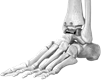
Wrist joint Ankle joint?
Saddle Joint
This type of joint is present in between the bones of thumb.
Fixed/Immovable Joint
This type of joint does not allow movement of bones. In our body fixed joint are found in skull and hip bones.
Note: Ligaments are strong elastic tissues that joints the bones together.
Tendons are strong, tough tissues that joint muscles to bones.
Nervous System
The nervous system controls the different organs of our body.
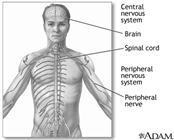
Brain
Brain is a very important organ. It controls our body movements and helps us to store information in our memory. The human brain has three parts:
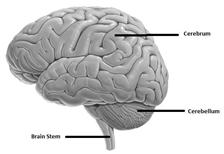
Cerebrum
It is the largest part of the human brain and is responsible for learning, memory, intelligence and logic. It also controls functions of eyes, ears, nose and tongue.
Cerebellum
It is situated below the cerebrum and is responsible for muscle coordination and for maintaining the balance of our body.
Medulla Oblongata or the Brain Stem
It controls activities such as heartbeat, breathing swallowing and sneezing.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a thick cord of nerve tissue, which extends from the brain stem. It is protected by the backbone. The spinal cord is responsible for the transfer of information between the brain and the rest of the body. It even controls the actions that do not involve the brain. The automatic response of the body to an event is called a reflex action. Reflex actions are due to messages sent by the spinal cord. These actions are very fast. For example,
If you touch a hot object accidentally you withdraw your hand almost immediately.
Nerves
A network of nerves runs throughout our body. Sensory nerves pass through the spinal cord and carry messages of the body to the brain. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to the body.
Sense Organs
Our sense organs help us to see, hear, taste, smell and touch.
Skin
There are tiny nerve endings in our skin connected to spinal cord. These nerve endings help us to feel things. They also help us to detect heat, cold and pain. Skin is the largest external organ of human body.
Eyes
Eyes help us in seeing the various objects around us. Each eye has a lens. When we see an object the light passes through the lens and image is created and the message from this image is carried to brain. The brain recognizes the image and help us see things.
Ears
Ears help us in hearing. They also help us maintaining body balance. It consist of external, middle and internal ear.
Nose
Nose helps us to smell a variety of objects, from flowers to rotten eggs.
Tongue
Tongue helps us in tasting things. Different regions of the tongue help us in tasting different kind of substances.
Nutrition
Nutrition is defined as the process through which organisms take in and utilises materials necessary to support life. Food contains chemical substances called nutrients that are required by all living organisms. Our body requires carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals and vitamins. In addition to the five nutrients, our body also requires water and roughage.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Large amount of food that we eat consists of carbohydrates. The simplest form of carbohydrate is sugar such as glucose and fructose. For example, glucose is present in food items like jams, jellies, etc. and fructose is present in various fruits such as banana, apple, etc.
Complex form of carbohydrate is starch. Starch is present in food items such as wheat, rice, potato, etc. Glucose is stored in our body as glycogen.
Fats
Fats contain carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. Energy given by one gram of fat is more than the energy given by one gram of carbohydrate. Fat is present in food items such as butter, ghee, milk, etc. Our body takes long time to break down fat than to break down carbohydrate. Fats can be stored in the body. If the carbohydrates consumed are more than the required quantity, then excess amount is converted into fats and is stored in the body.
Proteins
Proteins contain nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. Proteins are required for the growth and repair of the body. Our hairs, nails, skin and muscles are made up of proteins. Protein is found in food items such as pulses, soya bean, nuts, egg, meat, etc. Protein cannot be stored in our bodies. If excess amount of protein is consumed then it is excreted from the body in the form of urea as urine or is stored as fats.
Vitamins
Vitamins are required for the healthy functioning of the body. However they are required in very small quantity by our bodies. If required quantities of vitamins are not present in our diet, then one can fall ill. The various vitamins required by our body are vitamin A, B-complex,
C, D, E and K. Vitamin B-complex includes vitamin \[{{B}_{1}}\],
\[{{B}_{2}}\], \[{{B}_{6}}\]and \[{{B}_{12}}\].
Our body gets vitamins from outside sources such as plants. Vitamin D can be manufactured in the body in the presence of sunlight.
|
Vitamin |
Source |
Function |
Deficiency Disease |
|
\[A\] |
Spinach, carrots, pumpkins, butter sweet potatoes, fish-liver oil, |
Keeping eyes hair and skin healthy |
Poor vision, night blindness, lower resistance to disease |
|
\[{{B}_{1}}\] |
Eggs meat, all cereals, yeast, milk |
Helps in proper functioning of digestive and nervous system |
Weakness and beriberi |
|
\[{{B}_{2}}\] |
Eggs, peas, beans, milk, green vegetables, fish, meat |
Keeping skin and mouth healthy |
Poor growth, bad skin sores in mouth |
|
\[{{B}_{6}}\] |
Wheat, other cereals, potatoes, tomatoes, meat, fish, peanuts |
Keeping skin, nervous and digestive systems healthy |
Pellagra |
|
\[{{B}_{12}}\] |
Animal products such as meat, fish, liver, eggs, milk |
Helps in the formation of blood and proper growth |
Anaemia |
|
\[C\] |
All fresh fruits, especially citrus, guava, amla tomatoes |
Keeping gums and joints healthy and building resistance to infections |
A disease called scurvy bleeding gums, loose teeth and aching joints |
|
\[D\] |
Fish-liver oil, milk, butter, sunlight helps the body to produce this vitamin |
Building strong bones and teeth |
Rickets in children and soft bones in adults |
|
\[E\] |
Olive oil, almonds sunflower oil, broccoli, pumpkin,mangoes |
Protect body tissues from free radicals, keep immune system strong |
Muscle weakness |
|
\[K\] |
Green vegetables, tomatoes yolk of egg |
Clotting of blood |
|
Minerals
Minerals are also required in small quantities by our body. Various minerals are sodium potassium, calcium, magnesium, chlorine, iron, fluorine, sulphur, phosphorus and iodine.
Water
Most of the weight of a person is due to water content in the body. Water is very essential for the existence of organisms. Water carries the digested food around the body. Water is the constituent of blood and carries chemicals and gases throughout the body. Water is responsible for regulating the body temperature.
Roughage
Roughage or fibre is required for the smooth functioning of digestive system. Roughage swells up in the intestine by absorbing water and helps in smooth movement of digested food in intestine. Fibre is present in whole grain flour, whole pulses, green peas, leafy vegetables and fruits.
Balanced Diet
A diet that contains all the nutrients required by the body in the right proportion is called a balanced diet.
Deficiency Diseases
If there is not a proper intake of food then a person suffers from malnutrition. The malnourished body does not function properly, and the person can suffer from diseases.
Children suffering from malnutrition have slow mental and physical growth and catches infection easily.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
