 Indian?s rich culture is the crowning
glory of Indian civilisation. The multitude of literary works and the
magnificent architecture of ancient India are testimony to India?s\[legac{{y}^{1}}\].
Numerous monuments all over the country stand witness to the glory of India.
There is voluminous wisdom and knowledge in the literary tradition. These are
important sources of history and help us to reconstruct and understand the
past.
INDIAN ARCHITECTURE
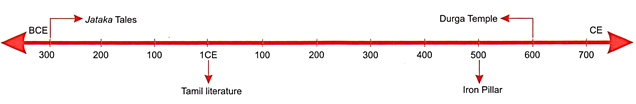
THE IRON PILLAR
Have you seen or heard about the
iron pillar at Mehrauli in Delhi. It was made about 1500 years ago and has not
rusted till now. This tells us about the remarkable metallurgical skills of the
Indian craftsmen in ancient times. The Iron Pillar is about 22 ft. high and
weighs 6 tons. It is said to have been built at the time of Chandragupta
Vikramaditya. It has a Sanskrit inscription in Brahmi script. It mentions a
king named Chandra who is probably Chandragupta II of the Gupta dynasty.
STUPAS
The word stupa literally means 'a
heap7. A stupa is a domed building which houses Buddhist relics. These can be
bones, ashes more...
Indian?s rich culture is the crowning
glory of Indian civilisation. The multitude of literary works and the
magnificent architecture of ancient India are testimony to India?s\[legac{{y}^{1}}\].
Numerous monuments all over the country stand witness to the glory of India.
There is voluminous wisdom and knowledge in the literary tradition. These are
important sources of history and help us to reconstruct and understand the
past.
INDIAN ARCHITECTURE
THE IRON PILLAR
Have you seen or heard about the
iron pillar at Mehrauli in Delhi. It was made about 1500 years ago and has not
rusted till now. This tells us about the remarkable metallurgical skills of the
Indian craftsmen in ancient times. The Iron Pillar is about 22 ft. high and
weighs 6 tons. It is said to have been built at the time of Chandragupta
Vikramaditya. It has a Sanskrit inscription in Brahmi script. It mentions a
king named Chandra who is probably Chandragupta II of the Gupta dynasty.
STUPAS
The word stupa literally means 'a
heap7. A stupa is a domed building which houses Buddhist relics. These can be
bones, ashes more... 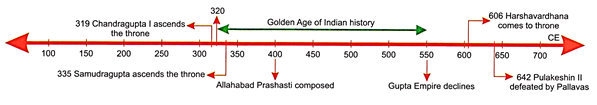 Starting 320 CE to 550 CE, the
Indian subcontinent witnessed one dynasty rise which set the model of a
classical civilisation. The period was marked by extensive inventions and
discoveries in science, technology, engineering, art, literature, logic,
mathematics, astronomy and philosophy. Historians have therefore named this
period as the Golden Age of Indian History.
PRASHASTI
Have you ever heard of a
Prashasti7 In Sanskrit, the word means 'in praise of. These were composed in
praise of some ruler. There is a famous Allahabad Prashasti. It is a stone
pillar inscription. It was engraved on the Ashokan pillar in Kausambi near Allahabad.
It is one of the most important sources of information about Samudragupta who
was a famous ruler of the Gupta dynasty. It was composed by Harisena, the court
poet and minister of Samudragupta in the 4th century CE.
WHAT THE ALLAHABAD PRASHASTI TELLS
US
The Prashasti more...
Starting 320 CE to 550 CE, the
Indian subcontinent witnessed one dynasty rise which set the model of a
classical civilisation. The period was marked by extensive inventions and
discoveries in science, technology, engineering, art, literature, logic,
mathematics, astronomy and philosophy. Historians have therefore named this
period as the Golden Age of Indian History.
PRASHASTI
Have you ever heard of a
Prashasti7 In Sanskrit, the word means 'in praise of. These were composed in
praise of some ruler. There is a famous Allahabad Prashasti. It is a stone
pillar inscription. It was engraved on the Ashokan pillar in Kausambi near Allahabad.
It is one of the most important sources of information about Samudragupta who
was a famous ruler of the Gupta dynasty. It was composed by Harisena, the court
poet and minister of Samudragupta in the 4th century CE.
WHAT THE ALLAHABAD PRASHASTI TELLS
US
The Prashasti more... 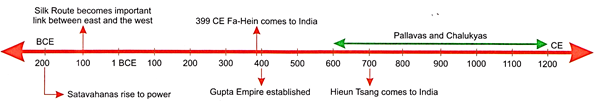 Did you ever imagine that more
than 2,000 years ago, people from distant lands as far as Greece would come to
India there were no airplanes, no trains and no motor vehicles? Well Alexander
did, long journeys motivated by a desire to conquer foreign lands. Enthused
with adventures form a big slice of man?s history. Let us see how these
journeys and eventually the contacts with distant lands shaped and affect
history.
After the collapse of the Mauryan
Empire, several small kingdoms came up. The most important development was the
arrival of foreign tribal groups in India.
The Indo- Greeks conquered much of
northern India including parts of Uttar Pradesh. The most famous rules was
Menander I. He converted to Buddhism. The Indo-Greeks issued coins, the first
of which were minted under Menander I.
The
Second Urbanisation
Summary
1.
From
the 1st century BCE to about 4th century CE, India underwent huge
transformation.
2.
During
this period, there was a spurt in agricultural production which led to the
emergence of many towns and cities.
3.
This
phase also opened up a network of internal and overseas trade routes.
4.
It
saw the introduction of currency and witnessed the development of numerous arts
and crafts including ceramics.
5.
Archaeologists
have found thousands of coins made of copper or silver with the design punched
on the metal. These are called punch marked coins.
6.
Pottery
of a different kind has been found. This pottery is called Northern Black
Polished Ware.
7.
Craftsmen
and artisans formed associations called guilds or shrenis. The enormous
manufacturing activity was maintained by these guilds.
8.
Arikamedu
was a very important trading centre and port.
Did you ever imagine that more
than 2,000 years ago, people from distant lands as far as Greece would come to
India there were no airplanes, no trains and no motor vehicles? Well Alexander
did, long journeys motivated by a desire to conquer foreign lands. Enthused
with adventures form a big slice of man?s history. Let us see how these
journeys and eventually the contacts with distant lands shaped and affect
history.
After the collapse of the Mauryan
Empire, several small kingdoms came up. The most important development was the
arrival of foreign tribal groups in India.
The Indo- Greeks conquered much of
northern India including parts of Uttar Pradesh. The most famous rules was
Menander I. He converted to Buddhism. The Indo-Greeks issued coins, the first
of which were minted under Menander I.
The
Second Urbanisation
Summary
1.
From
the 1st century BCE to about 4th century CE, India underwent huge
transformation.
2.
During
this period, there was a spurt in agricultural production which led to the
emergence of many towns and cities.
3.
This
phase also opened up a network of internal and overseas trade routes.
4.
It
saw the introduction of currency and witnessed the development of numerous arts
and crafts including ceramics.
5.
Archaeologists
have found thousands of coins made of copper or silver with the design punched
on the metal. These are called punch marked coins.
6.
Pottery
of a different kind has been found. This pottery is called Northern Black
Polished Ware.
7.
Craftsmen
and artisans formed associations called guilds or shrenis. The enormous
manufacturing activity was maintained by these guilds.
8.
Arikamedu
was a very important trading centre and port.
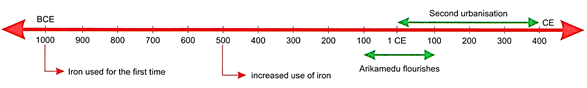 From the 1st century BCE to about
the 4th century CE, India underwent huge transformation. During this
period, iron was widely used. This period is known as the 'second
urbanisation?.
During this period, there was a
spurt in agricultural production which led to the emergence of many towns and
cities. This phase also opened up a network of internal and overseas trade
routes. It saw the introduction of currency and witnessed the development of
numerous arts and crafts including ceramics.
INCREASE IN AGRICULTURAL
PRODUCTION
There
were many factors which led to the increase in agricultural production. These
were:
? Introduction of Iron
Technology: Iron came into use in India in about 1000 BCE. It was
increasingly used after 500 BCE. The use of iron was of vital importance for
the expansion of agriculture. Iron axes were now used in clearing thick forests
and iron-tipped ploughshares ploughed the land better.
? Better Irrigation: This
was essential for better productivity. The kings funded the digging of canals,
wells, tanks and artificial lakes. This was also done with the help of iron
tools.
? Better Agricultural
Techniques: Farmers began to use the method of transplantation in which the
seeds were first more...
From the 1st century BCE to about
the 4th century CE, India underwent huge transformation. During this
period, iron was widely used. This period is known as the 'second
urbanisation?.
During this period, there was a
spurt in agricultural production which led to the emergence of many towns and
cities. This phase also opened up a network of internal and overseas trade
routes. It saw the introduction of currency and witnessed the development of
numerous arts and crafts including ceramics.
INCREASE IN AGRICULTURAL
PRODUCTION
There
were many factors which led to the increase in agricultural production. These
were:
? Introduction of Iron
Technology: Iron came into use in India in about 1000 BCE. It was
increasingly used after 500 BCE. The use of iron was of vital importance for
the expansion of agriculture. Iron axes were now used in clearing thick forests
and iron-tipped ploughshares ploughed the land better.
? Better Irrigation: This
was essential for better productivity. The kings funded the digging of canals,
wells, tanks and artificial lakes. This was also done with the help of iron
tools.
? Better Agricultural
Techniques: Farmers began to use the method of transplantation in which the
seeds were first more...  Do you know what an empire is? How
is it different from a kingdom? Have you ever wondered who built the first
empire in India? Let us explore in this chapter.
RISE OF THE FIRST EMPIRE IN INDIA
The foundation of the first empire
in India was laid by the Mauryan Dynasty in Magadha. The Mauryan dynasty had
three great emperors? Chandragupta Maurya, Bindusara and Ashoka.
Chandragupta Maurya laid the
foundation of India's first empire in Magadha in 321 BCE. He met Chanakya (also
known as Kautilya) who was a wise and shrewd Brahmin. With his help,
Chandragupta laid the foundation of a strong empire.
The empire stretched from Bengal
and Assam in the east to Afghanistan and Baluchistan in the west and Kashmir
and Nepal in the north to the Deccan Plateau in the south. It included large
cities like Pataliputra and more...
Do you know what an empire is? How
is it different from a kingdom? Have you ever wondered who built the first
empire in India? Let us explore in this chapter.
RISE OF THE FIRST EMPIRE IN INDIA
The foundation of the first empire
in India was laid by the Mauryan Dynasty in Magadha. The Mauryan dynasty had
three great emperors? Chandragupta Maurya, Bindusara and Ashoka.
Chandragupta Maurya laid the
foundation of India's first empire in Magadha in 321 BCE. He met Chanakya (also
known as Kautilya) who was a wise and shrewd Brahmin. With his help,
Chandragupta laid the foundation of a strong empire.
The empire stretched from Bengal
and Assam in the east to Afghanistan and Baluchistan in the west and Kashmir
and Nepal in the north to the Deccan Plateau in the south. It included large
cities like Pataliputra and more... 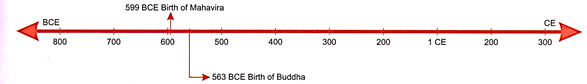 In the Later Vedic Age, ceremonies
and sacrifices became increasingly complicated. The caste system led to
differences amongst the people. People were dissatisfied and began thinking.
What was the meaning of all these rituals? What right did the brahmins have to
claim themselves as superior to the rest. This spirit of enquiry prevailed
towards the end of the later Vedic period.
THE UPANISHADS
Upanishad is a Sanskrit word
meaning sitting down near a teacher to receive instruction. In ancient times,
the pupils sat near the guru to receive knowledge from him. The Upanishads are
part of the Later Vedic literature
(lOOO-600 BCE)
During this time, there were many
unanswered Questions in the minds of the people. They discussed who had created
the world and why there was so much suffering in it. They wanted to know the
truth about God and the world They thought about the purpose of their
existence. They wanted to know the mysteries of life and what happened after
death. The ideas and teachings of these new thinkers are collected In books
known as the Upanishads.
WHAT DO THEY TELL US
Early
Kingdoms and Republics
Summary
1.
By the end of the Rig Vedic period, many territorial
states called janapadas arose as people stopped moving from one place to
another. These states became stronger and bigger and were called mahajanapadas.
2.
Buddhist texts tell us that there were 16 mahajanapadas.
3.
These mahajanapadas were either republican or
monarchial. In a republic (gana-sangha), the territory was governed by
an assembly and not a hereditary monarch.
4.
Important advancements in agriculture occurred which
led to increased agricultural production.
5.
The raja needed resources for maintaining an
army and also for fortifying the cities. So, the people had to pay taxes to the
king who appointed officials to collect them.
6.
Of all the mahajanapadas, Magadha came into
prominence. It became the seat of a powerful monarchy and the center of an
extensive empire.
7.
Magadha's favourable geographical location enabled it
to control the whole lower Gangetic plain.
8.
Vajji was a powerful republican state or gana-sangha.
In the Later Vedic Age, ceremonies
and sacrifices became increasingly complicated. The caste system led to
differences amongst the people. People were dissatisfied and began thinking.
What was the meaning of all these rituals? What right did the brahmins have to
claim themselves as superior to the rest. This spirit of enquiry prevailed
towards the end of the later Vedic period.
THE UPANISHADS
Upanishad is a Sanskrit word
meaning sitting down near a teacher to receive instruction. In ancient times,
the pupils sat near the guru to receive knowledge from him. The Upanishads are
part of the Later Vedic literature
(lOOO-600 BCE)
During this time, there were many
unanswered Questions in the minds of the people. They discussed who had created
the world and why there was so much suffering in it. They wanted to know the
truth about God and the world They thought about the purpose of their
existence. They wanted to know the mysteries of life and what happened after
death. The ideas and teachings of these new thinkers are collected In books
known as the Upanishads.
WHAT DO THEY TELL US
Early
Kingdoms and Republics
Summary
1.
By the end of the Rig Vedic period, many territorial
states called janapadas arose as people stopped moving from one place to
another. These states became stronger and bigger and were called mahajanapadas.
2.
Buddhist texts tell us that there were 16 mahajanapadas.
3.
These mahajanapadas were either republican or
monarchial. In a republic (gana-sangha), the territory was governed by
an assembly and not a hereditary monarch.
4.
Important advancements in agriculture occurred which
led to increased agricultural production.
5.
The raja needed resources for maintaining an
army and also for fortifying the cities. So, the people had to pay taxes to the
king who appointed officials to collect them.
6.
Of all the mahajanapadas, Magadha came into
prominence. It became the seat of a powerful monarchy and the center of an
extensive empire.
7.
Magadha's favourable geographical location enabled it
to control the whole lower Gangetic plain.
8.
Vajji was a powerful republican state or gana-sangha.
 How many states does India have?
Maharashtra, Manipur, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu etc., are all states of
India and India has 29 states. But what exactly is a state? In social sciences,
a. state is defined as the political body of a centralised government
exercising its authority within a certain territory. In simple words, it is an
area of land (sometimes sea) controlled by a single, independent government.
So, is India a state? The answer is yes. India is a republic state. Let us find
out about the emergence of early forms of republic states in India.
By the end of the Rig Vedic
period, the position of the ruler became very important. He was extremely
powerful and lived a luxurious life. We have read that earlier the rulers were
chosen by the jana. But by 1000 BCE, this trend was changing. Sometimes, a
person became a raja by performing the ashvamedha or horse sacrifice.
The king who organised it was
considered very powerful. During this sacrifice, a special
How many states does India have?
Maharashtra, Manipur, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu etc., are all states of
India and India has 29 states. But what exactly is a state? In social sciences,
a. state is defined as the political body of a centralised government
exercising its authority within a certain territory. In simple words, it is an
area of land (sometimes sea) controlled by a single, independent government.
So, is India a state? The answer is yes. India is a republic state. Let us find
out about the emergence of early forms of republic states in India.
By the end of the Rig Vedic
period, the position of the ruler became very important. He was extremely
powerful and lived a luxurious life. We have read that earlier the rulers were
chosen by the jana. But by 1000 BCE, this trend was changing. Sometimes, a
person became a raja by performing the ashvamedha or horse sacrifice.
The king who organised it was
considered very powerful. During this sacrifice, a special
 The
Vedic Age
Summary
1.
The
Aryans were nomadic people who came to India from the north-west.
2.
They
settled down and gradually took to agriculture.
3.
Our
knowledge of the Aryans comes from the Vedas.
4.
The
Rigveda gives information about the Early Vedic Age.
5.
The
period when the Aryans first settled in India is known as the Early Vedic Age
(1500 BCE to 1000 BCE).
6.
During
this period, the kingdoms were tribal in character.
7.
The
period between 1000 BCE to 600 BCE is known as the Later Vedic Age.
8.
The
king now became very powerful and the status of women declined.
9.
Megalithic
burials have been found in many places in India.
10.
Inamgoan
is believed to have been occupied from 1600 BCE to 700 BCE.
The
Vedic Age
Summary
1.
The
Aryans were nomadic people who came to India from the north-west.
2.
They
settled down and gradually took to agriculture.
3.
Our
knowledge of the Aryans comes from the Vedas.
4.
The
Rigveda gives information about the Early Vedic Age.
5.
The
period when the Aryans first settled in India is known as the Early Vedic Age
(1500 BCE to 1000 BCE).
6.
During
this period, the kingdoms were tribal in character.
7.
The
period between 1000 BCE to 600 BCE is known as the Later Vedic Age.
8.
The
king now became very powerful and the status of women declined.
9.
Megalithic
burials have been found in many places in India.
10.
Inamgoan
is believed to have been occupied from 1600 BCE to 700 BCE.
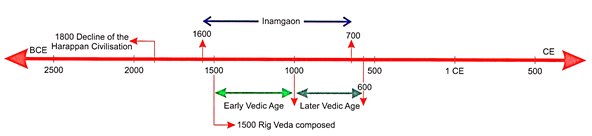 Have you ever
heard or recited the Gayatri Mantra? It is from the oldest text in India called
the Rigveda. There are four Vedas. The Rigveda is the oldest among them. The
Vedic Age is the period during which the Vedas were composed. This period from
1500 BCE to 600 BCE, is often called the Vedic Age.
Earlier, we have
read about the Harappan Civilisation. Slowly it declined and by around 1800
BCE, people again began living a simple life in villages. About this time, some
people entered India from the north-west. They called themselves 'Arya' meaning
'noble ones'. A new culture developed in India with the arrival of the Aryans.
They did not come to India to invade and plunder and go back. They settled down
in the plains and took to agriculture. They first settled in seven places in
the Punjab region which they called Sapta Sindhu. These Aryans who settled in
India are called Indo-Aryans.
STUDY OF
VEDAS
Our knowledge of the Aryans comes
from the Vedas. The Vedic Age gets its name from the four Vedas. Historians have
studied these texts carefully. They provide an insight into the life of the
Vedic Age.
LANGUAGES
The Aryans spoke
a language more...
Have you ever
heard or recited the Gayatri Mantra? It is from the oldest text in India called
the Rigveda. There are four Vedas. The Rigveda is the oldest among them. The
Vedic Age is the period during which the Vedas were composed. This period from
1500 BCE to 600 BCE, is often called the Vedic Age.
Earlier, we have
read about the Harappan Civilisation. Slowly it declined and by around 1800
BCE, people again began living a simple life in villages. About this time, some
people entered India from the north-west. They called themselves 'Arya' meaning
'noble ones'. A new culture developed in India with the arrival of the Aryans.
They did not come to India to invade and plunder and go back. They settled down
in the plains and took to agriculture. They first settled in seven places in
the Punjab region which they called Sapta Sindhu. These Aryans who settled in
India are called Indo-Aryans.
STUDY OF
VEDAS
Our knowledge of the Aryans comes
from the Vedas. The Vedic Age gets its name from the four Vedas. Historians have
studied these texts carefully. They provide an insight into the life of the
Vedic Age.
LANGUAGES
The Aryans spoke
a language more... 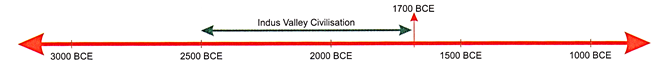 The
first civilisations came about in river valleys. The first four river valley
civilisations of the world were: Mesopotamia along the Tigris and Euphrates
rivers), China (along the River Hwang Ho), Egypt (along the Nile River) and
Indus Valley (along the Indus River).
THE STORY OF HARAPPA AND
MOHENJODARO
The British were laying the
railway line connecting the cities of Karachi and Lahore in 1856. The labourers
once an out of bricks and used baked bricks from some ancient ruins near the
railway lines. These bricks were used to ake9 3 miles of railway track. It was
discovered only later that these bricks were almost 5000 years old! Alexander
Cunningham, the director of the Archaeological Survey of India visited this
place, Harappa in 1872. He found stone tools, seals and pottery of an ancient
civilisation. Also, nearby was a mound called "Mohenjodaro" meaning
'mound of the dead". Often children playing there found articles like
bangles, dices, broken clay toys etc. it was suspected that this place was once
inhabited by people. Excavations were started there and initially two cities
were discovered, Harappa and Mohenjodaro. These were called the Indus Valley
Civilisation. Harappa was Discovered first, so it is also called the Harappan
civilisation. This civilisation is believed to have existed between 2500 BCE to
about 1700 BCE.
IMPORTANCE OF THE DISCOVERIES
The discovery of these two cities
changed the whole idea of how the Indian civilisation began. It was believed
that before the Aryans came to more...
The
first civilisations came about in river valleys. The first four river valley
civilisations of the world were: Mesopotamia along the Tigris and Euphrates
rivers), China (along the River Hwang Ho), Egypt (along the Nile River) and
Indus Valley (along the Indus River).
THE STORY OF HARAPPA AND
MOHENJODARO
The British were laying the
railway line connecting the cities of Karachi and Lahore in 1856. The labourers
once an out of bricks and used baked bricks from some ancient ruins near the
railway lines. These bricks were used to ake9 3 miles of railway track. It was
discovered only later that these bricks were almost 5000 years old! Alexander
Cunningham, the director of the Archaeological Survey of India visited this
place, Harappa in 1872. He found stone tools, seals and pottery of an ancient
civilisation. Also, nearby was a mound called "Mohenjodaro" meaning
'mound of the dead". Often children playing there found articles like
bangles, dices, broken clay toys etc. it was suspected that this place was once
inhabited by people. Excavations were started there and initially two cities
were discovered, Harappa and Mohenjodaro. These were called the Indus Valley
Civilisation. Harappa was Discovered first, so it is also called the Harappan
civilisation. This civilisation is believed to have existed between 2500 BCE to
about 1700 BCE.
IMPORTANCE OF THE DISCOVERIES
The discovery of these two cities
changed the whole idea of how the Indian civilisation began. It was believed
that before the Aryans came to more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
