Category : 6th Class
Learning Objectives
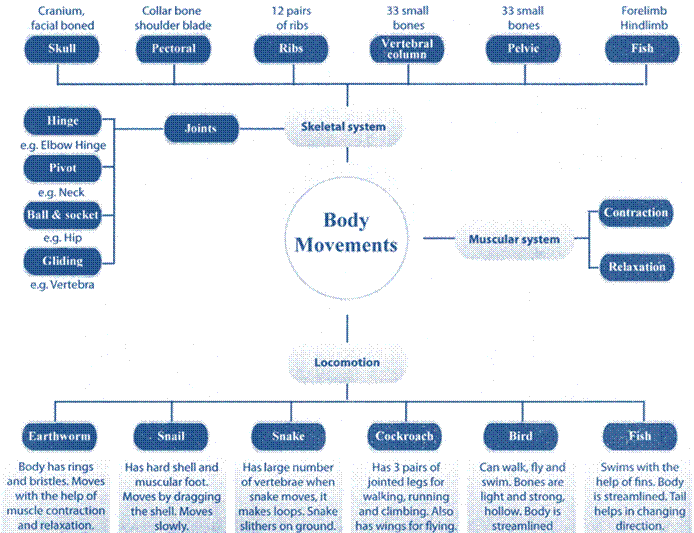
1. Locomotion is movement of animals from one place to another.
2. Skeleton in humans is made of bones and cartilages.
3. Bones are joined to muscles by tendons.
4. Where two bones meet the place is called a joint.
5. The skull, backbone, shoulder bones, hip bones and ribs form the skeleton system.
6. Movements In various organisms like snail, earthworm, fish, snake and birds are different.
Living things differ from non-living things in that living things show movements of their body parts. Even when we are at rest our body shows some movements like blinking of eyes. Animals move from one place to another. For this purpose they show various kinds of movements like walking, running, flying, creeping, slithering crawling, etc.
Movements: A change in the position of any object is called movement. Many movements take place in our body and also in other organisms' body.
Locomotion: When movement results in change of position of the whole organism, it is called locomotion.
Examples of Movements in the Human Body:
(a) Movement of eyelids.
(b) Movement of the heart muscles.
(c) Movement of teeth and jaw.
(d) Movement of arms and legs.
(e) Movements of head.
(f) Movements of neck.
Movement of some organs happens because of the team work of bones and muscles. In such cases, movement is possible along a point where two or more bones meet.
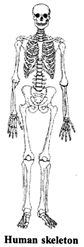
Human body movements: Humans can move their various body parts indifferent ways. We can move some parts of our body in different directions and some body parts can be moved only in one direction. Our body is made up of a frame work of bones called skeleton.
1. Bones are made of hard substance.
2. Cartilages are soft and elastic.
3. In the bone marrow, red blood cells are produced.
4. Bones are of many shapes and sizes. Some are flat, some are cylindrical and some are spherical.
5. The longest bone of our body is femur and the smallest bone is found in our internal ears.
6. Cartilages are found in our nose and external ears.
7. Skeleton system extends from the top of our head to the tip of the toes.
Functions of skeleton:
Bones are held together by strands of tissues called ligaments. Points where two bones join are called joints. There are 206 bones in a human body.
DESCRIPTION OF SKELETON
(a) Skull: The bony part of head is called skull. The skull is made up of 22 bones joined together. These bones are not movable except the lower jaw bone. It has two parts; the cranium or the brain box and the facial bones. The cranium covers and protects the brain. The facial bones form the upper and lower jaws and some other bones. The eye sockets are also part of skull.

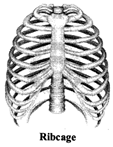
(b) Ribcage: Ribs are curved bones in the body. There are 12 pairs of ribs.
The ribs are curiously bent. They join the chest bone and the back bone together to form a box. This is called a ribcage.
Ribcage protects the internal organs of the body like heart, lungs.
Cartilage attaches 10 of them to the breast bone at the front.
Two ribs are free and are called floating ribs. The ribs allow certain kind of movement of the chest during breathing.
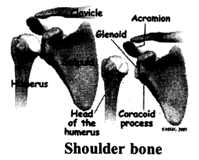
(c) Shoulder bone or Pectoral girdle: The shoulder bone is formed by the collar bone and the shoulder blade. It is attached to the upper part of their b-cage and to the upper arm bone.
Do You Know
The longest bone is the femur or thigh bone, which forms ¼ of the body height. The shortest bone is the stirrup in the ear.
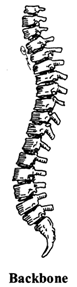
4. (d) Backbone: The backbone is a long hollow, rod like structure running from the neck to the hips. Back bone is made up of 33 small bones place done over the other. These small bones are called vertebrae. It provides support to the body and protects spinal cord.
(e) Pelvic bones: The pelvic bones form a large, basin shaped frame at the lower end of the back bone, to which legs are attached. The pelvic bone sencloses the portion of our body below the stomach. It is formed by the fusion of three bones, the hip bones and the tail parts of the back bone; to from a large bony bowl. The thigh bones are attached to the hip bone.
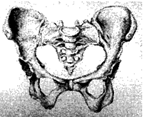
Hipbone
BONE JOINTS
The places where two or more bones meet are called joints. There are various kinds of joints.
(a) Ball and socket joint
(b) Hinge joint
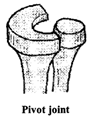
(c) Pivot joint
(d) Fixed joint.
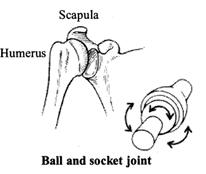
(a) Ball and socket joint: The rounded end of one bone fits into cavity (hollow space) of the other bone is called ball and socket joint. Such joints allow movements in all directions. Ex. shoulder joints, hip joints.
(b) Hinge joint: A hinge joints allow the movements of bones in only in one direction. Forwards and backwards. Ex. elbow and knee joints. The movement by this joint is not more than 180 degrees. The wrist has double hinge joint.
Do You Know
There are more than 350 Joints in our body.
The biggest joint is in the knee.
The bandiest joint is in the shoulder.
The tiniest joist is in the ear. It is smaller than letter ‘a’.
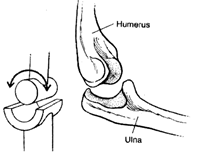
Hinge joint
(c) Pivot joint: Such joints allow only rotation against one another. In it acylindrical bone rotates in a ring. It allows us to bend our head forward and backward and turn the head to our right and left.
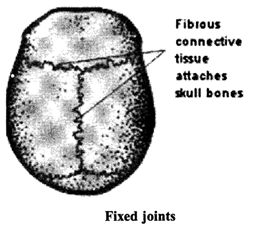
(d) Fixed joints: In some joints, the bones are held so tightly together that they cannot move at all. Such joints are called fixed joints. E.g. joint between the skull and the upper jaw.
Do Know You
Many bones are curved like the skull bones because it makes them much stronger than if they were flat.
MUSCLES
Muscle is a fibrous tissue in the body which has ability to contract. When muscle contracts, it shortens and pulls the bone due to which the bone move at that joint. A muscle can only pull a bone it cannot push a bone. The muscles joined to our bones work in pairs. When one muscle of a pair contracts, then the other muscle of a pair is relaxed. A contracted muscle can come back to its original position only when the other muscle of the pair pulls it by contracting itself. Muscles are attached to the bones by fibres called tendons.
Do You Know
The body’s bandiest muscle is the one you use to talk, eat, drink and lick your lips. It’s your tongue.
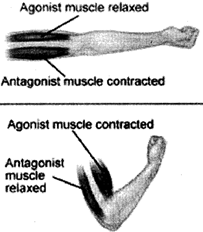
The skeleton and muscles play important role in the movement of animals.
The skeleton is made of bones joined together by fbres called ligaments.
Before birth our skeleton is made up of cartilage and is soft.
Later these cartilages get changed to bones. Bones become hard because of deposits of calcium and phosphorus.
LOCOMOTION
Animals differ from plants in that they show quick movements. Plants show slow movements. Most of the animals move from one place to another.
However some animals like sponges, corals, sea anemones remain fixed atone place. They simply show body movements but no locomotion.
Why animals move?
Do You Know
Animals without Bones: All animals do not have bones.
Bones are present in animals with backbones that is vertebrates.
Animals move in search of food.
They move to escape from enemies and predators.
To get better habitat.
To find mate for reproduction.
Gait of animals: Different animals have different organs for locomotion,
Earthworm: The body of earthworm is made up of many rings joined end to end. It has muscles which help to extend and shorten the body. Under its body it has large number of bristles which are connected with muscles. This bristles help to get grip on the ground.
During movement, the earthworm first extends the front part of body, keeping the rear portion fixed to the ground. Then it fixes the front end and release the rear end. It then shortens the body and pull the rear end forward. This makes it forward by small distances. Repeating such muscle contraction and relaxations the earthworm can move through soil. Its body secrete a slimy substance to help movement.
![]()
Snail: the body of snail is covered with a hard and in flexible shell. It has an opening with a lid. The snail drags the shell while moving. The head comes out through the opening in the shell. The snail has muscular foot which helps in locomotion. The muscular foot is made up of strong muscles. The foot is attached to the belly and it produces slow wavy movements. Hence a snail moves slowly.
Cockroach: A cockroach has three pairs of jointed legs, which help it to walk, run and climb. It also has two pairs of wings; for flying. Large and strong muscles help in the movement of legs. The body is covered by chitin, alight protective material. Chitin is shed regularly so that the body can grow.
Birds: Birds can walk on the ground and fly as well. Some birds can also swim in the water.
A bird has streamlined body. Its bones are light and strong. They are hollow and have air spaces between them. The hind limbs of birds are modified as claws, which help it to walk and to perch. The breast bones are modified to hold massive flight muscles which help in moving wings up and down.
Birds have special flight muscles and the forelimbs are modified as wings.
The wings and tail have long feathers, which help in flying. Birds show two types of flight; gliding and flapping.
Snake: The body of snake consists of a large number of vertebrae. The adjoining vertebrae, ribs and skin are inter connected with slender body muscles.
When the snake moves, it makes many loops on its sides. The forward push of the loops against the surface makes the snake move forward. Movement of snake is called slithering movement. Many snakes can swim in water also.
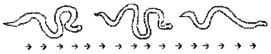
Fish: Fish swims with the help of fins. They have two paired fins and an unpaired fin. The body of a fish is streamlined to reduce friction; while moving in water. They have strong muscles, which help in swimming. When a fish swims; its front part curves to one side and the tail part stays in the opposite direction. In the next move, the front part curves to the opposite side and the tail part also changes its position to another side. The tail fin helps in changing direction.
Do You Know
Both the squid and octopus move via jet propulsion.
Underwater divers wear fin like flippers on their feet to help them move easily in water.
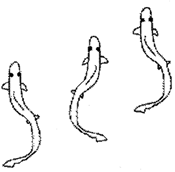
Movement of fish
Key words
Concept Map
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
