





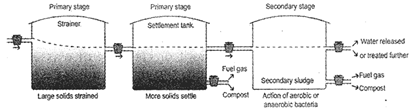
 Then the sewage is passed to settlement tank to settle down the suspended solids to the bottom. The solids settled at the bottom of the settlement tank are called primary sludge. The sludge is used for producing compost and biogas. After this the sewage undergoes secondary treatment. In this, organic matters break down by the action of bacteria. This is done in open tanks called aeration tanks. Aerobic bacteria that needs oxygen act on the sewage in the aeration tanks. Air is blown into these tanks to speed up the process.
Sometimes the organic matters in the sewage break down by anaerobic bacteria in closed tanks. The solids get settled at the bottom of tank by the action of bacteria and are called biological or secondary sludge. The sewage can further undergo tertiary treatment before being discharged into water bodies. In this, the sewage passes through sand filters, man-made ponds containing reeds and other organisms that clean out dissolve chemicals.
Then the sewage is passed to settlement tank to settle down the suspended solids to the bottom. The solids settled at the bottom of the settlement tank are called primary sludge. The sludge is used for producing compost and biogas. After this the sewage undergoes secondary treatment. In this, organic matters break down by the action of bacteria. This is done in open tanks called aeration tanks. Aerobic bacteria that needs oxygen act on the sewage in the aeration tanks. Air is blown into these tanks to speed up the process.
Sometimes the organic matters in the sewage break down by anaerobic bacteria in closed tanks. The solids get settled at the bottom of tank by the action of bacteria and are called biological or secondary sludge. The sewage can further undergo tertiary treatment before being discharged into water bodies. In this, the sewage passes through sand filters, man-made ponds containing reeds and other organisms that clean out dissolve chemicals.



 Deforestation, particularly in the tropical rain forests, has become a major environmental concern, as it can destabilize the earth's temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide levels. To maintain the environmental balance and to control pollution, deforestation or shrinking of forests should be controlled.
Deforestation, particularly in the tropical rain forests, has become a major environmental concern, as it can destabilize the earth's temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide levels. To maintain the environmental balance and to control pollution, deforestation or shrinking of forests should be controlled.  In the picture above, a Stevenson screen is shown, which is used for the temperature or humidity measurement of atmosphere. Covers of the Stevenson screen protect it from destructive elements. Holes on the walls allow air passing through it. Stevenson screen is an important measuring instrument in the weather station.
In the picture above, a Stevenson screen is shown, which is used for the temperature or humidity measurement of atmosphere. Covers of the Stevenson screen protect it from destructive elements. Holes on the walls allow air passing through it. Stevenson screen is an important measuring instrument in the weather station.





You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
