Category : 9th Class
Diversity in Living Organisms
Diversity in Living Organism
This world is full of living and non-living things. Large variety of living organisms is found on this planet. There is a great diversity among them. From the microorganisms to well-developed animals, one can notice the diversity at all levels.
Basis of Classification
Classification is a method of arranging organisms into groups or sets on the basis of similarities and differences. The study of classification is known as taxonomy. The process of classification began hundreds of years ago. First animals were classified according to whether they lived on
Land, in water or in the air, but this classification was not adequate. So the need of more accurate form classification was realised and thus some characteristics were used as a basis for making the broadest divisions for making groups and subgroups.
Classification and Evolution
All living things are categorised on the basis of their body design the and function. The characteristics that came into existence earlier are likely to be more basic than characteristics that have come into existence later. This clearly indicates that the classification of life forms is directly and very closely related to the evolution. Charles Darwin the renowned biologist first described the idea of evolution in 1859 in his book “The Origin of Species”.
Hierarchy of Classification
R. H. in 1969 proposed five kingdom classification. They are as following:
Five Kingdom Classification
|
Characters |
Monera |
Protista |
Fungi |
Plantae |
Animalia |
|
Cell type |
Prokaryotic |
Eukaryotic |
Eukaryotic |
Eukaryotic |
Eukaryotic |
|
Cell wall |
Noncellular (polysaccharide + amino acid |
Present in some |
Present (without cellulose) |
Present (cellulose) |
Absent |
|
Nuclear membrane |
Absent |
Present |
Present |
Present |
Present |
|
Body organization |
Cellular |
Cellular |
Multiceullar/loose tissue |
Tissue/organ |
Tissue/organ/organ system |
|
Mode of nutrition |
Autotrophic (chemosyn-thetic and photosynthetic) and Hetero-trophic (sapro-phyte/para-site) |
Autotrophic (Photosyn- thetic) and Hetero-trophic |
Heterotrophic (Saprophytic/Parasitic) |
Autotrophic (Photosyn-thetic |
Heterotrophic (Holozole/Saprophytic etc.) |
Monera: The organisms that come in this category do not have a defined nucleus or organells. They of nutrition in these organisms can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. The organisms of this group are bacteria, blue-green algae, etc.
Protista: It consists of unicellular eukaryotic organisms. Some of these organisms use appendages such as hair like cilia or whip like flagellum. Their mode of nutrition can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. The organisms of this group are unicellular algae, protozoan amoeba, etc.
Fungi: They are the heterotrophic and eukaryotic organisms. They may be unicellular or multicellular. They have a cell wall containing a mixture of chitin and cellulose. They use decaying organic material as food and are therefore, called saprophytes. The organisms of this group are yeast, mushroom, rhizopus, etc.
Plantae: They are the multicellular eukaryotes with cell walls. Their mode of nutrition is autotrophic and they use chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Plantae can be further classified in the following types:
Kingdom Plantae
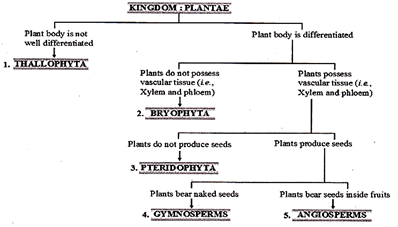
Examples:
Thallophyta Bryophyta Pteriophyta

Chara Riccia Equisetum
Gymnosperms


Ginkgo Conifer
Angiosperms


Monocotyledon Dicotyledon Mango
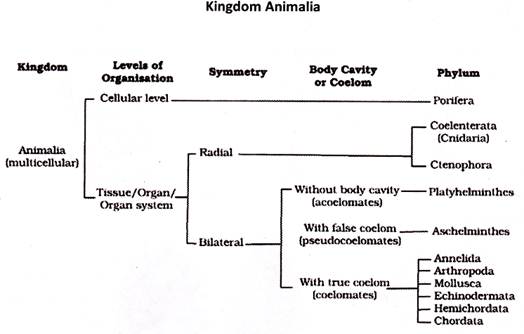
Animalia: They are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms without cell walls. The mode of nutrition is heterotrophic. Their cells do not have cell walls and most of the animals are mobile. They are classified into the following groups:
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
