 TYPES OF DRAWING
TYPES OF DRAWING
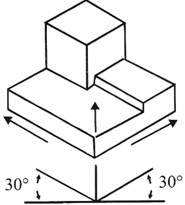
 Isometric Drawing
Representation of the object in figure below is called an isometric drawing. This is one of a family of three-dimensional views called pictorial drawings. In an isometric drawing, the object's vertical lines are drawn vertically, and the horizontal lines in the width and depth planes are shown at 30 degrees to the horizontal. When drawn under these guidelines, the lines parallel to these three axes are at their true (scale) lengths. Lines that are not parallel to these axes will not be of their true length.
Figure An Isometric Drawing
Isometric Drawing
Representation of the object in figure below is called an isometric drawing. This is one of a family of three-dimensional views called pictorial drawings. In an isometric drawing, the object's vertical lines are drawn vertically, and the horizontal lines in the width and depth planes are shown at 30 degrees to the horizontal. When drawn under these guidelines, the lines parallel to these three axes are at their true (scale) lengths. Lines that are not parallel to these axes will not be of their true length.
Figure An Isometric Drawing
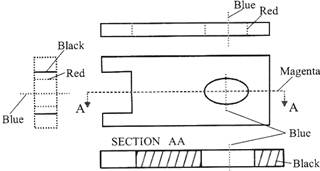
 A engineering drawing should show everything: beaa complete understanding of the object should be possible from the drawing-
If the isometric drawing can show all details and all dimensions on one drawing, it is ideal. One can pack a great deal of information into an isometric drawing. However, if the object in figure above had a hole on the back side, it would not be visible using a single isometric drawing. In order to get a more complete view of the object, an orthographic projection may be used.
Orthographic Drawing
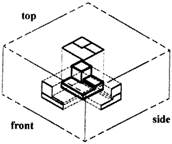
Imagine that we have an object suspended by transparent threads inside a glass box, as in figure below.
Figure - The block suspended in a glass box
A engineering drawing should show everything: beaa complete understanding of the object should be possible from the drawing-
If the isometric drawing can show all details and all dimensions on one drawing, it is ideal. One can pack a great deal of information into an isometric drawing. However, if the object in figure above had a hole on the back side, it would not be visible using a single isometric drawing. In order to get a more complete view of the object, an orthographic projection may be used.
Orthographic Drawing
Imagine that we have an object suspended by transparent threads inside a glass box, as in figure below.
Figure - The block suspended in a glass box
 Then draw the object on each of three faces as seen from that direction. Unfold the box (figure below) and you have the three views. We call this an "orthographic" or "multi-view" drawing.
Figure - The creation more...
Then draw the object on each of three faces as seen from that direction. Unfold the box (figure below) and you have the three views. We call this an "orthographic" or "multi-view" drawing.
Figure - The creation more... |
|
Only numerical value Ex. Refractive index, dielectric constant etc. |
| Only magnitude ex, Mass, charge etc. | |
| Magnitude and direction Displacemnt, torque etc. |
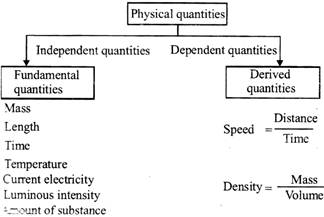 The physical quantities which do not depend upon other Physical quantities are called fundamental quantities. In M.K.S System the fundamental quantities are mass, length and time
In standard International system the fundamental quantities are mass, length, time, temperature, illuminatig power current and amount of substance, The physical quantities which depend on fundamental quantities are called derived quantities e, g. speed, acceleration, force, etc
UNITS
The unit of a physical quantity is the reference standard used to measure it.
For the measurement of a physical quantity a definite magnitude of quantity is taken as standard and the name given to this standard is called unit.
Properties of Unit
(a) The unit should be well-defined.
(b) The unit should be of some suitable size.
(c) The unit should be easily reproducible.
(d) The unit should not change with time.
(e) The unit should not change with physical conditions like pressure, temperature etc.
(f) The unit should be universally acceptable.
Types of Units
The physical quantities which do not depend upon other Physical quantities are called fundamental quantities. In M.K.S System the fundamental quantities are mass, length and time
In standard International system the fundamental quantities are mass, length, time, temperature, illuminatig power current and amount of substance, The physical quantities which depend on fundamental quantities are called derived quantities e, g. speed, acceleration, force, etc
UNITS
The unit of a physical quantity is the reference standard used to measure it.
For the measurement of a physical quantity a definite magnitude of quantity is taken as standard and the name given to this standard is called unit.
Properties of Unit
(a) The unit should be well-defined.
(b) The unit should be of some suitable size.
(c) The unit should be easily reproducible.
(d) The unit should not change with time.
(e) The unit should not change with physical conditions like pressure, temperature etc.
(f) The unit should be universally acceptable.
Types of Units
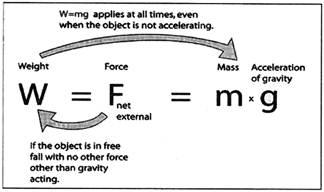 The value of g allows us to determine the net gravity force if it were in freefall and that net gravity force is the weight. Another approach is to consider "g" to be the measure of the intensity of
Ac gravity field in Newtons/kg at our location. We can view the weight as a measure of the mass in kg times the intensity of the gravity field, 9.8 Newton's/kg under standard conditions.
Density
Density (p) is defined as the mass of a substance per unit volume.
The value of g allows us to determine the net gravity force if it were in freefall and that net gravity force is the weight. Another approach is to consider "g" to be the measure of the intensity of
Ac gravity field in Newtons/kg at our location. We can view the weight as a measure of the mass in kg times the intensity of the gravity field, 9.8 Newton's/kg under standard conditions.
Density
Density (p) is defined as the mass of a substance per unit volume.
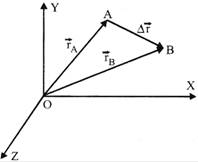 Position vector of Aw.r.t. O=\[\overrightarrow{OA}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\overrightarrow{{{r}_{A}}}={{x}_{1}}\,\,\hat{i}+{{y}_{1}}\,\,\hat{j}+{{z}_{1}}\,\,\hat{k}\]
Position vector of B w.r.t. O\[=\overrightarrow{OB}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\overrightarrow{{{r}_{B}}}={{x}_{2}}\,\,\hat{i}+{{y}_{2}}\,\,\hat{j}+{{z}_{1}}\,\,\hat{k}\]
Displacement \[=\overrightarrow{AB}=({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})\,\,\hat{i}+({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})\,\,\hat{j}+({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})\,\,\hat{k}\]
\[\Delta \overrightarrow{r}=\Delta x\,\,\hat{i}+\Delta y\,\,\hat{j}+\Delta z\,\,\hat{k}\]
Characteristics of displacement
(i) It is a vector quantity.
(ii) The displacement of a particle between any two points is equal more...
Position vector of Aw.r.t. O=\[\overrightarrow{OA}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\overrightarrow{{{r}_{A}}}={{x}_{1}}\,\,\hat{i}+{{y}_{1}}\,\,\hat{j}+{{z}_{1}}\,\,\hat{k}\]
Position vector of B w.r.t. O\[=\overrightarrow{OB}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] \[\overrightarrow{{{r}_{B}}}={{x}_{2}}\,\,\hat{i}+{{y}_{2}}\,\,\hat{j}+{{z}_{1}}\,\,\hat{k}\]
Displacement \[=\overrightarrow{AB}=({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})\,\,\hat{i}+({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})\,\,\hat{j}+({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})\,\,\hat{k}\]
\[\Delta \overrightarrow{r}=\Delta x\,\,\hat{i}+\Delta y\,\,\hat{j}+\Delta z\,\,\hat{k}\]
Characteristics of displacement
(i) It is a vector quantity.
(ii) The displacement of a particle between any two points is equal more...  i.e., W= (F cos q) S=F S cos q or W=\[\overrightarrow{F.}\,\overrightarrow{S}\]
In terms of rectangular components, work done
W=\[\overrightarrow{F.}\,\overrightarrow{d}\]
\[W=(\hat{i}\,{{F}_{x}}+\hat{j}\,{{F}_{y}}+\hat{k}\,{{F}_{Z}}).(\hat{i}\,\,dx+\hat{j}\,dy+\hat{k}\,\,dz)\]
\[={{F}_{x}}dx+{{F}_{y}}dy+{{F}_{Z}}dz\]
Units of work
SI unit: joule (J). One joule of work is said to be done when a force of one newton displaces a body by one metre in the direction of force
\[1\,\,joule={{10}^{7}}erg\]
Dimensions of work:
Work = force, displacement
\[=[ML{{T}^{-2}}][L]=[M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}}]\]
Work Done in Pulling and Pushing an Object
\[F=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg}{\cos \theta +\mu \sin \theta }=force\,\,required\,to\,pull\,on\,object\] force required to pull an object \[W=F\,\,d=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg\,\,d}{\cos \theta +\mu \,\,\sin \,\theta }\]
Similarly, work done in pushing an object
\[W=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg\,\,d}{\cos \theta +\mu \,\,\sin \,\theta }\]
Work Done by a Variable Force
\[W=\int\limits_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{Fdx=}\]area under F-x curve with proper algebraic sign.
Work done by external force when spring is elongated from \[{{x}_{1}}to\,{{x}_{2}}\]
Work done in small displacement dx, dW = Fdx
Total work done, W=\[\int\limits_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{Fdx=k\,\,\int\limits_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{xdx}}\]
\[F=kx\]
The constant k is the spring constant or force constant.
\[W=\frac{1}{2}k{{x}_{2}}^{2}-\frac{1}{2}k{{x}_{1}}^{2}\]
Conservative Force
A force is said to be conservative, if the work done, by or against the force
(i) is independent of path and depends only on initial and final positions.
(ii) does not depend on the nature of path followed between the initial and final positions.
Examples of conservative force: All central forces are conservative like gravitational, electrostatic, elastic force, restoring force due to spring etc.
SPECIAL POINTS
(a) Work done along a closed path or in a cyclic process is zero. i.e.\[i.e.\,\,\oint{F.dx=0}\]
(b) If \[\overrightarrow{F}\] is a conservative force, then \[\overrightarrow{\Delta }\times \overrightarrow{F}=0\]
Non-conservative Force
A force is said to be non-conservative, if work done, by or against the force in moving a body depends upon the path between the initial and final positions.
The work done in a closed path is not zero in a non-conservative force field.
Examples of non-conservative force: Air resistance, viscous force etc.
Energy
The energy of a body is defined as the capacity of doing work or ability of the body to do work.
It is a scalar quantity.
The dimensional formula of energy is \[[M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}}]\]. It is the same as that of work. The unit of energy are the same as that of work Le,, joule in S. I. system and erg in CGS system.
Kinetic Energy
It is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion. If v be the velocity acquired by the block after travelling a distance x,
then kinetic energy
\[K=W=Fx=m.a.x=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\] \[[\therefore {{v}^{2}}=2ax]\]
Work Energy Theorem for a Variable Force
The work done by the resultant force in displacing the particle from\[{{x}_{0}}\] to x is
\[W=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}f-\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}_{i}\]
'The work done by more...
i.e., W= (F cos q) S=F S cos q or W=\[\overrightarrow{F.}\,\overrightarrow{S}\]
In terms of rectangular components, work done
W=\[\overrightarrow{F.}\,\overrightarrow{d}\]
\[W=(\hat{i}\,{{F}_{x}}+\hat{j}\,{{F}_{y}}+\hat{k}\,{{F}_{Z}}).(\hat{i}\,\,dx+\hat{j}\,dy+\hat{k}\,\,dz)\]
\[={{F}_{x}}dx+{{F}_{y}}dy+{{F}_{Z}}dz\]
Units of work
SI unit: joule (J). One joule of work is said to be done when a force of one newton displaces a body by one metre in the direction of force
\[1\,\,joule={{10}^{7}}erg\]
Dimensions of work:
Work = force, displacement
\[=[ML{{T}^{-2}}][L]=[M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}}]\]
Work Done in Pulling and Pushing an Object
\[F=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg}{\cos \theta +\mu \sin \theta }=force\,\,required\,to\,pull\,on\,object\] force required to pull an object \[W=F\,\,d=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg\,\,d}{\cos \theta +\mu \,\,\sin \,\theta }\]
Similarly, work done in pushing an object
\[W=\frac{\mu \,\,Mg\,\,d}{\cos \theta +\mu \,\,\sin \,\theta }\]
Work Done by a Variable Force
\[W=\int\limits_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{Fdx=}\]area under F-x curve with proper algebraic sign.
Work done by external force when spring is elongated from \[{{x}_{1}}to\,{{x}_{2}}\]
Work done in small displacement dx, dW = Fdx
Total work done, W=\[\int\limits_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{Fdx=k\,\,\int\limits_{{{x}_{1}}}^{{{x}_{2}}}{xdx}}\]
\[F=kx\]
The constant k is the spring constant or force constant.
\[W=\frac{1}{2}k{{x}_{2}}^{2}-\frac{1}{2}k{{x}_{1}}^{2}\]
Conservative Force
A force is said to be conservative, if the work done, by or against the force
(i) is independent of path and depends only on initial and final positions.
(ii) does not depend on the nature of path followed between the initial and final positions.
Examples of conservative force: All central forces are conservative like gravitational, electrostatic, elastic force, restoring force due to spring etc.
SPECIAL POINTS
(a) Work done along a closed path or in a cyclic process is zero. i.e.\[i.e.\,\,\oint{F.dx=0}\]
(b) If \[\overrightarrow{F}\] is a conservative force, then \[\overrightarrow{\Delta }\times \overrightarrow{F}=0\]
Non-conservative Force
A force is said to be non-conservative, if work done, by or against the force in moving a body depends upon the path between the initial and final positions.
The work done in a closed path is not zero in a non-conservative force field.
Examples of non-conservative force: Air resistance, viscous force etc.
Energy
The energy of a body is defined as the capacity of doing work or ability of the body to do work.
It is a scalar quantity.
The dimensional formula of energy is \[[M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}}]\]. It is the same as that of work. The unit of energy are the same as that of work Le,, joule in S. I. system and erg in CGS system.
Kinetic Energy
It is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion. If v be the velocity acquired by the block after travelling a distance x,
then kinetic energy
\[K=W=Fx=m.a.x=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\] \[[\therefore {{v}^{2}}=2ax]\]
Work Energy Theorem for a Variable Force
The work done by the resultant force in displacing the particle from\[{{x}_{0}}\] to x is
\[W=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}f-\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}_{i}\]
'The work done by more... 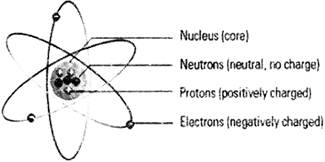 In the atom, there are three sub-atomic particles — Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Protons and Neutrons are located right in the nucleus (centre or core) of the atom. Around the nucleus, here are electrons that are constantly moving very quickly. The electrons move because they have some energy. Neutrons have no charges. Protons are positively charged. Electrons are negatively charged, and they encircle the nucleus. Elections encircle the nucleus because opposite charges (negative charge electrons and positive charge protons) are attracted to each other, and alike charges tend to move away from each other.
In the atom, there are three sub-atomic particles — Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. Protons and Neutrons are located right in the nucleus (centre or core) of the atom. Around the nucleus, here are electrons that are constantly moving very quickly. The electrons move because they have some energy. Neutrons have no charges. Protons are positively charged. Electrons are negatively charged, and they encircle the nucleus. Elections encircle the nucleus because opposite charges (negative charge electrons and positive charge protons) are attracted to each other, and alike charges tend to move away from each other.
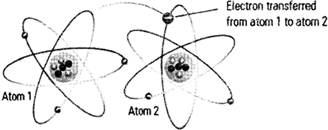 The encircling electron can move from one atom to the other.
When Protons and fast moving Electrons interact, electricity is produced. to simple terms, electricity is the interaction of Protons in the atom and the fast moving of Electrons around it. It is the flow of' electrons
BASIC ELECTRICITY
Electricity is the flow of electrons from one place to another. Electrons can flow through any material, but does so more easily in some than in others.
Since electrons are very small, as a practical matter they are usually measured in very large number. A Coulomb is
\[6.24\times {{10}^{18}}\]
electrons. However, electricians are mostly intersted in electrons in motion. The flow of electons is called current, and is measueed in AMPS. One amp is equal to a flow of one coulomb per second through a wire.
Making electrons flow through a resistance reqires an attractive force to pull them. This force, called Electro-Motive Force or EMF, is measured in volts. A Volt is the force required to push Amp through I Ohm of resistance.
As electrons flow through a risstance, it performs a certain amount of work. It may be in the form of heat or a magnetic field or motion, but it does something. That work is called Power, and is measured in Watts. One Watt is equal to the work performed by 1 Amp pushed by 1 Volt through a resistance.
Electrical Circuit
An electrical circuit is a path or line through which an electrical current flows. The path may be closed (joined at both ends), making it a loop. A closed circuit makes electrical current flow possible. It may also be an open circuit where the electron flow is cut short because the path is broken. An open circuit does not allow electrical current to flow. Below is a basic set of symbols that you may find on circuit diagrams.
The encircling electron can move from one atom to the other.
When Protons and fast moving Electrons interact, electricity is produced. to simple terms, electricity is the interaction of Protons in the atom and the fast moving of Electrons around it. It is the flow of' electrons
BASIC ELECTRICITY
Electricity is the flow of electrons from one place to another. Electrons can flow through any material, but does so more easily in some than in others.
Since electrons are very small, as a practical matter they are usually measured in very large number. A Coulomb is
\[6.24\times {{10}^{18}}\]
electrons. However, electricians are mostly intersted in electrons in motion. The flow of electons is called current, and is measueed in AMPS. One amp is equal to a flow of one coulomb per second through a wire.
Making electrons flow through a resistance reqires an attractive force to pull them. This force, called Electro-Motive Force or EMF, is measured in volts. A Volt is the force required to push Amp through I Ohm of resistance.
As electrons flow through a risstance, it performs a certain amount of work. It may be in the form of heat or a magnetic field or motion, but it does something. That work is called Power, and is measured in Watts. One Watt is equal to the work performed by 1 Amp pushed by 1 Volt through a resistance.
Electrical Circuit
An electrical circuit is a path or line through which an electrical current flows. The path may be closed (joined at both ends), making it a loop. A closed circuit makes electrical current flow possible. It may also be an open circuit where the electron flow is cut short because the path is broken. An open circuit does not allow electrical current to flow. Below is a basic set of symbols that you may find on circuit diagrams.
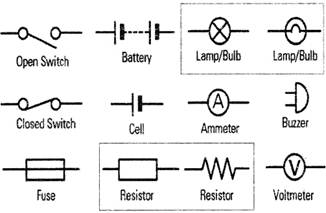 It is very important to know the basic more...
It is very important to know the basic more... 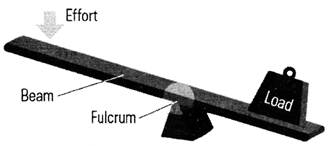 The beam is simply a long plank. It may be wood, metal or any durable material. The beam rests on a fulcrum (a point on the bar creating a pivot).
When we push down one end of a lever, we apply a force (input) to it. The lever pivots on the fulcrum, and produces an output (lift a load) by exerting an output force on the load. A lever makes work easier by both increasing input force and changing the direction of input force.
The Three Lever Classes
The parts of the lever are not always in the same arrangement. The load, fulcrum, and effort may be at different places on the plank.
Class One Lever
In this class, the Fulcrum is between the Effort and the Load. The mechanical advantage is more if the Load is closer to the fulcrum.
Examples of Class One Levers include seesaws, boat oars and crowbar
The beam is simply a long plank. It may be wood, metal or any durable material. The beam rests on a fulcrum (a point on the bar creating a pivot).
When we push down one end of a lever, we apply a force (input) to it. The lever pivots on the fulcrum, and produces an output (lift a load) by exerting an output force on the load. A lever makes work easier by both increasing input force and changing the direction of input force.
The Three Lever Classes
The parts of the lever are not always in the same arrangement. The load, fulcrum, and effort may be at different places on the plank.
Class One Lever
In this class, the Fulcrum is between the Effort and the Load. The mechanical advantage is more if the Load is closer to the fulcrum.
Examples of Class One Levers include seesaws, boat oars and crowbar
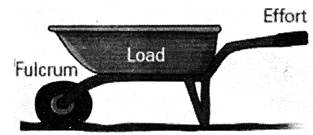
 Class Two Lever
In this class, the Load is between the Effort and the Fulcrum. The mechanical advantage is more if the load is closer to the fulcrum.
Examples of Class Two Levers include wheelbarrows.
Class Two Lever
In this class, the Load is between the Effort and the Fulcrum. The mechanical advantage is more if the load is closer to the fulcrum.
Examples of Class Two Levers include wheelbarrows.
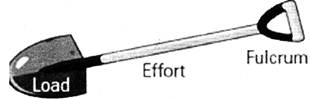
 Class Three Lever
In this class, the Effort is between the Load and the Fulcrum. The mechanical advantage is more if the effort is closer to the load. An example of Class Three Lever is a garden shovel.
Class Three Lever
In this class, the Effort is between the Load and the Fulcrum. The mechanical advantage is more if the effort is closer to the load. An example of Class Three Lever is a garden shovel.
 MACHINE
A machine is any device that does work. Machines make our lives easier because they reduce the amount of energy, power, and time we need to get one thing done by magnifying our input force.
Machines come in many sizes, shapes and forms. Some machines are very simple in its makeup and use whilst others are very complex. For example, a spade is a machine (a simple machine), and a space shuttle is a machine too (a complex machine),
Simple Machines
A simple machine is a tool, device or object with few moving parts that help us do work. Simple machines have been in use for a very long time. Early humans used simple machines to push, pull, lift, divide and crush things. They used simple machines to row rafts over water, build houses, split firewood, and carry heavy more...
MACHINE
A machine is any device that does work. Machines make our lives easier because they reduce the amount of energy, power, and time we need to get one thing done by magnifying our input force.
Machines come in many sizes, shapes and forms. Some machines are very simple in its makeup and use whilst others are very complex. For example, a spade is a machine (a simple machine), and a space shuttle is a machine too (a complex machine),
Simple Machines
A simple machine is a tool, device or object with few moving parts that help us do work. Simple machines have been in use for a very long time. Early humans used simple machines to push, pull, lift, divide and crush things. They used simple machines to row rafts over water, build houses, split firewood, and carry heavy more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
