Answer:
(i) Acetvlation When active hydrogen atom of
alcohol,phenol or an amine is replaced by acetyl ![]() group to formcorresponding
ester or amide, the reaction is known asacetylation. Reagents used are acid
chloride or acid anhydride inpresence of a base like pyridine or dimethyl
aniline.
For example:
group to formcorresponding
ester or amide, the reaction is known asacetylation. Reagents used are acid
chloride or acid anhydride inpresence of a base like pyridine or dimethyl
aniline.
For example:
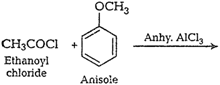
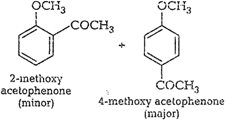 (ii) Cannizzaro reaction
Aldehydes which do not have any
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
Aldehydes which do not have any![]() -hydrogen
atom, undergo sell oxidation and reduction(disproportionation) reaction on
treating with concentrated alkali.
This reaction, is called
Cannizzaro reaction. As a result, onemolecule of aldehyde is reduced to alcohol
while another isoxidized to carboxylic acid salt.
For example:
-hydrogen
atom, undergo sell oxidation and reduction(disproportionation) reaction on
treating with concentrated alkali.
This reaction, is called
Cannizzaro reaction. As a result, onemolecule of aldehyde is reduced to alcohol
while another isoxidized to carboxylic acid salt.
For example:
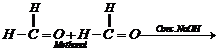
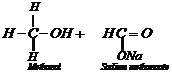 (iii) Cross aldol condensation
When aldol condensation is carried outbetween two different aldehydes and or
ketones, it is called crossaldol condensation. If both the reactants contain
(iii) Cross aldol condensation
When aldol condensation is carried outbetween two different aldehydes and or
ketones, it is called crossaldol condensation. If both the reactants contain ![]() -hydrogenatoms,
it gives a mixture of four products.
For example:
Please consult solution of Q. 9.
(iv) Decarboxylation Carboxylic
acids lose carbon, dioxide moleculeto produce hydrocarbons on heating their
sodium salts withsodalime (a mixture of NaOH and CaO in ratio 3:1). This
reactionis called decarboxylation.
For example:
-hydrogenatoms,
it gives a mixture of four products.
For example:
Please consult solution of Q. 9.
(iv) Decarboxylation Carboxylic
acids lose carbon, dioxide moleculeto produce hydrocarbons on heating their
sodium salts withsodalime (a mixture of NaOH and CaO in ratio 3:1). This
reactionis called decarboxylation.
For example:
![]()
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
