Answer:
1. Werner?s theory of
co-ordination compounds. The main points of postulates to explain the bonding
are:
(1) In
co-ordination compounds, the metals posses two types of valencies.
(i) Primary
valencies
are those which a metal posses in the formation of its simple salts and it
corresponds to its oxidationstate. The primary valency of metal ion is always
satisfied by a negative ion. For example, the primary valencies of Ag, Cu, Co
and Pt in the formation of their simple salts AgCl, CuSO4, CoCl3
and PtCl4 are 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively. The primary valencies are
indicated by dotted lines, since they are non-directional in nature.
Primary valencies
are ionisable.
(ii) Secondary
valencies
are those which a metal posses during the formation of its complex ion.
Secondary valencies are directional in nature and are non-ionisable. For
example, in complex compounds : [Ag(NH3)2Cl], [Co (NH3)6]
Cl3 and [Pt(NH3)] Cl4 the secondary valencies
of Ag+, Co3+ and Pt4+ are 2, 6 and 6
respectively. The secondary valency corresponds to the coordination number of
the metal ion or atom.
These are indicated
by thick lines.
On the basis of the
Werner theory, the complex CoCl3.6NH3 of [Co(NH3)6]
Cl3 i.e. hexaamminceobalt(III) chloride can be represented as;
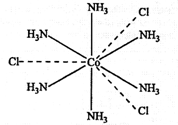 where three dotted
lines indicate the three primary valency (or oxidation state) of cobalt; while
six thick lines indicate its secondary valencies (or co-ordination number).
2. The ligands
which satisfy secondary valuency occupy the fixed position in space. Thus the
geometry of the complex is determined by the number and arrangement of the
ligands around the central metal atom (or ion).
where three dotted
lines indicate the three primary valency (or oxidation state) of cobalt; while
six thick lines indicate its secondary valencies (or co-ordination number).
2. The ligands
which satisfy secondary valuency occupy the fixed position in space. Thus the
geometry of the complex is determined by the number and arrangement of the
ligands around the central metal atom (or ion).
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
