Answer:
(i) Zone refining
Fractional Crystallisation. This method is employed for preparing extremely pure
metals used as semiconductor (e.g. Si, Ge etc.)
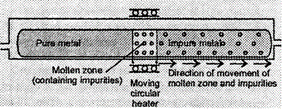 This method is
based upon the principle that impurities are more soluble in the melt than in
the solid state f metal. In this method, the impure metal is converted into a
bar which is heated at one end with a moving circular heater (fig.) so that
this end melts and forms a molten zone or the melt.
As the heater is
slowly moved along the length of the rod, the pure metal crystallizes out of
the melt whereas the impurities pass into the adjacent molten zone. This process
is repeated several times till the impurities are completely driven to one end
of the rod which is then cut off and discarded. The process isusually carried
out in an inert, atmosphere to prevent the oxidation of the metal.
(ii) Column
chromatography. It
is based on the principle that different components of a mixture are
differently adsorbed on an adsorbent. Here a suitable adsorbent like alumina
(Al2O3) is packed in a column and this constitutes the
stationary phase. The mixture to be separated is taken in a suitable solvent
and the solution is poured on the top of the column of the adsorbent. Different
components of the mixture are adsorbed to different extents. The components are
then eluted out by a suitable solvent (which acts as a mobile phase). The
weakly adsorbed component will be eluted more rapidly than a more strongly
adsorbed component. Different components of the mixture are collected in the
form of different fractions in separate conical flasks.
This method is
based upon the principle that impurities are more soluble in the melt than in
the solid state f metal. In this method, the impure metal is converted into a
bar which is heated at one end with a moving circular heater (fig.) so that
this end melts and forms a molten zone or the melt.
As the heater is
slowly moved along the length of the rod, the pure metal crystallizes out of
the melt whereas the impurities pass into the adjacent molten zone. This process
is repeated several times till the impurities are completely driven to one end
of the rod which is then cut off and discarded. The process isusually carried
out in an inert, atmosphere to prevent the oxidation of the metal.
(ii) Column
chromatography. It
is based on the principle that different components of a mixture are
differently adsorbed on an adsorbent. Here a suitable adsorbent like alumina
(Al2O3) is packed in a column and this constitutes the
stationary phase. The mixture to be separated is taken in a suitable solvent
and the solution is poured on the top of the column of the adsorbent. Different
components of the mixture are adsorbed to different extents. The components are
then eluted out by a suitable solvent (which acts as a mobile phase). The
weakly adsorbed component will be eluted more rapidly than a more strongly
adsorbed component. Different components of the mixture are collected in the
form of different fractions in separate conical flasks.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
