Connective Tissue
Category : 11th Class
It connects and supports all the other tissues, the intercellular element predominating. The cellular element is usually scanty. In function this tissue may be mechanical, nutritive and defensive. It is a tissue made up of matrix (abundant intercellular substance or ground substance) and living cells that connects and support different tissues. All connective tissues in the body are formed by mesoderm.
Structure
There are large intercellular spaces between the cells. Intercellular spaces are filled with large amount of extracellular materials formed of insoluble protein fibres lying in an amorphous, transparent ground substance called matrix. Ageing of an animal body is associated with deterioration in its connective tissues.
Functions
(1) Their chief function is to bind other tissues together in the organs.
(2) Certain connective tissues such as adipose tissues store fat.
(3) Skeletal connective tissues like bones and cartilages provide the body with a supporting skeletal frame work.
(4) Fluid connective tissues such as blood and lymph transport various materials in the body.
(5) Plasma cells synthesize antibodies, viz., macrophages. Lymphocytes ingest cell debris, harmful bacteria and foreign matter. Thus these cells of connective tissues are protective in function.
(6) The jelly-like ground substance of connective tissues acts as shock absorber around some organs such as eye balls and kidneys.
(7) The bone marrow produces blood cells.
(8) Areolar tissue acts as packing material in various organs.
(9) Collagen fibres of connective tissue help in repair of injured tissues.
Types of connective tissues
Connective tissue proper possess soft viscous semisolid or semi-fluid matrix. It is divided into following types :
(1) Areolar Tissue : Areolar tissue is loose connective tissue, possess transparent gelatinous, highly vascular and sticky matrix which have variety of cells and fibres. It allows movement of part connected by it (Muscle and their compound). Areolar tissue mainly consist of different types of cells and fibres.
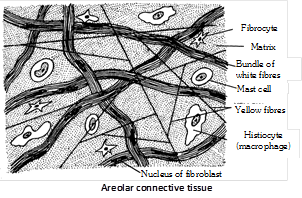
(i) Cells of areolar tissue : It has following types –
Fibroblast : It is most abundant cells, produces fibres, called as fibroblasts in their young active phase and fibrocytes when old and inactive. It synthesize proteins (Collagen, elastin and reticulin). These are undifferentiated mesenchyme stem cells, capable to give rise other cells of connective tissue. Collagen and elastin are formed by fibroblasts.
Histiocytes or Macrophages or Clasmatocytes : These are polymorphic cells. These are amoeboid cells and these are main phagocytes of connective tissue. They are having most active lysosomes and phagocytise dead cells and pathogens. Macrophages remove the dead cells and damaged cells and clean the body so called scavenger cell. All types of macrophages take part in phagocytosis.
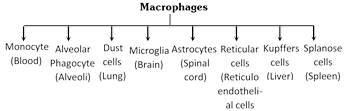
Reticular cells : Present only in the reticular tissue and stellate in appearance. Infact they are modified fibroblast producing reticular fibres.
Mast cells : Mast cells were discovered by Paul Echrlich. It is large, irregular ovoid cells found in areolar tissue. and its number increase during allergies. It produces or secretes histamine (vasodilator), serotonin (vasoconstrictor) and heparin (anticoagulant). Histamine dilate the blood vessels in allergic and inflammatory conditions. Heparin checks the clotting of blood inside the blood vessels. Serotonin act as vasoconstrictor to arrest bleeding.
Lymphocytes : These are the smallest, less numerous and spherical or ovoid cells resembling lymphocytes of blood and lymph. These actively move about by pseudopodia. Their function is to form and carry antibodies. That is why, they are seen in large numbers of sites of inflammation.
Plasma cells (Plasmacytes) : These are usually small and rounded, superficially resembling lymphocytes but are sluggishly amoeboid and short-lived (only 2 or 3 days). These are the most potential antibody-forming cells of body presumably, mature lymphocytes (B-lymphocytes form antibody) transform into plasma cells or proliferate to form plasma cells.
Fat or Adipose cells (Adipocytes or Lipocytes) : A few, large and spherical cells occur in areolar tissue, singly or in clusters around small blood vessels. Each cell contains a large globule of fat surrounded by a thin peripheral layer of cytoplasm having a nucleus.
Eosinophils : These cells closely resemble the eosinophilic leucocytes of blood. These probably play a phagocytic role in inflammatory and allergic reactions.
Chromatophores : These are pigment cell present in specialised areas such as skin and eye. They are much branched and packed with pigment granules. They are stellate (Star like) cells, which are phagocytic in nature. They phagocytes melanin producing cells and retain melanin hence they provide colour to the skin and other organs. Melanin is black pigment which protects body from ultraviolet rays of sun.
Mesenchyme cells : These are reserve undifferentiated cell which can be transformed into other types of cells when needed.
(ii) Fibres of areolar tissue : These are made up with protein and non living structures of protein produced by fibroblasts and present in matrix of connective tissue and are of three types –
Collagenous fibres : These are the most abundant fibrous element of areolar and other connective tissues. There are long, unbranched fibres of a soluble and shining collagen protein (tropo collagen). These fibres are more strengthful and provide maximum tensile strength. These are colourless and hyaline, yet called white fibres to distinguish them from yellow elastin fibres. Collagen protein is the most abundant protein of the body constitutes 25% the total body protein. Collagen fibre can be stained by eosin. When collagen fibres are removed from the areolar tissue they become loose and elastic. e.g. Bone, Cartilage, Ligement and tendon.
Yellow elastin fibres : Formed of elastin protein, these fibres are less numerous, thinner, branched, anastomosing, and of a pale yellow colour. These are very elastic and remain streched due to tension in the areolar tissue, when broken in teased preparations, these coil and curl like tense wires. Elastin is probably the most resistant of all body proteins to chemical changes. Thousands of years old ‘mummies’ still have their arteries intact due to well-preserved elastin fibres. They are the orceinophilic i.e. stained by orcein.
Reticulin fibres : These are delicate, freely branching and inelastic fibres of reticulin protein, found interwoven, to form networks. These are very abundant in embryos, new born babies and in healing and regenerating wounds. In areolar tissues of adults, these are mostly replaced by collagen fibres, but remain abundant in lymphoid and blood forming tissues and in the stroma of pancreas, liver etc. They are stained with AgBr and \[AgN{{O}_{3}}\] hence are called Argentophillic or Argyrophillic. On boiling collagen and reticular fibres both convert in glue.
(2) White fibrous tissue : It is modified form of areolar tissue. Only collagen fibres are present in the matrix and cells are mainly fibroblasts, present at the joints between skull bones and makes them immovable, also found in the dermis of higher mammals. It is of two types –
(i) Tendons : A tendon is non-elastic but flexible tissue consists of parallel bundles of collagenous fibres between which rows of fibroblasts are present. It joins the muscles to bones. It also form chordae tendinae which joins the cusps of atrioventricular valves of heart with the wall of ventricles.
(ii) Sheath : In a sheath, the bundles of white fibres lie in a criss-cross manner. The fibroblasts are not in rows but are scattered in the areolae. The sheath form protective covering.

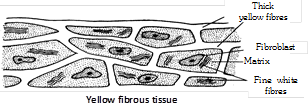
(3) Yellow fibrous tissue : The matrix is with numerous and closely packed yellow or elastin fibres which are similar to but thicker than those of areolar connective tissue. It is elastic and flexible. It forms wall of blood vessels, lungs, true vocal chords, trachea, capsule of spleen and bronchioles. It also forms sheet in ligaments. Ligaments is a modified yellow elastic fibrous tissue and connects bone to bone.
(4) Adipose tissue : It is modified form of areolar tissue made up of specialized large spherical fat cells (below the skin) or adipocytes. Adipose tissue chiefly act as “Food reserves” or fat depots for storage and metabolism of lipids. Besides this, they also act as heat insulators and pressure, pull and push absorbers. Adipocytes are of two types:
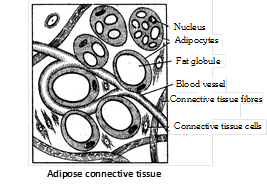
(i) Unilocular adipocyte (White adipose tissue) : Common fat of body, having single large fat globule, maintain body temperature, found beneath skin subcutaneous fat panniculus adiposus, blubber of whales and elephants, hump of camel and tail of merino sheep, yellow bone marrow, around kidneys and blood vessels, mesentries, omenta and the fat bodies of frog.
(ii) Multilocular adipocyte (Brown fat) : Each multilocular adipocytes have several small fat globules, contain more number of mitochondria, found in rats and other rodents, polar bear, penguins, seal, walrus, in new born human babies and hibernating mammals (rats and other rodents) on oxidation it yields about 20 times more energy than ordinary fat.
(5) Reticular tissue : It is a modified form of areolar connective tissue characterized by the matrix is fluidy in nature. The matrix contains large number of stellate-shaped reticular cells, each with a number of protoplasmic processes. Reticular tissue is found in spleen, thymus, tonsils, lymph glands, liver, bone-marrow, lamina propria of mucosa of stomach and intestine. The reticular cells act as phagocytes and form a part of defence system of the body.
(6) Myeloid tissue : It is modification of reticular tissue. Its ground substance is plasma. It posses heavy network of reticular fibres. In active form the cells are myeloblasts. It is found in red bone marrow or haemopoitic tissue and fat reserve of yellow bone marrow.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
