Glands
Category : 11th Class
Glandular epithelium are specialized for secretory activity. A cell, tissue or organ which secretes a useful chemical material is known as gland. Glands are made up of cuboidal epithelial cells which are more secretory. All glands arise as folding of epithelia. The golgi body in gland cells are larger and more secretory. Most of the glands of body are merocrine types. It originate from all three germinal layers. (ecto, meso and endoderm). Liver is the largest gland of the body and lined by glandular epithelium.
Types of glands
(1) Unicellular gland : It consist of unicellular gland cells which are called as goblet cells or chalice cells. They secrete mucous and found in mucosa of intestine and stomach. Mucous lubricates the food for easy peristalsis. Their life span is about \[2\,\,\,\,3\] days.
(2) Multicellular gland : It consist of many cells and are generally located in underlying connective tissue e.g. gastric and intestinal glands.
(3) Exocrine gland : These are those glands which discharge their secretory products into ducts. It is also called ducted glands or glands of external secretion. e.g. Salivary glands, Mammary glands and Tear glands.
(4) Endocrine gland : It is often called ductless gland, because they discharge their secretory products (hormones) directly into the blood. e.g. Pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid and adrenal glands.
(5) Heterocrine gland : These are those glands which are partly endocrine and partly exocrine in function. e.g. Pancreas.
Structural classification of exocrine glands
Multicellular exocrine glands are classified by structure, using the shape of their ducts and the complexity (branching) of their ducts system as distinguishing characteristics. Shape include tubular and alveolar (Sac like). Simple exocrine glands e.g. intestinal glands, mammalian sweat glands, cutaneous glands of frog etc. have only one duct leading to surface. Compound exocrine glands have two or more ducts e.g. liver, salivary glands etc.
|
Type |
Example |
|
Simple tubular |
Intestinal glands, crypts of Lieberkuhn in ileum. |
|
Simple coiled tubular |
Sweat glands in man |
|
Simple branched tubular |
Gastric (stomach) gland, and Uterine gland. |
|
Simple alveolar |
Mucous gland in skin of frog, Poison gland of toad and seminal vesicle. |
|
Simple branched alveolar |
Sebaceous glands |
|
Compound tubular |
Brunner?s gland, bulbourethral gland and liver. |
|
Compound alveolar |
Sublingual and submandibular salivary gland |
|
Compound tubulo alveolar |
Parotid salivary glands, Mammary gland and Pancreas. |
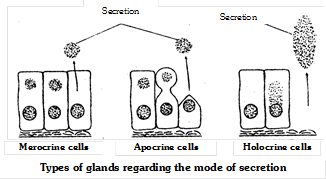
Classification of glands on the basis of their mode of secretion
(1) Apocrine gland : Apocrine glands collect their secretory products near the apex or tip, of the cell and then release it into a duct by pinching off the distended end. This process results in some loss of cytoplasm and damage to the cell. e.g. Mammary glands. (Modified sweat gland)
(2) Holocrine gland : Holocrine glands collect their secretory products inside the cell and then rupture completely to release it. These cells self destruct to complete their functions. e.g. Sebaceous glands. In case of rabbit sebaceous glands are found in dermis of skin. Pineal body and thymus can also be considered as holocrine gland.
(3) Merocrine gland : Merocrine glands (Eccrine or Epicrine glands) discharge their secretory product directly through the cell or plasma membrane, without injury to the cell wall and without loss of cytoplasm. e.g. Sweat glands, exocrine region of vertebrate pancreas, salivary glands and intestinal glands etc.
Classification of glands on the basis of nature of product
(1) Mucous gland : Secret slimy mucous e.g. goblet cells, palatine gland, gland of uterus, some gastric gland and gland of colon.
(2) Serous gland : Produce watery secretion. e.g. pancreas, parotid, salivary gland, sweet gland and intestinal gland.
(3) Seromucous gland : Secrete mixed liquid. e.g. Most gastric gland, sublingual, submaxillary salivary gland, pancreas.
(4) Cytogenic gland : They produce cells e.g. Testis and ovary.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
