Some Representative Animals
Category : 11th Class
![]()
(1) Ascaris lumbricoides, the common roundworm belong to the class Rhabditea of the phylum Nemathelminthes. It is the most common endoparasite in the small intestine of human beings. It is monogenetic, i.e., without any secondary host. The worm is more common in children.
(2) The body is elongated, unsegmented, cylindrical with tapering ends and four streaks-two lateral, one ventral and one dorsal.
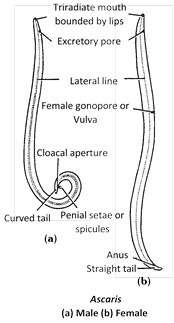
(3) Sexes are separate with sexual dimorphism. Male is smaller than female with curved tail, two penial setae (copulatory organs) and cloaca. Female is with straight posterior end of the body and posterior transverse anus and separate gonopore situated ventrally 1/3 from the anterior end. In both the excretory pore is situated mid-ventrally, a little behind the mouth. Ventral surface of male bears fifty pairs preanal and five pairs postanal papillae. These sensory papillae are absent in female.
(4) Mouth both in male and female is terminal, triradiate surrounded by three denticulate lips. One median dorsal and two ventrolateral. Dorsal lip bears two sensory double papillae (tangoreceptors). Both sensory papillae and amphids (chemoreceptors) are present on ventrolateral lips.
(5) Body wall consists of outer cuticle, middle epidermis and inner longitudinal muscle layer. Circular layer is absent. Cuticle is thick which is protects the body of the parasite from mechanical injury and also is resistant to action of digestive enzymes of the host. The epidermis is syncytial (coenocytic) with scattered nuclei and without partition walls.
(6) The body cavity of Ascaris is pseudocoel formed by vacuoles originated from persistent embryonic blastocoel.
(7) There is no alimentary canal and digestive gland. The parasite absorbs digested food of the host so their is no need of digestive organs. Absorption occurs through the general body surface. Salivary glands do not occurs in Ascaris.
(8) Respiratory system is absent, respiration is anaerobic.
(9) Excretory system is H-shaped. It is consists of a single excretory cell or renette cell. Excretory products are ammonia and urea.
(10) Sense organs are simple like labial papillae, cervical papillae, anal papillae, amphids and phasmids.
(11) Ascaris is dioecious or unisexual. Testes is single and median, so male Ascaris is monarchic (monodelphic). Only anterior part of testis is functional, so testis (also ovary) is telogonic.
(12) Ascaris sperm is peculiar without flagellum, tail less, asymmetrical and amoeboidal.
(13) Female Ascaris has paired ovaries so female Ascaris is didelphic.
(14) Copulation occurs in the intestine of host. Fertilization in the lower part of uteri. The egg is mammilated, oval, m-shape with three protective covering?outer protein layer, middle chitinous shell and inner membrane made of esterified glycosides.
(15) Embryonic development takes place only outside the body of human host in soil because it requires low temperature, more oxygen and suitable moisture.
(16) Inside the shell the zygote develops into rhabditiform larva or first stage juvenile in 10-14 days.
(17) The larva of first stage is not infective. It rests for a week and completes first moult within egg and becomes second stage rhabditiform larva which is infective.
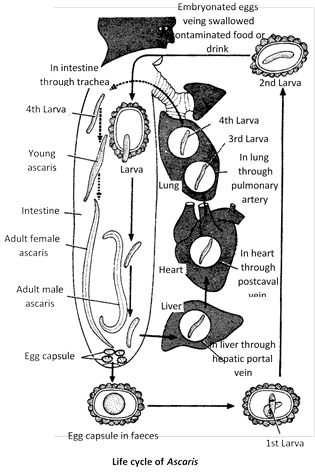
(18) The transmission of infective stage through embryonated egg takes place by contaminated food and water.
(19) The embryonated egg passes into the intestine of man and second stage larva hatches out from the egg.
(20) Three types of migration by Ascaris larva are ? primary migration, secondary migration and aberrant migration.
(21) Primary migration is from intestinal wall \[\to \] hepatic portal \[\to \] liver \[\to \]hepatic vein \[\to \] heart \[\to \] pulmonary artery \[\to \] lungs.
(22) Secondary migration is from lungs back to intestine of the host ; lungs \[\to \]bronchi \[\to \]trachea \[\to \]pharynx \[\to \]gullet \[\to \]oesophagus \[\to \]stomach \[\to \]intestine.
(23) In lungs, larva complete its second and third moulting (becomes third and fourth stage larva). In small intestine it completes fourth or final moulting and becomes fifth stage of larva.
(24) Duration of wandering journey from intestine to intestine is about three weeks. Within 8-10 weeks adult Ascaris starts reproduction.
(25) Aberrant migration is the migration from lungs to brain, spinal cord, eyes, etc.
(26) Ascaris is pathogenic. It cause the disease, ascariasis. Most pathogenic larva of Ascaris is fourth stage in larva.
(27) Main symptoms of ascariasis are ? abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and colic pain.
(28) Toxin produced by Ascaris may interfere with protein digestion.
(29) Ascariasis can be treated by antihelminthetic drugs such as oil of Chenopodium, Santonin, Antipar, Tetrachloroethylene, Alcopar, Decaris, Diethylcarbamazine, etc.
Ancylostoma duodenale : It is an endoparasite of human small intestine. The parasite is monogenetic. It is popularly called old world hookworm. Adults live in the intestine of man and feed upon blood. No secondary host. Juveniles penetrate through the skin of hand and feet. It causes ?Ancylostomiasis?.
Some other nematode parasite
Wuchereria bancrofti : It is a digenetic parasite. Human being are primary host while female mosquito mostly of culex and Aedes species is the secondary or intermediate host.
Adults live in human lymph vessel and lymph glands. It is a viviparous nematode, larvae called-microfilaria. Larvae appear in cutaneous blood (superficial blood) in midnight. Presence of few worms not harmful. They block lymph glands and lymph vessels, swell body parts like arms, scrotum and mammary glands. This results in the disease 'Elephantiasis' or 'Filariasis'
Enterobius Vermicularis (Pin worm) : This worm inhabits human caecum, colon, appendix and rectum. It is monogenetic, no intermediate host. Eggs contain rhabditiform larva. It cause 'Oxyurasis', the main symptom being itching of anal parts.
Dracunculus medinensis : It is a digenetic endoparasite with man being the primary host and cyclops as the secondary or intermediate host. It is also called 'Fiery serpent'. The adult worms occur in the subcutaneous tissue, especially of arms, shoulders and legs, forming blisters. Female is very long while male is short. The guinea worm disease has been eradicated from India. The last case was reported from the Jodhpur district of Rajasthan in July 1996.
Loa loa (Eye worm) : It is a filarial roundworm of central and western Africa. The adult migrates through the subdermal connective tissues of human host. Sometimes they pass across the eyeball. Local swelling accompanies these migrations. Tabanid flies act as transmitting vectors.

Common Names
|
Ascaris - Common roundworm Ancylostoma - Hookworm Necator - Hookworm Wuchereria - Filarial worm Enterobius (Oxyuris) - Pinworm Trichuris - Whipworm Dracunculus - Guinea worm Loa loa - Eye worm Strongyloides - Thread worm |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
