Geometrical Figures
Category : 4th Class
Geometrical Figures
Introduction
In our day to day life we come across a number of objects. All the objects has a specific shape and size. We recognize a number of objects by their shape. Therefore, to know about the objects and of their shapes is very important. In this chapter we will study about the shapes of different geometrical figures.
Point
To show a particular location, a dot (.) is placed over it, that dot is known as a point.
\[\centerdot \,\xrightarrow{{}}A\]
A is a point
Line Segment
Line segment is defined as the shortest distance between two fixed points. It has fixed length.
![]()
How many line segments are there in the following figure?
Solution:
There are 6 line segments in the given figure.
Ray
It is defined as the extension of a line segment in one direction up to infinity.
![]()
How many rays are there in the following figure?

Solution: There are 12 rays.
Line
Line is defined as the extension of a line segment up to infinite in either direction.
![]()
How many lines are there in the following figure?
Solution: There are two lines.
Angle
Inclination between two rays having common end point is called angle.

\[\angle ABC\] is a angle
A Right Angle
An angle whose measure is exactly \[90{}^\circ \]is a right angle.
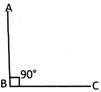
\[\angle ABC\]is a right angle
An Acute Angle
An angle whose measure is less than \[90{}^\circ \]is an acute angle.
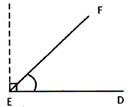
\[\angle DEF\]is an acute angle.
An Obtuse Angle
An angle whose measure is greater than \[90{}^\circ \] but less than \[180{}^\circ \]is an obtuse angle.

\[\angle LMN\]is an obtuse angle
The following angle is a____.

Solution: It is an obtuse angle, because its measure is greater than\[90{}^\circ \].
Polygon
A Simple closed figure formed of three or more line segments is called a polygon. Line segments which form a polygon are called its sides. The point at which two adjacent sides of a polygon meet, is called a vertex of polygon. In the given figure, triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon and hexagon, all are examples of polygon.
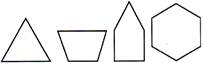
Types of Polygons
Regular and Irregular Polygon
A regular polygon has all sides equal and all angles equal, otherwise, it is an irregular polygon.

Simple and Complex Polygon
A simple polygon has only one boundary and it does not cross over itself. A complex polygon intersects itself.

Names of Polygons
Names of polygons based on their number of sides are given in the following table:
|
Name |
Number of Sides |
Number of vertices |
Number of Angles |
Shape |
|
Triangle |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Quadrilateral |
4 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Pentagon |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
|
Hexagon |
6 |
6 |
6 |
|
Triangle
The geometrical shapes having three sides are called triangles. There are various types of triangles.

Equilateral Triangle
A triangle whose all sides are equal is called equilateral triangle.

Triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle.
Isosceles Triangle
A triangle whose two sides are equal is called isosceles triangle.

In triangle ABC AB = AC = 4 cm hence, triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle.
Scalene Triangle
A triangle whose sides are unequal is called scalene triangle. In the figure below side lengths of triangle ABC are not equal hence, triangle ABC is a scalene triangle.

A Right Angle Triangle
A triangle whose one angle is a right angle is called right angled triangle. In the picture below triangle ABC is a right angle.
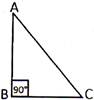
Acute Angled Triangle
A triangle with all the angles as acute angles is called acute angled triangle.

Obtuse Angled Triangle
A triangle with one angle as obtuse angle and other two angles are acute angles is called an obtuse angled triangle.

Name the triangle whose all sides are equal.
Solution:
Equilateral triangle
Name the triangle given below

Solution:
Right angled triangle because one angle is right angle.
Quadrilateral
The geometrical figure having four sides is called quadrilateral.
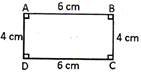
Rectangle
Rectangle is a quadrilateral in which:
(i) All angles are of\[90{}^\circ \].
(ii) Opposite sides are equal.
Square
Square is a quadrilateral, in which:
(i) All angles are of\[90{}^\circ \].
(ii) All sides are equal.
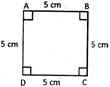
Note: Sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \]and sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is \[180{}^\circ \]
Circle
Circle is a closed curved line whose all points are at the same distance from a given point in a plane.
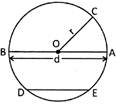
In the above circle, 0 is the centre of the circle. OA, OB and OC are radius of the circle. AB is the diametre of the circle.
Chord
A line segment joining two distinct points which lie on the circle is called chord of the circle.
In the figure given above DE and AB are chord of the circle.
Radius
Radius of a circle is half of the diametre.
In the figure given under circle, OA, OB and OC are radius of the circle.
Diametre
Diametre is the largest chord of the circle.
In the figure given under circle, AB is the diametre of the circle.
Diametre of a circle is 8 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Solution:
\[Radius=\frac{Diametre}{2}=\frac{8}{2}cm=4cm\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
