Non-Verbal Reasoning
Category : 4th Class
Non-Verbal Reasoning
Learning Objectives
What is Non Verbal Reasoning?
Non verbal reasoning is a figure based reasoning. It has no language at all. To solve non verbal problems one has to find out the pattern of pictorial presentation in the given figure. To get the more clear concept about non verbal reasoning, let us see the types of problems coming before you.
Analogy
Simple meaning of analogy is similarity. But, in terms of reasoning, the meaning of analogy is logical similarity in two or more things. In problems based on Analogy, we will usually be given one pair of images that are connected in a particular way and the first image of the second pair. We have to find the correct image to complete the second pair in the same way as the first pair.
Example:
1. Find the matching pair.
![]()
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: In first figure of left pair, middle figure becomes the outer figure outer figure becomes inner figure and inner figure becomes middle figure. In both figures of left pair, outer figures and inner figures are shaded, while middle figure is unshaded.
2. Identify the relation between figures of the first pair and complete the second pair.
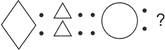
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
3. Find the matching pair.
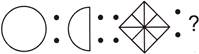
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
4. Identify the relation between figures of the first pair and complete the second pair.
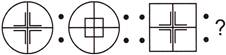
(a)  (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
5. Which of the given options complete the second pair?
![]()
(a)  (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) 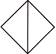 (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
6. Identify the relation between figures of the first pair and complete the second pair.
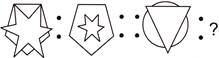
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Classification (Odd One Out)
Classification of figures or shapes tests our ability to work out, which shapes are similar and which are different in a given set of options. We need to use our observation skills to compare the given shapes, symbols and find the visual link or links.
Example:
1. Which is the odd one out?
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 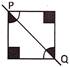
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Figures in option (a), (b) and (c) are symmetrical along PQ. But figure in option (d) is not symmetrical along PQ.
2. Which of the following figures is same as the given problem figure?

(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: By matching shaded parts of given circle, we find that figure in option (b) is same as the problem figure.
3. Which shape is the odd one out?
(a) 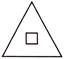 (b)
(b) 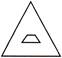
(c) 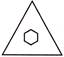 (d)
(d) 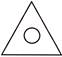
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
4. Identify the odd one out.
(a) 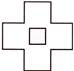 (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
5. Find the odd one out.
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
6. Which figure is the odd one?
(a) 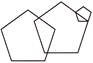 (b)
(b) 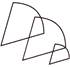
(c)  (d)
(d) 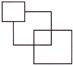
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
7. Which of the following figures is the odd one?
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c) 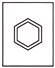 (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
8. Which figure is the odd one?
(a)  (b)
(b) 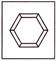
(c) 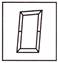 (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
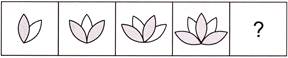
Figure Series
A figure series is a sequence of many elements made of figures. To solve these types of questions, we observe shapes within shapes and patterns within patterns.
Example:
1. What comes next?
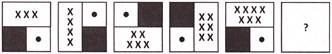
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Here, the square rotates one step anticlockwise in every next figure and one X is increasing in every next figure.
Hence, required figure is in option (c).
Direction for (2 and 3): Each of the questions has a series of figures, out of which one is missing. Select the option figure which would complete the given series.
2.
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
3.
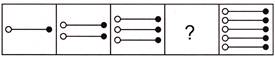
(a) 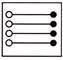 (b)
(b) 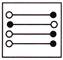
(c) 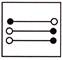 (d)
(d) 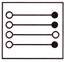
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
4.
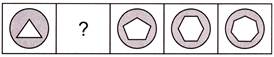
(a) 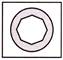 (b)
(b) 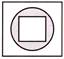
(c) 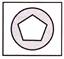 (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
5.
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Embedded Figures
If a figure contains another figure as one of its parts, the figure part is called embedded figure. In Such types of questions, a figure is given followed by four parts such that one of them is embedded in the given figure. We have to identify such part.
Example:
1. In which one of the following figures, the figure given below is exactly embedded as one of its part?
![]()
(a) 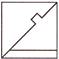 (b)
(b) 
(c) 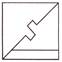 (d)
(d) 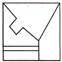
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: Figure given in question is a part of the figure given in option (b).
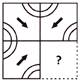
2. In which one of the following figures, the figure given below is exactly embedded as one of its part?
![]()
(a) 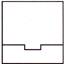 (b)
(b) 
(c) 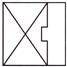 (d)
(d) 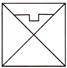
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Figure given in question is a part of the figure given in option (c).
3. Which of the following options will complete the figure?
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation: Let us complete the figure.
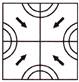
Figure given in option (a) is the required part of figure
4. Which of the following part is exactly embedded in given figure?

(a)  (b)
(b) 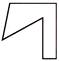
(c) 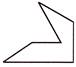 (d)
(d) 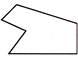
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: The required embedded part given in option (c) is shaded here:

5. Which of the following options is not embedded in the given figure?
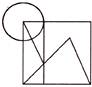
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) 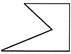
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) 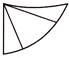
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
6. In which of the following figures is the shape 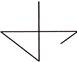 hidden?
hidden?
(a) 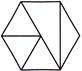 (b)
(b) 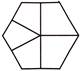
(c) 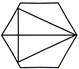 (d)
(d) 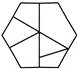
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
7. In which figure is the shape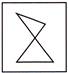 hidden?
hidden?
(a) 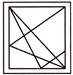 (b)
(b) 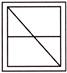
(c) 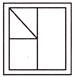 (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Geometrical Shapes
Geometric shapes come from geometry which is the maths of shapes made of points and lines. Some shapes are simple such as the triangle, square and circle, while other shapes are complex. While solving non verbal reasoning based on geometrical shapes, following points are important:
Example:
1. How many horizontal lines are there in the given figure?

(a) 4 (b) 6
(c) 12 (d) 8
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Here, given figure is symmetrical about the dotted line.
Now, number of horizontal lines on the left of dotted line is 4.
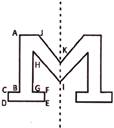
Hence, total number of horizontal lines is \[4\times 2\text{ }=\text{ }8\].
2. Select the odd one out.
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) ![]()
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Figures given in options (a), (b), (c) and (e) have exactly one line of symmetry. Figure given in option (d) has no line of symmetry.
3. Number of circles in the given figure is:
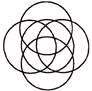
(a) 4 (b) 5
(c) 6 (d) 7
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation:
There are 5 circles in the given figure.
4. Number of triangles in the given figure is:
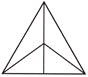
(a) 9 (b) 7
(c) 8 (d) 6
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Here, triangles are:
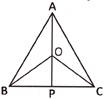
ABP, ACP, ABC, AOB, AOC, OBP, OCP and OBC
Therefore, the number of triangles is 8.
5. Which one of the following figures has a line of symmetry?
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
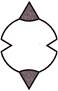
(c) 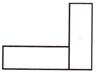 (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation:
Only the figure given in option (b) has a line of symmetry.
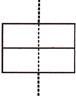
6. How many lines of symmetry are there in the given figure?
(a) Zero (b) One
(c) Two (d) Four
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation:
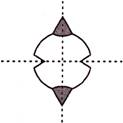
There are two lines of symmetry in the given figure.
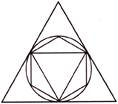
7. Which one of the following has more than one line of symmetry?
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (e) is correct.
Explanation:
All figures have exactly one line of symmetry.
8. How many triangles are there in the figure?
(a) 8 (b) 11
(c) 13 (d) 10
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation:
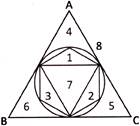
There are three small triangles 1, 2, 3; four medium triangles 4, 5, 6, 7 and one large triangle ABC. Therefore, total 8 triangles are there in the given figure.
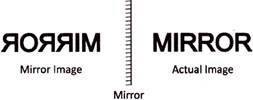
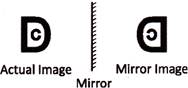
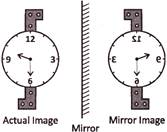
Mirror Images
In a plane mirror, if we lift our right hand, the image in the mirror shows our left hand and if we lift our left hand, the image shows our right hand. Therefore, in a mirror image, the left part of an object becomes right part and the right part becomes left part.
Left Hand Side (LHS)
\[\rightleftarrows\]
Right Hand Side (RHS)
For example,
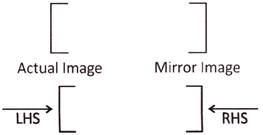
Mirror Image of Capital Letters and Numbers (1 to 9):
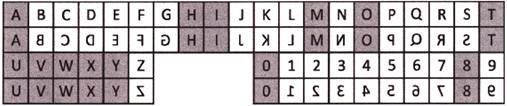
Example:
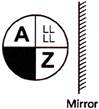
1. Find the mirror image of the combination of letters given below.

Mirror
(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation:
2. The correct mirror image of the following is:

(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation:
3. Which one of the following figures is the mirror image of given figure?
(a)  (b)
(b) 
(c)  (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation:
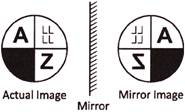
4. Which one of the following is mirror image of the given figure?
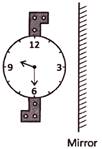
(a) 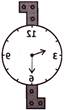 (b)
(b) 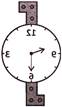
(c) 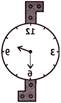 (d)
(d) 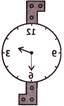
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation:
5. Find the mirror image of given below combination of letters.

(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation:

6.

(a) ![]() (b)
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]() (d)
(d) ![]()
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct
Explanations:
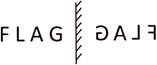
Commonly Asked Question
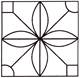
1. Which of the following option will complete the figure?
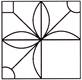
(a) 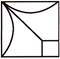 (b)
(b) 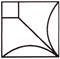
(c)  (d)
(d) 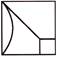
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation:
2.

(a) 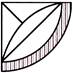 (b)
(b) 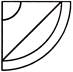
(c)  (d)
(d) 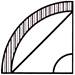
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation:
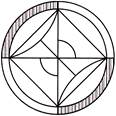
3.
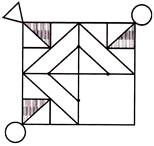
(a) 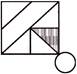 (b)
(b) 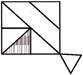
(c) 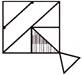 (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation:
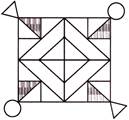
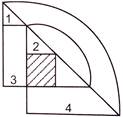
4. How many horizontal lines are there in the given figure.
(a) 2 (b) 4
(c) 8 (d) 7
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanations:
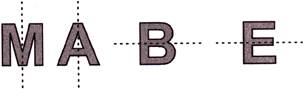
5. How many letters given below have at least one line of symmetry?
N A T I O N
(a) 4 (b) 5
(c) 6 (d) 7
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation:
![]()
6. How many letters given below have at least one line of symmetry?
M O B I L E
(a) 3 (b) 4
(c) 5 (d) 6
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct
Explanations:
![]()
7. Rahul folds a piece of paper along dotted line. If dotted line is the line of symmetry, then which of the following options is correct complete image?
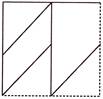
(a)  (b)
(b) 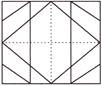
(c) 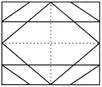 (d)
(d) 
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation:
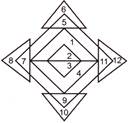
8. Count the number of triangles.
(a) 25 (b) 19
(c) 14 (d) 12
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation:
9. Find the odd one out.
(a) 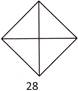 (b)
(b) 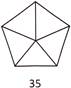
(c) 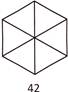 (d)
(d) 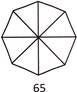
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation:
\[4\times 7=28\],
\[5\times 7=35\],
\[6\times 7=42\], similarly
\[8\times 7=56\].
10. Number of triangles in the given figure is:
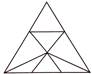
(a) 8 (b) 10
(c) 11 (d) 13
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation:
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
