NUMBER SYSTEM
FUNDAMENTALS
- Numbers are expressed by means of figures- 0, 1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 are called digits.
Out of these digits, 0 is called insignificant digit and rest are called significant digits.
Numerals
- A group of figures representing a number is called a numeral
Place value of a digit in Hindu-Arabic System
|
Periods
|
Crores
|
Lakhs
|
Thousands
|
Ones
|
|
Places
|
Ten Crores
100000000
|
Crores
10000000
|
Ten Lakhs 1000000
|
Lakhs 100000
|
Ten Thousands
10000
|
Thousands
1000
|
Hundreds 100
|
Tens
10
|
Ones
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- In Hindu-Arabic system, the first three places of a numeral from right side make the ones period, the next two places make the thousand period, the next two places make the lakh period and next places make the Crore Period.
Place value of a digit in international system
|
Periods
|
Millions
|
Thousand
|
Ones
|
|
Places
|
Hundred Millions
100000000
|
Ten Millions
10000000
|
Millions
1000000
|
Hundred Thousands 100000
|
Ten Thousands 10000
|
Thousands
1000
|
Hundreds
100
|
Tens
10
|
Ones
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- In international numeral system, the three places of a numeral from right side make the ones period, rest three places make the thousand places and rest three places make the million places.
Inserting Commas
- A comma is inserted after each period in Indian system as well as in International system.
Example:
10 Lakhs = 10, 00, 000
10 Million = 10,000,000
Fundamental Operation of Numerals
- Addition\[\mathbf{(+)}\]: On adding two or more numbers, the number obtained is called sum.
- Subtraction\[\mathbf{(-)}\]: In operation of subtraction the larger number is called minuend and smaller number is called subtrahend. The number found out on subtraction is called difference.
- Multiplication\[\mathbf{(\times )}\]: Multiplicand \[\times \] Multiplier= Product. When any number is multiplied by 1 the product is the number itself and on multiplying any number 0, the product is 0.
Example: \[31\times 1=31,\,\,72\times 0=0\]
Division (+)
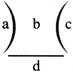
a=Divisor, b= Dividend, c= Quotient, d= Remainder
Example:
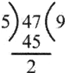
- In above operation, Divisor =5, Dividend = 47,Quotient = 9 and Remainder = 2
Divisibility Test
If the last digit of a number is even or 0 then it is divisible by 2
Example: 3240, 3296 etc.
- Divisibility test for 3: A number is divisible by 3, if sum of the digits is divisible by 3.
Example: 3246, 4122 etc.
- Divisibility test for 4: if the best last two digits of a number is either 0 or divisible by 4 then the number is divisible by 4.
Example: 1800 is divisible by 4 because its last two digits are 0.1864, Is divisible by 4 because 64 is divisible by 4.
- Divisibility test 5: If the last digit of a number is either 0 or 5 then it is divisible by 5.
Example: 1350, 1355, 6525, 1800. All these numbers are divisible by 5.
- Divisibility test for 6: A number which is divisible by 2 as well as by 3 is also divisible by 6.
Example: 324696.
In 324696, the last digit is 6, which is even number, so it is divisible by 2. Sum of 324696 Is 30, 30 is also divisible by 3. Therefore, 324696 is divisible by 6.
- Divisibility test for 7: Double the digit at ones place, than find the difference between the number obtained in previous step and the number formed by rest of its digit. Repeat this process until you find a number which is divisible by 7.
Example: 2401
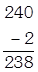
Again,
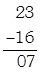
Which is divisible by 7. Hence, 2401 is divisible by 7.
- Divisibility test for 8: If the sum of digits are 0 or its last three digits are divisible by 8 then the number is divisible by 8.
Example: 12000, 20416. These both numbers are divisible by 8.
- Divisibility test for 9: If the sum of digits of a number is divisible by 9, it is also divisible by 9.
Example: 8937, 48231 etc. Both numbers are divisible by 9, because the sum of digits of the numbers is divisible 9.
- Divisibility test for 10: A number is divisible by 10, when its unit place is 0.
Example: 1710, 2350 etc.
- Divisibility test for 11: If the difference between the sum of digits at odd places and the sum of digits at even places is divisible by either 0 or divisible by 11 then it will be divisible by 11.
Example: 13312024, 8030 etc.
In 13312024 sum of digits at odd places= 1 + 3 + 2 + 2 = 8
Sum of digits at even places = 3 + 1 + 0 + 4 = 8. So, difference =0, hence, 13312024 is divisible by 11.
In 8030, sum of digits at odd places= 8 + 3 = 11, sum of digits at odd places = 8 + 3 = 11, sum of digits at even places= 0 + 0 = 0
\[\therefore \] Difference =11 ? 0 = 11, which is divisible by 11, hence 8030 is divisible by 11.
BODOMAS Rule
- In BODOMAS\[\to \]B stands for bracket, O stands for of, D stands for division, M stands for multiplication, A stands for addition, S stands for subtraction.
- Thus, to simplify an expression, first of all brackets are to be removed and then operations of division, multiplication, addition and subtraction should by executed.

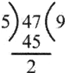
![]()
![]()
