VOICE & NARRATION
Category : 6th Class
VOICES
In grammar, the quality of a verb that indicates whether its subject acts (active voice) or is acted upon (passive Voice). Compare the following sentences · Ram helps Hari. · Hari is helped by Ram. While both sentences express the same meaning, there is a difference in their construction, the difference of Voice. In sentence I, the subject Ram is the doer of the action and thus it is in Active voice, the verb is in the Active Voice. In sentence II, the subject is Hari to whom the action is done and thus the verb is in the Passive Voice allowing are some examples of active and passive voice sentences
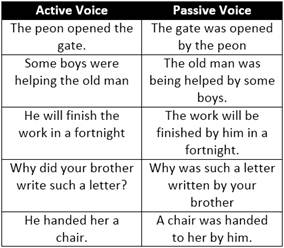
Following are the rules for transformation of voice.
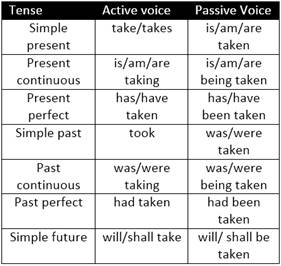
1. When changing a passive voice sentence to an Active voice sentence if the agent is absent in the given sentence you can use any vague agents such as someone, they, people etc. e.g.,
2. My pen has been stolen. (Passive)
3. Someone has stolen my pen. (Active)
4. I was asked my name. (Passive)
5. They asked me my name. (Active)
6. English is spoken all over the world. (Passive)
7. People speak English all over the world. (Active)
NARRATION
Narration refers to a speech. The word narration comes the Latin word 'Narrat? that means relating or telling something to somebody Narration is of two types:
(a) Direct Narration
(b) Indirect Narration
(a) Direct Narration: In Direct Narration, we just quote the exact words of a speaker without making any change in it. Here we use comma quotation for the Reported Speech. Farid said, "I read the Holy Quran everyday" (The Reported Speech) Nancy said to me, "I am beautiful." (The Reporting Verb) Sujata said, "I want a pen." Nancy said to Kona, "I must leave the place now" (The Reported Verb)
(b) Indirect Narration: But in the Indirect Narration, we modify the speech of a speaker in our own way in order to report it to other person or people. Here we leave out the comma quotation ("?..") and use 'that' as conjunction and we must change the persons. Farid said that she read the Holy Quran everyday Nancy told me that she was beautiful. Sujata said that she wanted a pen. Nancy told Kona that she had to leave the place then. Note: The use of 'that' as conjunction after the Reporting Verb in the Reported Speech is optional.
NECESSARY CHANGES IN TENSES
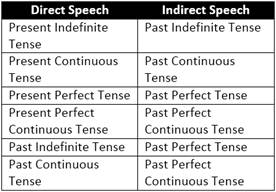
Note: 'Past Perfect Tense 'and Past Perfect Continuous Tast Tense in the Reported Speech do not undergo any change with the exception of persons.
NECESSARY CHANGES IN WORDS
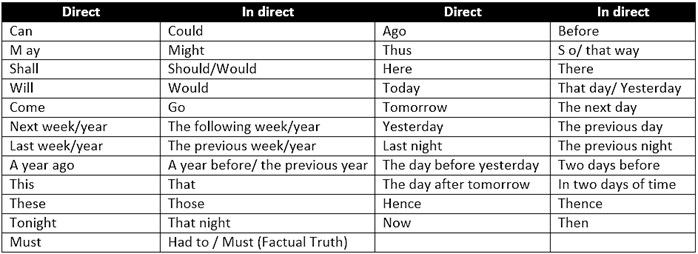
He said, "I went to the theatre last night." He said that he had gone to the theatre the night before. He said, "I am having a party next weekend." He said that he was having a party the next weekend.
He said, "I am staying here until next week." He said that he was staying there until the following week. Rony said, "I came over from London 3 years ago." Rony said that he had come over from London 3 years before. The teacher said, "Students must obey their parents." The teacher said that students must obey their parents. (The verb is not changed because it is a factual truth.) Narration includes these sentences as following: (a) Assertive Sentence, (b) Interrogative Sentence, (c) Imperative Sentence, (d) Optative Sentence and (e) Exclamatory Sentence
ASSERTIVE SENTENCE
Rulel 1: If the Reported Speech is Universal Truth I Scientific Truth I Natural Truth I Habitual Truth I Factual Truth, we don't make any change in the Reported Speech rather we change the person only.
The teacher said, "God is one."
The teacher said that God is one. (Universal Truth)
He said, "Fire burns."
He said that fire bums. (Scientific Truth)
Nancy said, "It is hot in the summer."
Nancy said that it is hot in the summer. (Natural Truth)
The teacher said, "Physical exercise is good for health."
The teacher said that physical exercise is good for health. (Habitual Truth)
Mamun said, "Farah is my cousin."
Mamun said that Farah is his cousin. (Factual Truth)
Rulel 2: If the Reporting Verb is in the Present Tense I the Future Tense I the Present Perfect Tense, they don't undergo any change.
Javed says or will say, "I am right."
Borney says or will say that she is right.
Roma has said to me, "I have just taken my breakfast." (First Person)
Roma has told me that she has just taken her breakfast. (Here w changed the persons only)
He said to me, "You are a liar." (Second Person)
He told me that I was a liar.
Note: 'Said to' is changed into 'told' but 'said' remains unchanged.
Note: 'First Person' in the Reported Speech indicates the 'Subject' of the Reporting Verb and the 'Second Person' in the Reported Speech indicates the 'Object' of the Reporting Verb.
Rulel 3: Sometimes, introductory portion of the Reported Speech may remain absent. In such a situation, we should guess the possible speaker.
"I shall do my duty"
He says or will say that he will do his duty.
He said that he would do his duty
Note: 'Reporting Verb' is not always more than one.
Note: Subjective Case converted into Subjective Case, Possessive Case changed into Possessive One and Objective Case transformed into Objective One.
Rulel 4: Sometimes, the Reporting Verb is mentioned after the Reported Speech and it is possible.
"I am happy now." - said Nancy.
Nancy said that she was happy then.
Note: When we change, any Direct Speech into Indirect Speech, it becomes an Assertive Sentence. No matter, whether it is an Assertive Sentence or Optative Sentence or Imperative Sentence or Exclamatory Sentence
or Interrogative Sentence.
Rulel 5: 'Yes' - replied in the affirmative, Wo'- replied in the negative, 'Please' - kindly and 'Sir' I 'Madam' - politely / respectfully / with respect.
The student said to me, "I am sorry, Sir"
The student told me politely that he was sorry.
"Yes, sir," the student replied. I have done my duty."
The student respectfully replied in the affirmative that he had done his duty
The students said to the teacher, "Please, explain the matter again, Sir."
The students requested the teacher politely to explain the matter again.
Rulel 6: If there are two or more than two Past Tenses in the Direct Speech, they do not undergo any change but we only change the persons.
George said, "I came home, took bath and ate my meal."
George said that he came home, took bath and ate his meal.
Rulel 7: Students often change 'it' into 'that' but that is wrong. It remains unchanged in the Indirect Speech.
He said to me, "I know it well."
He told me that he knew it well.
Rulel 8: Changes in the tag questions:
He said to me, "You are going to the play ground, aren't you?
He asked me whether it was true that I was going to the playground.
Rulel 9: All 3rd Person Pronouns will remain unchanged.
He said, "She is busy with her toy"
He said that she was busy with her toy.
Rulel 10: 'So' = that is why, 'But' = with dissatisfaction
He said to me, "I am unwell. So I shall not go to school."
He told me that he was unwell and that is why he would not go to school.
The boy said, "I have come to chop your wood. "But you are too small to chop wood," said the woman.
The boy said that he had come to chop her wood. With dissatisfaction, the woman told him that he was too small to chop the wood.
Rule 11: Assertive Sentence with question mark: (Use 'Being surprised' with the reporting verb and follow the rules of doing interrogative sentence.)
He said to me "You are angry with me?"
Being surprised he asked me if I was angry with him.
Rule 12: Well, you see (if used within inverted comma) Omit them and do in general way.
The teacher said, "Well Raven, I shall reward you."
The teacher told Raven that he would reward him.
Note: ‘Vocative Case' in the Reported Speech becomes the 'Object' of the Reporting Verb in the Indirect Speech.
Rule 13: If we find any Complex Sentence in the Direct Speech, we may change one Clause or both the Clauses in the Indirect Speech.
Mita said to me, "You were my good friend when you were a student of Saint Joseph" (Complex Sentence)
Mita told me I had been her good friend when I had been a student of Saint Joseph.
He said to Ratul, "You were mere a boy when I saw you last." (Complex Sentence)
He told Ratul he had been mere a boy when he had seen him last.
Rule 14: When we report something that is still true:
Rajan said, "People in Africa are starving." (The fact is still true.)
Rajan said that people in Africa are starving.
UNREAL PAST TENSE
Rule 15: Unreal Past Tense after 'wish', 'would rather / sooner', 'had better', 'used to', 'ought to', 'would',
‘could’, 'might', 'must not', 'need not' and 'it is time' don't change rather we change the person in the Indirect Speech.
"We wish we did not have to take exams", said the children.
The children said they wished they did not have to take exams.
"It is time we began planning our holidays", he said.
He said that it was time they began planning their holidays.
They ought to widen this road", I said.
I said that they ought to widen the road.
He explained, "I know the place well because I used to live here."
He explained that he knew the place well because he used to live there.
She said to her hubby, "You had better take warm water for gurgling."
She told her bubby that he had better take warm water for gurgling.
He said, "You must not tell anyone."
He said that she must not tell anyone.
(Alternatively): He told her not to tell anyone.
He said, "You needn't wait."
He said that I needn't wait.
He said to me, "I used to meet him in the afternoon."
He told me that he used to meet him in the afternoon. (With that)
He told me he used to meet him in the afternoon. (Without that)
Rule 16: The 2nd and the 3rd Conditional Sentences remain unchanged rather we change the persons.
"If I had a permit, I could get a job", he said.
He said that if he had a permit, he could get a job. (The 2nd Conditional Sentence)
"If she had lov6d Wilson", he said, "She would not have left him."
He said that if she had loved Wilson, she would not have left him. (The 3rd Conditional Sentence)
Rule 17: When there is uncertainty as to the particular person to whom the pronoun in the Indirect Speech refers, the name of the person should be mentioned in the brackets.
He said to the Ram, "You are wrong."
He told Ram that he (Ram) was wrong
Harry said to Jatin, "You will pass."
Harry told Jatin that he (Jatin) would pass.
INTERROGATIVE SENTENCE (?)
Rulel 1: We use ask (ed) / want (ed) to know / enquire (ed) in the Indirect Speech in the place of said / said to and we don't change the Interrogative Pronouns /the Interrogative Adjectives / the Interrogative Adverbs transformation.
My mother said to me, "How are you now?"
My mother asked me how I was then.
"Where are you staying next week?, my friend said to me.
My friend wanted to know where I was staying the following week.
Note: Who, where, which, when, how, why, what, whom, whose and the rest are the Interrogative Pronoun / Interrogative Adjectives / Interrogative Adverbs.
Rulel 2: If any Interrogative Sentence commences with just an Auxiliary Verb rather than the Interrogative Pronouns / Adjectives / Adverbs, we use if/ whether.
My teacher said to me, "Are you making a noise?"
My teacher asked me if or whether I was making a noise.
The noble man said to the poor man, "Have you taken anything for lunch?"
The noble man asked the poor man if he had taken anything for lunch.
Bunty said to me, "Do you want to help me?"
Bunty asked me if I wanted to help her.
Note: 'Whether' is more formal than 'If. Either of them can be used but 'whether' is preferable when there a matter of choice.
Note: 'Do', 'Does' and 'Did' are removed in the Indirect Speech if they are used as Auxiliary.
Rulel 3: If there is a Present participle phrase with the reporting verb, it will come in front of the reporting verb in doing the indirect speech. But if it is not present participle phrase then the position of it will remain unchanged.
"Are you brothers?" asked the mistress of the house turning to the Dervishes.
Turning to the Dervishes the Mistress of the house asked if they were brothers.
Note: Here in it, we don't use that in the Indirect Speech when we leave out comma quotations.
IMPERATIVE SENTENCE
We use tell, beg, implore (to ask sb to do sth in an anxious way because you want or need it very mud entreat (formal: to ask sb to do sth in a serious and often emotional way), encourage, forbid, recommend remind, urge, warn, ask, told and the rest in the place of 'said' or 'said to' in the Indirect Speech in the sentence.
Rulel 1: We use the Infinitive (to + verb present form)
The teacher said to his boys, "Do it at once."
The teacher advised his boys to do it at once. (The Infinitive)
Khona said to her teacher, "Grant me my prayer, Sir."
Khona politely requested her teacher to grant her prayer.
He said, "Lie down, Tom."
He told Tom to lie down.
She said, "You had better hurry. Bill."
She advised Bill to terry.
He said to his friends, "Please wait for me till I return."
He requested his friend kindly to wait for him till he returned.
Rulel 2: If the Reported Speech starts with 'Do not / Never', we use 'not to + verb in the Indirect Speech in the time of leaving out the comma quotations.
My father said to me, "Do not run in the sun."
My father advised me not to run in the sun.
My father forbade me to run in the sun.
My teacher said, "Never tell a lie."
My teacher advised me not to tell a lie.
Rulel 3: The Modals must, would and could are not normally changed in the Indirect Speech. You should also note that some sentences with would and could are Interrogative in form but Imperative in nature.
He said to me, "You must leave the place."
He told me I must leave the place. (Assertive Sentence)
He said to me, "Would you help me to do the sum?"
He requested me to help him to do the sum. (Imperative Sentence)
I said to her, "Could you give me a cup of tea?"
I requested her to give me a cup of tea. (Imperative Sentence)
Rule 4: Calling in the name of person (The name will be added as object of reporting verb)
He said, "Raven, don't misbehave with anyone."
He advised Raven not to misbehave with anyone.
Rulel 5: Calling in the name of relations
The student said, "Sir, please forgive me." (Addressing as brother/sister/friend/sir)
Addressing as sir the student requested kindly to forgive him.
Rulel 6: By Allah/by God/by Jove/by my love/by my life (Swearing by Allah/God/Jove/Life/Love)
"By Allah," she replied, "I will not forget you."
Swearing by Allah, she replied that she would not forget me.
Rulel 7: Imperative sentence with tag question
He told me, "Shut the door, will you?" (Tag question will be omitted and rules of imperative sentence will be followed.)
He asked/requested me to shut the door.
Rulel 8: When 'let denotes a proposal, the Reporting Verb should be changed in to 'propose' or 'suggest and 'let' be replaced by 'should.
Bunty said, "Let's have a walk."
Bunty proposed that we should have a walk.
He said to me, "Let's go home."
He suggested to me that we should go home.
Rulel 9: But when 'Let' does not express a proposal, the Reporting Verb does not change, only 'let' is changed into 'may' or 'might' or 'might be allowed or any other verb as per the relevant meaning.
He said, "Let me have a glass of milk."
He wished that he might have a class of milk.
Rulel 10: It is often safer for the students to use 'tell' in the Indirect Speech, when there be any doubt about the proper word to introduce the Reported Speech.
I said to him angrily, "Leave me alone."
I told him angrily to leave me alone.
OPTATIVE SENTENCE
We use 'wish' or 'pray' in the Optative Sentence in the place of 'said to' or 'said.
My grandfather said, "May you live long."
My grandfather wished that I might live long.
The teacher said to the boy, "God bless you." (Optative Sentence without May)
The teacher prayed for the boy that God might bless him.
He said, "Would that I were here,"
He wished that he had been there.
They said," 0 that! We had won the match."
They wished that they had won the match.
Note: "Would that" and "O that" are removed in the Indirect Speech.
EXCLAMATORY SENTENCE (!)
We use hurrah - exclaim with joy, alas - exclaim with sorrow, fie - exclaim with shame, wow - exclaimed with wonder/surprise, cry out, 'wish' or 'pray' in the place of 'said' I 'said to'
The boy said, "What a piece of good news it is!"
The boy exclaimed with joy that it was a piece of very good news.
She said, "Had I the wings of a bird!"
She strongly wished that she had the wings of a bird.
Farhad said, "Good-bye, my friends!"
Farhad said good-bye to his friends.
Farhad bade his friends good-bye..
The poor boy cried, "Alas! I am undone."
The poor boy exclaimed with sorrow that he was done.
The maidservant said, "By Allah! I know nothing about the stolen purse."
The maidservant swore by Allah that she knew nothing about the stolen purse.
I said to them, "Bravo! You played very well."
I applauded them that they had played very well. (Bravo - applauded)
My friend said to me, "Thanks! /Congratulations!"
My friend thanked/congratulated me.
The girl said, "Help! Help!"- The girl cried out for help.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
