Electricity and Magnets
Category : 6th Class
Electricity and Magnets
Electricity
Electricity is a form of energy called electrical energy. We can convert electrical energy into various other forms of energies easily.
Electric Circuit
The path through which electric current can flow is known as electric circuit. A simple electric circuit is made up of a bulb, wire and an electric cell. An electric cell has two terminals: a positive terminal and a negative terminal. A wire is connected from positive terminal to negative terminal of the cell and the bulb is connected to the wire so that current can flow through bulb.
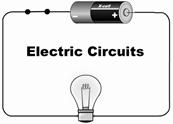
Closed Circuit: When there is no gap in an electric circuit or the normal path of current has not been interrupted, the circuit is known as closed or complete circuit.
Open Circuit: When there is a gap in an electric circuit or the normal path of current has been interrupted, the circuit is known as an open circuit or incomplete circuit.
Conductors and Insulators
The substances which allow electric current to pass through them are called conductors. For example, copper, gold, silver, aluminium, iron, etc. are good conductors of electricity.
The substances which do not allow electric current to pass through them are called insulators.
For example, wood, plastic, paper, rubber, etc are insulators.
Electric Cell
An electric cell is a device which can generate electric current in a closed circuit. It is small and easily portable so it is very useful for us. There are a number of machines like watches, calculators, toys, cars, etc. in which electrical cell is used to produce electric current. Dry cell, button cell, solar cell are the examples of electric cell.
Dry Cell
A dry cell is a cylindrical device in which a number of chemicals are stored. It has a metal cap on one side called positive terminal and a metal sheet at other side called negative terminal. It produces electric current from the chemical stored inside it.

Electric Bulb
An electric bulb is a device which produces light energy using electrical energy. It consists of a glass bulb fixed on a metal case, a thin wire fixed between the two thick wires called filament of the bulb and the gas filled inside the glass bulb. When electric current passes through the filament, it emits light which makes the bulb glow.

Magnet
Magnet is a substance which attracts magnetic materials such as iron, nickel, steel and cobalt. Magnets are of different shapes and sizes. For example, U-shaped magnet, cylindrical magnet, bar magnet, etc. Each magnet has two poles, south pole and north pole.
Magnetic Materials: The materials which are attracted by a magnet are called magnetic materials. For example, iron, nickel, steel and cobalt are magnetic materials. Magnetic materials can be converted into magnets by the process of magnetization.
Non-Magnetic Materials: The materials which are not attracted by a magnet are called non-magnetic materials. For example, copper, aluminium, air, water, rubber, etc. are non-magnetic materials.
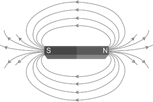
Magnetic Field
When we bring any magnetic material such as iron, nickel, cobalt near a magnet, it experiences a force. Magnetic field is the region around a magnet in which a magnetic material experiences force applied by the magnet.
Magnetic Compass:
It is a magnetized needle pivoted freely at a point. It is used to find the direction.
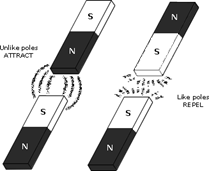
Force of Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets
When north pole of a magnet brought near the north pole of another magnet, force of repulsion is experienced between them. And when north pole of a magnet is brought near the south pole of another magnet, force of attraction is experienced between them. So we can say like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
Uses of Magnet
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
