WATER: A PRECIOUS RESOURCE
Category : 7th Class
Learning Objectives
INTRODUCTION
About 3000 million years ago the first life form originated in Oceans that covered the Earth. Water is essential for life. We cannot imagine life without water. Not only is water necessary for carrying out the various reactions that occur inside our bodies, it is also required by the industries and laboratories.
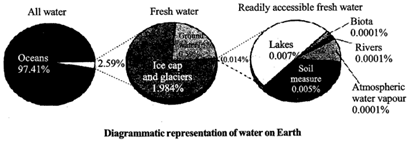
Availability of Water on Earth
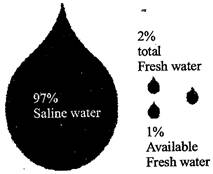
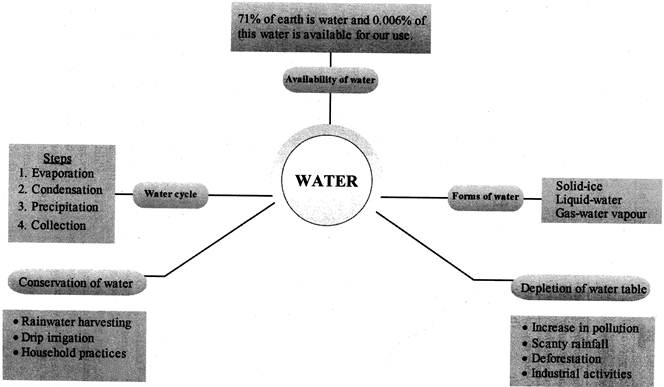
Nearly 71 percent of the earth is covered by water in the form of oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, ice, ground water and moisture in the air. However, most of it is not fit for human consumption. Water that is fit for human consumption is called freshwater. Only 0.006 percent of the water on the earth is actually available for our use.
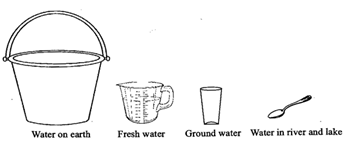
If a bucketful of water shows the total water on the earth, then a mug of water shows the total freshwater available on the earth. Out of this, a glass of water shows the water which is available as groundwater. About one-fourth spoonful of water shows all the water available in lakes and rivers of the world. In nature, water exists in three forms: solid, liquid and gas.
Forms of Water
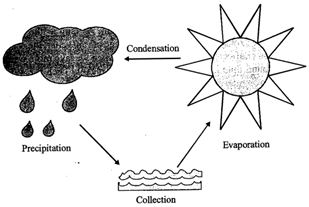
Water Cycle
Water is available in all the three states of matter. Ice is the solid state, water is the liquid state and vapour is the gaseous state; in which water is available. The water on the earth keeps on changing in all the three states in a cycle. This is known as water cycle. The water cycle helps in keeping the amount of water on the earth as constant.
Do you know?
Following are the main steps of water cycle in nature:
Evaporation: Water from the surface of the earth keeps on evaporating and turns into vapour. The water vapour also comes from green plants through transpiration.
Groundwater, an Important Source of Water
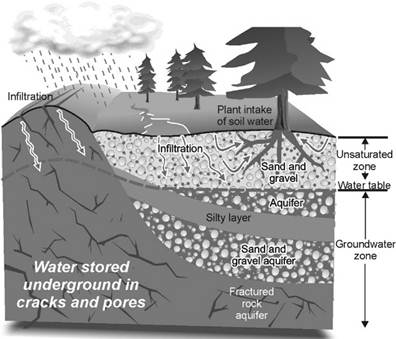
Groundwater is the most important source of water for us. The water is stored under the ground; between layers of rocks. The upper limit of groundwater at a place is called the water table at that place. Water table is usually higher in the plains but is very low in the plateaus. This is the reason it is easier to install a hand-pump in the northern plains. On the other hand, it takes a heavy drilling machine to install a tube-well in the plateaus.
Do you know?
Depletion of water table
If you dig a hole in the ground, you'll reach moist soil at a certain depth. Soon, you'll reach a depth at which all space between the soil particles and cracks in the rocks are filled with water. The upper limit of this depth is called the water table. Rainwater and water from other sources, like rivers and ponds, seep through the soil. This water fills the empty spaces and cracks deep below the ground. This is known as infiltration. Sometimes, ground water accumulates between layers of hard rock. This is known as an aquifer. Water in aquifers can be drawn with tube wells and hand pumps. Plants use ground water and release it in the form of water vapour during transpiration. This completes the cycle of returning the water to the clouds. The clouds then release the water through precipitation, and the cycle starts all over again. As long as the water drawn from the ground is replenished by seepage of rain water, me water table remains unaffected. The problem starts when we take more water from the ground than is replenished by natural means. Then the water table goes down, and it is said to have been depleted. Due to growing human population, there is an increased demand for potable water. There is more need for drinking water and also for water for other purposes; like irrigation, economic activities and recreation. The supply of water either remains the same or has decreased, but demand has been continuously increasing. The mismatch in supply and demand is resulting in depletion of water table and most of the places are facing acute shortage of water.
Growing population means, there is more demand for food grains and hence farming is being done on a larger scale. More farming means more consumption of water for irrigation.
Growing population also means more construction of houses and pucca roads. This has created an impervious layer of concrete above the ground at most of the places. This has adversely affected the natural recharge of underground aquifers.
Forests have been cut to clear land for meeting the demand of a growing population. Trees make the rocks pervious to water and thus facilitate recharge of underground aquifers. Reduced forest cover has also hampered the natural recharge of underground aquifers.
Do you know?
Uneven Rainfall:
India is a large country. Some parts of the country get excess rainfall, while some other parts get deficient rainfall. As a result, while some parts of the country are flooded during the rainy season, many other parts suffer from draught like conditions. Uneven rainfall also adds to the problem of water shortage.
Reasons for depletion of the water table:
Water management is the continuous matching of water resources with the water requirements of a place. Water management essentially involves activities that identify sources of water, prevent wastage of water, and implement recycling of water. It may also include treatment of water to make it suitable for human consumption.
Conservation of Water
Instead of letting rainwater run off into the sea, it can be used to recharge ground water. This is known as rainwater harvesting. Rainwater harvesting can be used to raise the water table in arid areas. It can also be used to create water storage areas.

Collection of rainwater for future use is called rainwater harvesting. India has a long history of different rainwater harvesting structures; especially in rain deficient areas. For example; tankas and bawris had been in use in the northwestern part of India; especially in Rajasthan. Tanka is an underground tank to collect rainwater. Bawri is an open tank in which water used to be collected. Steps were made around the bawri so that one can easily access the water. Rainwater harvesting can also be done in modem homes. The runoff rainwater from the rooftop should be collected in an underground reservoir. Such reservoirs are usually filled with sand and gravel to filter out impurities from water. The water can either be used directly or can be channelized to recharge the underground water.
Do you know?
Drip Irrigation:
Drip irrigation is a method through which maximum number of plants can be irrigated with minimum use of water. For this, pipelines are laid throughout the rows of plants. Pipes are pierced at strategic points to release water in droplets. This helps in saving the water which is an important but scarce resource.
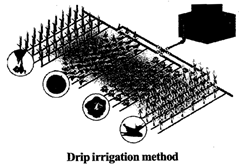
Farming, which typically requires huge quantities of water, can also benefit from good water management. Drip irrigation is an economical way of using water. Plants need water to absorb nutrients from the soil and make their food. Without water, plants would die, and greenery would be lost. This, in turn, would mean the end of all life on the earth, because without plants, there would be no food, oxygen or rainfall. There would also be many other problems.
Steps one can take to conserve water:

KEY WORDS
CONCEPT MAP
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
