Notes - Architecture as Power
Category : 7th Class
Architecture as Power
The Taj Mahal is a famous monument and is one of the seven wonders of the world. It is undoubtedly, he finest example of Mughal Architecture. There are many other spectacular monuments like, Lal Quila, Sun temple, Meenakshi temple and monuments of Sikri that were built during the medieval period. These monuments are manifestations of composite form of art and architecture developed as a result of the assimilation of diverse cultures.
Have you ever visited Qutb Minar? It is a tall and appealing monument built during the medieval period by Qutb-ud-din Aybak. It stands adjacent to the Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque. It is unique in many ways. Its great height is enhanced by its tapering structure. The balconies have been skillfully projected. The use of ribbed and angular projections and the red and white sandstones add further to its beauty. The verses from the holy Quran are carved on sandstone walls of Qutb Minar. This monument served the purpose of calling people for prayer in the mosque. The foundation of Qutb Minar was laid by Qutb-ud-din Aybak but its construction was completed by his successor Iltutmish in 1230 AD.

Inscriptions and balcony of Qutb Minar
India is a treasure house of architectural art. Though architecture has flourished in India through many centuries/ it was during the medieval period that architecture was at its zenith. There was immense impact of foreign style of architecture during this period. Both the Delhi Sultans and the Mughals brought in different styles of architecture. Thus, the medieval period witnessed a wide variety of architecture. Some of them were indigenous and some were the contributions of foreign invasions.
INDIAN ARCHITECTURE IN THE MEDIEVAL PERIOD
Many monuments were built during this period. Rulers spent enormous money on construction. Temple building was regarded as a sacred duty of the rich and kings. Temple building was sponsored because it was a pious act bringing religious merit. The Muslim invaders built mosques to show their power, wealth and victories. The buildings built by the Mughals impart a sense of ruler power and were a potent symbol of authority.
The Mughal wealth is reflected in the opulence of their architecture. The buildings made by Shah Jahan are lavish and display the superb wealth and status of the Mughal emperor. Tombs were built by emperors in an effort to be remembered. Forts were built as safeguards from invasions and were also a measure of the ruler's strength.
The monuments are important sources of information about the medieval period. They give information about the religious beliefs of the people, the state of economy, the state of the empire and the materials and techniques used. The lavish palaces bear witness to the extravagant lifestyles of the rulers. The forts throw light on the defence tactics and intelligence of the rulers. Basically, two types of structure were built. The first type was the structures built for public use like gardens, mosques, temples, wells and tanks. The second type was the structures for personal use and security like palaces and forts.
Q. why did Shah Jahan build such lavish monuments?
ARCHITECTURE OF PUBLIC USE MONUMENTS
The public use monuments were gardens, mosques, temples, baolis, havelis, tanks and bazaars. The rulers constructed these for the welfare of people. Also, they wanted to earn the admiration, respect and gratitude of the people.
MOSQUES

Jama Masjid
The Muslim rulers required places of worship and built many grand mosques. The Jama Masji in Delhi, Badshahi Masjid in Fatehpur Sikn Quwwat-ul-lslam Mosque in Delhi, Jaamat Khan. Mosque and Khirki Mosque are well-known.
Jama Masjid of Delhi is the largest mosque in India. It has a spacious courtyard that car accomodate 25,000 people. The Jama Masjid is covered with intricate carvings and has versed- inscribed from the holy Quran and has three gateways, four towers and two minarets. The gateways in the north and south are led by a fleet of steps. The main entrance is on the eastern side and was probably used by the emperors. The tower of the Jama Masjid has distinctive storeys with projecting balconies.
World Heritage Sites?UNESCO maintains an International World Heritage Programme. Since 1972, UNESCO is working in this direction and by 2015; 1031 sites were identified as World Heritage Sites, out of which; 25 cultural and 7 natural heritage sites are located in India.
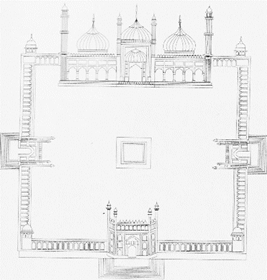
The Plan of Jama Masjid
TEMPLES

The Plan of Brihadeshwara Temple

Brihadeshwara Temple
Many exquisite temples were built with marvelous carvings and varied architectural styles. In India, temples were more than mere places of worship. They were sacred buildings and were symbolic reflection of the ruler and his richness and devotion. The temple was a miniature model of the world ruled by the king. They also gave a glance into the society of the medieval period. They served as a sacred meeting place of the community. There is a symbolic meaning in the sculptures of these temples. These pronounce the age old custom and traditions of India. Many of these temples have found a place in the list of World Heritage Sites.
Sun Temple
The Sun Temple is located in Konark. It was built in 1250 AD, during the reign of the Ganga dynasty king Narasimhadeva I, to celebrate his victory over the Muslims. It is dedicated to the Sun God or Sun/a. It has been declared a world heritage site by UNESCO. The entire temple has been conceived as a chariot of the Sun God with 24 wheels and seven horses who drag the temple. Two lions depicted as crushing elephants under their feet, guard the entrance. A flight of steps leads to the main entrance. There are three images of the Sun God, positioned to catch the rays of the Sun at dawn, noon and sunset. The walls of the temple are beautifully carved. This temple is popularly known as "The Black Pagoda".
Rajarajeshwara Temple
During the times of Cholas (900-1155 A.D.), temple architecture in the South reached its climax. Rajarajeshwara temple is located in the town of Thanjavur in Tamil Nadu. It was built by Rajaraja I of the Chola dynasty. It was later called Brihadeshwara Temple by the Marathas. The walls of the temple are elaborately carved with mural of gods and princes. Surrounded by fortified walls, the temple has 216 feet high tower or uimana. On the top of the Vimana there is a monolithic Shikhara, which is presumed to weigh 80 tons. It is an enigma even nowadays how this gigantic heavy granite rock was lifted up to the height of 60 m. According to one theory, a 6 km long sloping scaffold must have been constructed.
GARDENS
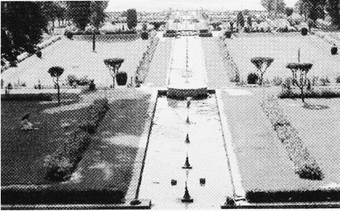
Nishat bagh
From the beginning of the Mughal Empire, the construction of gardens was a beloved imperial pastime. Babur, the first Mughal Emperor had a fine aesthetic taste and for him the most important aspect of architecture was regularity and symmetry. He laid out many gardens with running water channels. He described his favourite type of gardens as Chahar bagh this is a Persian-style garden layout with intersecting water channels thus dividing the garden into four parts. They were walled enclosures and the typical features were pools, fountains and canals inside the gardens.
The Agra garden, now known as the Ram Bagh, is thought to have been the first chahar bagh. Other famous Mughal Chahar bagh gardens are the Humayuns's Tomb Garden in Delhi, Shalimar Gardens and Nishat Gardens in Kashmir and Taj Mahal in Agra.
BAOLIS. BAAZARS AND TANKS
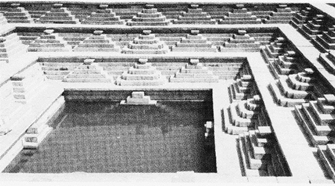
A Stepped Well
The "baolis" or step-wells were ancient water reservoirs built by rulers to provide a constant supply of water. A baoli was used to collect and store rainwater. They were unique and grand in their structure. They had inclined surrounding passageways, chambers and steps which provided access to the wells. The oldest existing Baoli in Delhi is Anangtal built in the tenth century, during the time of the Rajput Tomar dynasty, who ruled Delhi at that time. Iltutmish has to his credit the construction of several baolis, including the Gandhak-ki-baoli near Qutb Minar. Other baolis which are now in ruins include the Hauz Khas Baoli and the
Why were temples made and destroyed?
Temple building and its maintenance was regarded as a sacred duty of kings and the wealthy who keenly sponsored temple building. Temples were meant to show their power and wealth.
Many temples were destroyed by the invaders. The invaders displayed their power and demonstrated their heroism by plundering and destroying the places of worship. Also, the Hindu temples were very rich, so the Muslim invaders attacked temples to rob the riches. Mahmud of Ghazni raided the rich temples at Thanesar, Mathura, Kanauj, Somnath and Nagarkot. He plundered and destroyed them. His most famous raid was on the Somnath Temple in Gujarat.
Another reason behind temple destruction was that the worshipping of idols is against the Islamic beliefs. The attacks on the temples clearly highlight the war against the non- Muslims. Destroying the idols of Hindu gods and demolishing their temples, harmed the sentiments and beliefs of the Hindu people who were being conquered. However, some temples were not destroyed because they were built in comparatively remote places thus were not accessible to the invaders. To sum up, it can be said that displaying the political might and military success were the common reasons behind making and destroying the temples.
Ugrasen Baoli. Rani ki Vav at Patan, Gujarat has been recently declared as world heritage site. Many bazaars were planned and constructed. These were busy places where traders came to sell their goods. The Chandni Chowk was a bazaar made during this period. The Meena Baazar was where the royal ladies shopped. The rulers often constructed tanks or reservoirs for the welfare of the people. Sahastralinga Tank or

Harmandir-Sahib
Sahastralinga Talav is a medieval artificial water tank in Gujarat. It was made by the Solanki Dynasty. Sometimes tanks were made outside places of worship, for example the Meenakshi Temple and the Golden Temple have tanks in their premises.
ARCHITECTURE OF PRIVATE USE MONUMENTS
FORTS
Most of the Indian forts were built as a defense mechanism to keep the enemy away. Forts were a potent symbol of authority. Thus, they were a measure of the monarch's strength. These forts housed important buildings and protected them from invasions. Some of the notable forts of Delhi are the Red Fort, Purana Qila and the Tughlucqabad Fort. Other notable forts are the Gwalior Fort and the Junagarh Fort.
The Red Fort (Lal Qila) at Delhi was built by Shah Jahan on the banks of river Yamuna. It is one of the massive forts in India. Shah Jahan built the Red Fort as the citadel of Shahjahanabad, his new capital at Delhi. It has halls of public and private audience {Diwan-i-Am and Diwan-i-Khas), domed and arched marble palaces, private apartments, a mosque and richly designed gardens.
The majestic Agra fort was built by the Mughals. It contains numerous impressive structures like the jahangiri Mahal, Khas Mahal, Diwan-i-Khass, Diwan-i-Am, Machchhi Bhawan and Moti Masjid.
HAVELIS
Havelis1 were the mansions of the kings, rich merchants and nobles, built especially in Rajasthan during the medieval period. These had massive courtyards and elaborate balconies. Intricate carvings and paintings adorned the walls. They showcase the glory and grandeur of the Rajputs.
FOUNDED TOWNS AND CITIES
Alauddin Khalji built his capital at Siri. The city Tughluqabad was founded by Ghiyasuddin Tughluq; the city of Jahanpana was built by Muhammad Tughluq and the Ferozabad palace and fort were built by Firoz Shah Tughluq Fatehpur Sikri was the first planned city of the Mughals. It was founded by Akbar as a mark
History Reveals
The Sheesh Mahal in the Agra fort was the dressing room for ladies of the harem. It was decorated with myriad glass pieces.

The Sheesh Mahal of Agra Fort
Of respect for Sheikh Salim Christi. The whole complex was on top of a hill by the side of an artificial lake. It had lofty buildings for private and public use. The Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan laid the foundation stone for a new capital of his kingdom which was known as Sliahjahanabad. It was secured and enclosed by about ten kilometers long well. Ten gates connected the city with the surrounding region.
TOMBS
The tombs were built with a desire to remember the great emperors. Some of the famous tombs are the tomb of Sher Shah Suri, 'Akbar's tomb at Sikandra and the Taj Mahal.
Sher Shah's mausoleum was built in Sasaram in Bihar in the center of a large pond. Humayun's tomb was built by Hamida Banu Begum in Delhi. It is the first garden-tomb on the Indian subcontinent. It is constructed in the center of a Chahar Bagh. The garden, divided in four main parts by shallow water channels is created to resemble the paradise garden described in the Quran.
Akbar's mausoleum is at Sikandra. Akbar himself started construction of this beautiful monument. The tomb is a five-storey building resting on a high stone platform. It is located right in the center of a Chahar Bagh. The Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan in the memory of his beloved wife, Mumtaz Mahal.
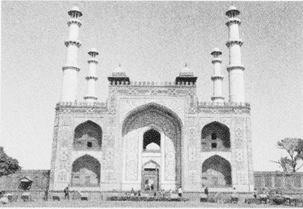
Sikandara, Akbar's tomb, Agra
History Reveals
Fatehpur Sikri was intended to be the joint capital with Agra, but was soon deserted because the water system could not support any residents.
THE ENGINEERING SKILLS, CONSTRUCTION STYLES AND BUILDING MATERIALS
The medieval monuments give us an understanding of the construction technologies used.
The "trabeate" or "corbelled" style was used in construction in India. Roofs, doors and windows were made by placing horizontal beams across vertical columns. This style has been used in the construction of the Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque. Islamic architecture introduced the "arcuate" style in which the weight of the superstructure was carried by an arch. A key stone was used here. The earliest example is the Alai Darwaza by the side of Qutb Minar.
The Muslim architecture had grandeur and spaciousness. The buildings were decorated with scrolls of flowers and verses of the Quran. No human or animal figures were used because it is against the Islamic beliefs. Geometrical or floral designs were interspersed with calligraphy and inlaid work. They added colour to their buildings by using red sandstone and glazed tiles. Use of pure white marble, inlay work of gold, silver and precious metals, cut and polished stones, gardens around tombs, minarets in the mosques and palace halls were some of the chief features of architecture during the Mughals. The walls were decorated with precious and semi-precious stones. This technique was called pietra dura.
History Reveals
Shah Jahan perfected Mughal architecture and his reign is known as the Golden Age of Mughal Architecture.
The Muslims also introduced new architectural features like dome, pointed arch and minarets. The dome had many advantages. It provided a pleasing skyline2 and was also a symbolic representation of the vault of heaven.
Also, the dome and arch dispensed the need for a large number of pillars to support the roof and thus enabled the construction of large halls with a clear view. These large halls were useful in mosques and palaces. Minarets are tall slender towers with onion shaped crowns. They had meeting balconies which were used for the call to prayer. They also provided natural ventilation and Functioned as air conditioning mechanisms.
The materials used differed from region to region depending upon the availability. Stone was widely used because of its durability. The cementing material used was mortar. The tughhluqs used, grey sandstone. The earlier Mughal buildings were made using red sandstone. Marble was increasingly used by the Mughals and Shah Janan used white marble in all his buildings.
CROSS REGIONAL ARCHITECTURAL INFLUENCES AMONG VARIOUS EMPIRES
The Muslim rulers of India contributed greatly to the development of a new style of architecture in India. They brought with them distinctive architectural ideas and designs which blended with the traditional Indian styles. The result was the Indo-Islamic style of architecture.
The Muslims used Hindu features like the bell, lotus and swastika in their buildings. They also began using the type of dome that was designed in Bengal. Some temples were constructed in architectural styles closely resembling the Mughal palaces of Fatehpur Sikri. Thus the medieval period in India witnessed a large variety of architecture.
SHAH JAHAN

Diwan-i?Khas, Red Fort
Shah Jahan was a prolific builder and he perfected Mughal architecture. He took keen interest in buildings and spent lavishly on constructions. When he first ascended the throne, he had renovation work done in the Agra Fort. Marble was used and inlay work with precious stones was done.
Shahjahanabad |
One of Shah Jahan's biggest protects was the construction of the city of Shahjahanabad. Today, it is known as the Red Fort. The Enormous walled city is built of red sandstone. The red fort is octagonal in shape and is surrounded by a moat. This fort had the emperor?s palace, mosques, gardens, markets, residences of the nobles and broad avenues with water channels. Also, there was a military, garrison, treasury and manufacturing units. Some of the important buildings were diwan-i-Aam, diwan-i-Khas and Mumtaz Mahal.
Jama Masjid
Another famous building made by Shah Jahan is the Jama Masjid in Delhi. Situated on a high platform, it is a huge building of red sandstone. Shah Jahan built many other mosques in Agra, Ajmer and Lahore.
Taj Mahal
Of all the buildings made by Shah Jahan, the crowning glory is the Taj Mahal. It is a world famous monument built in Agra on the banks of the river Yamuna. He built it in the memory of his beloved wife, Mumtaz Mahal. The Taj houses the tombs of both Mumtaz Mahal and Shah Jahan. It was constructed using material from all over India and Asia. Over 1000 elephants were used to transport building material during its construction. It is made entirely of white marble and 28 types of precious stones are inlaid into the marble. It stands on a raised terrace with 4 minarets at each comer. The minarets are believed to slant outwards so that in the event of an earthquake, they will fall away from the tomb. The perfect proportions add to its beauty. It glows like a pearl in the moonlight.
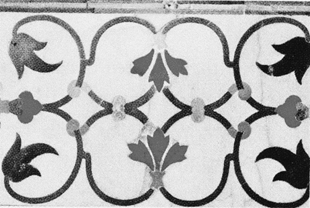
Pietra dura on the Taj Mahal

Roof Work in Taj Mahal
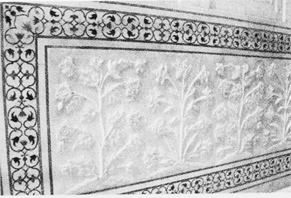
Flower Carvings on Taj Mahal
Shalimar Bagh
Shah Jahan also planned and built many gardens. The Shalimar gardens at Lahore were constructed by him and adorned with countless species of flowers and plants. This garden was made on the concept of Chahar Bagh. Mughal architecture reached its zenith under the patronage of Shah Jahan. His reign is known as the 'Golden Age of Mughal Architecture'.

The Shalimar Gardens, Pakistan
Around the World

The Cathedral Church of Florence designed by Brunelleschi
The Renaissance began in Italy. This was the most creative period in history. Rome was one of the centres of the classical world. This inspired the rebirth of culture. There were wealthy people willing to pay for sculpture, painting and architecture. Many great artists also lived in Italy. Filippo Brunelleschi designed the dome of Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore which is the cathedral church of Florence. This structure built without any frame or support did not collapse as people thought it would.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
