Notes - World Distribution Of Natural Vegetation And Wildlife
Category : 7th Class
World Vegetation Distribution of Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
If you visit a desert area, you will see camels, palm trees and cacti all around; while a hilly region will have plenty of oaks, pines, deodars and yaks, bears, leopards, etc. Similarly, a river or a pond or an ocean house fish of various kinds and plankton. Plants and animals are adapted to the environment in which they live. Here in this chapter, we will learn about the distribution of natural vegetation and wildlife.
The earth's environment provides suitable conditions for all forms of life to exist. Plants, animals and micro-organisms are the different forms of life on the earth. We often use the term vegetation for natural vegetation, but, in fact, there is a difference between the two. We know that plants grow where there is sufficient water, sunlight, soil and air. Plants which grow on their own without any human intervention are categorised as natural vegetation. Vegetation on the other hand, is the growth of plants controlled by humans. Natural vegetation depends largely on the climatic conditions of a region.
NATURAL VEGETATION AND WILDLIFE
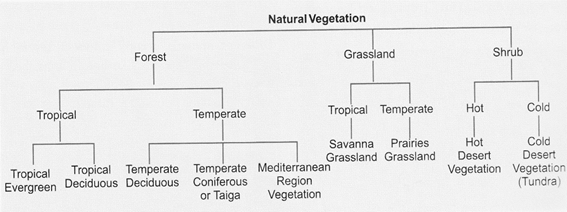
Classification of natural vegetation
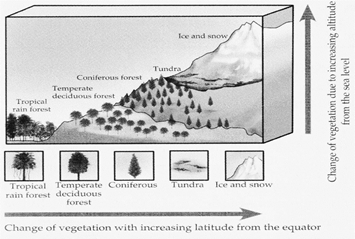
Climate determines the type of natural vegetation growing in a region. Latitude and altitude of a place determine the climate of a place. Hence, natural vegetation of a place also depends on the latitude and altitude of the place.
The surroundings in which an organism lives has both the living and non-living elements, and these surroundings constitute their environment. Our environment has two components?biotic and abiotic. All living beings, whether plants or animals, are affected by the air, temperature, water, light and soil. Each region consists of different set of plants, animals and microorganisms. Thus, each region has specific of plants and wildlife, which differ in size and type. The dwelling place of organisms, which provides them with suitable conditions To live, breed and flourish is called the habitat. All animals need a particular habitat for their development and growth.
Natural vegetation can be broadly grouped into three categories:
i. Forests
ii. Grasslands
iii. Desert Vegetation or Shrubs
FORESTS
The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that offer the earth with many kinds of life forms. Forests are found in areas where there is high rainfall over 500 millimetres. Forests are divided into Tropical and Temperate
Forests. These two are further subdivided: Tropical forest
1. Tropical Rainforests or Tropical Evergreen
2. Tropical or Deciduous Monsoon Forests
Temperate forest
1. Temperate Deciduous Forests
2. Temperate Coniferous Forests (Taiga)
3. Mediterranean Vegetation
Tropical Rainforests or Tropical Evergreen Forests
Location?Tropical Rainforests are found between latitudes 5°N and 5°S of the equator. They grow in the Amazon Basin (Brazil), West Africa (Southern Nigeria and Congo), South- East Asia (Indonesia) and North and North-East
Australia (State of Queensland).
Climate?the Tropical Rainforests experience high temperatures all the year round, (about 26°C) and very high annual rainfall, over 2,000 millimetres. There is high percentage of humidity. The warm, moist rising air causes convectional rain daily in the afternoon.
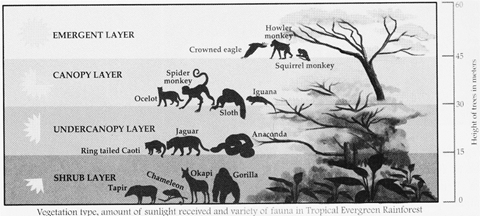
Vegetation and Animals-the forests are very dense and there is luxuriant growth of vegetation. Trees grow and shed their leaves at different times of the year, which gives the forests an evergreen appearance. Hardwood trees such as mahogany, ebony, meranti and rosewood are found in plenty. The top most layer of these forests is called the emergent followed by the canopy layer. The undercanopy layer is below the canopy layer and the forest floor is the shrub layer or ground layer.
Geography Reveals
The Democratic Republic of Congo is considered to be the "Natural Zoo of the World" because of its rich biodiversity.
Different animals occupy different layers of these forests. Animals like apes, sloths, bears also reptiles (snakes), insects, frogs, ant eaters and pygmallions dominate these forests. Rivers in these forests contain many species of fish and reptiles.
Geography Reveals
The Amazon rainforests are often called as the "Lungs of the Earth" because this region has most dense forests which produce oxygen in abundance.
Tropical Deciduous Monsoon Forests
Tropical Deciduous forests are also called Monsoon forests.
Location: These forests exist in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, South China and Northern Australia.
Climate: These forests experience an average annual rainfall of over 1500 millimetres. The average temperature measures around 20-40°C.
Vegetation and Animals: The vegetation is less dense as compared to the Equatorial Rainforests. Trees include teak, sal and sandalwood. Deciduous forests occupy the greatest area in India. These forests are home to a variety of wildlife that includes the Asiatic lion, leopard, rhinoceros, elephant, water buffalo, deer and antelope as well as different species of monkeys, reptiles and also birds.

Tropical Deciduous Monsoon Forests
Temperate Deciduous Forests
Location: The Temperate Deciduous Forests lie between 40° and 60° north and south of the equator. They are found in New Zealand and North-western parts of USA.
Climate: Areas having Temperate Deciduous Forests have lower temperatures and rainfall that affect the structure and characteristics of these forests. A wide range of temperature differences is experienced that can be between
-2°C and 18°C. The deciduous trees shed their leaves during autumn. For this reason, this season is also known as the fall. During winters, the ground is covered with snow and it is difficult for trees to get water from the frozen ground.

Temperate Deciduous Forest
Vegetation and Animals: Oak, chestnut, beech, sycamore and maple trees constitute the Temperate Deciduous Forests. Many animal species such as deer, foxes, squirrels and badgers are found here. Various kinds of birds also live in this region.

Animals of tropical region
Temperate Coniferous Forests (Taiga)
Location: The Temperate Coniferous Forests or Taiga lie between latitudes 50°N and 70°N. They are found in Alaska, Northern Canada, northern parts of Scandinavia, USA and Russia. They can be found in the high mountains of other regions as well.
Climate: Winter temperatures are below 0°C. Winters continue for about 6 months and rain occurs mostly in summers and is less than 500 millimetres a year.
Vegetation and Animals: Trees in the Temperate Coniferous Forests are tall, softwood, evergreen and conical in shape which allows the snow in winters to slide down easily. The needle-like
 Temperate Coniferous Forests
Temperate Coniferous Forests
Leaves have a small surface area which minimises water-loss through transpiration. Large areas of forests are covered with chir, spruce, pine and fir trees. They are used for making paper and newsprint.
Animals found here are hare, vole, reindeer, wolf, bear, etc. Very few birds are seen in this region
Mediterranean Vegetation
Location: The Mediterranean Vegetation grows between latitudes 30° and 45° north and south of the equator. It is found in areas lying around the Mediterranean Sea as well as in southern California (USA), in parts of Peru and in South- west Australia.
Climate: Regions of the Mediterranean Vegetation are hot and dry in summers and have mild wet winters.
Vegetation and Animals: Typical examples of the Mediterranean vegetation are maquis

Mediterranean Forests
Vegetation (a variety of scrub or cactus type plants) in Europe and chaparral vegetation (a kind of scrub) in California. Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, grapes and figs are grown in groves and orchards. These forests are known as the "Orchards of the World." There is not much wildlife here.

Gropes harvesting in the Mediterranean region
Geography Reveals
The Mediterranean Region is known as the "Orchards of the World" because maximum variety of fruit are found in this region only.
GRASSLANDS
These are the areas, where grasses form the main type of vegetation due to low rainfall. Grasslands are divided into (i) Tropical Grasslands or Savannas and (ii) Temperate Grasslands.
Tropical Grasslands or Savannas
Location: The Tropical Grasslands are found between 10° and 20° latitudes, in the tropical region. They are found mainly between the deserts and the equatorial forests. They are known by different names in different regions. In Venezuela, these grasslands are known as the Llanos, in Brazil as Campos, and in Africa and Australia, they are known as the Savannas. These grasslands are generally absent in Asia.

Savannas Grasslands
Climate: The summers are wet but the rainfall is untimely and unreliable measuring about 500 to 800 millimetres a year, and temperatures vary from 21°C to 32°C
Vegetation and Animals: The vegetation of the Tropical Savannas include long and short grasses with sharp blades, and scattered trees of baobab and acacia. Grasses grow to about 3 metres during the rainy season. Some grasses, such as the elephant grass, grow as high as 5 metres. During the dry season, these grasses wither and turn brown. These grasslands support herbivores such as zebras, giraffes and antelopes, as well as carnivores such as lions, hyenas and panthers.

Animals in the savanna Grasslands
Temperate Grasslands
Location: The Temperate Grasslands are found in the interior of those continents that lie on the mid-latitudes between 40° and 50° north and south of the equator. In the Southerr Hemisphere, they are spread over the interior
South Africa where they are known as Veld; the Murray-Darling Basin of Australia where they are known as the Downs and Paraguay and North Argentina in South America where they are known as the Pampas.

Prairie Grasslands
The Temperate Grasslands are also found in the Northern Hemisphere too. These areas include: North America where they are called Prairies; Russia and Eastern Europe where they are called Steppes and North and North-west China they are known as Xilingol.
Climate: The Temperate Grassland experience very long and cold winters, i.e. about five months and a temperature of 0°C or lower. The rainfall is low and unreliable, measuring less than 500 millimetres per annum.
Vegetation and Animals: Perennial grasses grow in the Temperate Grasslands. In the Prairies of North America, tall grasses grow where rainfall is higher than 500 millimetres as and shorter grasses grow where rainfall is lower than 400 millimetres. Scrubs and Spinifex grasses grow where rainfall is the lowest. Wild buffaloes, bisons, antelopes and Prairie dogs are the common in the regions of the Temperate Grasslands.
SHRUBS
Deserts are areas where rainfall is scarce. The vegetation in deserts is sparse. Desert vegetation is further divided into: Hot Desert Vegetation and Cold Desert Vegetation or Cold Tundra Vegetation.

Prairie Dog
Hot Desert Vegetation
Location: The Tropical deserts are found on the west coasts of continents between latitudes 20°N and 30°N as well as 20°S and 30°S of the equator. The Sahara and Namib Deserts in Africa, Simpson Desert in Australia, the Thar Desert in Asia and the Atacama Desert in South America are all examples of Tropical or Hot Deserts.

Hot desert vegetation
Climate: Temperatures in summers rise high with an average of around 30°C. Winter temperatures are very low. Cloudless skies cause intense loss of heat through ground radiation and therefore, temperatures are very low at night. Rainfall is irregular and very low, less than 250 mm a year. There is low humidity because of high rate of evaporation. Cold Ocean

Jack Rabbit
Currents along the western side of the continents are partly responsible for the lesser amount of rainfall in these areas. Besides, the winds that blow offshore also prevent rainfall.
Vegetation and Animals: Vegetation is very sparse in the Hot Tropical Deserts. However, some of the noted species of plants include cacti, mesquite, agave and thorny bushes. Bighorn sheep, camels, scorpions, tarantulas, vultures, coyotes, rattle snakes. Jack rabbits and lizards are the special animals found in the Hot Tropical
Desert. Their bodies are adapted to the extreme temperatures of deserts.
Cold Tundra Vegetation
Location: Cold Tundra Vegetation is found in the Arctic Region, Antarctic Region and on the mountain tops.
Climate: The Climate here is so cold that the ground is frozen for most part of the year. There is
Very low insolation due to the slanting angle of the Sun's rays; therefore, very less amount or Sun's heat reaches to these parts of the earth.

Tundra vegetation
Vegetation and Animals: Trees do not grow in these extreme conditions. In summers, some water is available in these regions as the ice melts, so vegetation comes to life. Tundra vegetation includes only a few short flowering plants, mosses and lichens. Seeds of flowering plants remain dormant during the long cold winter. Tundra plant have a very short life cycle. They complete their life cycle during summers in less than 60 days.
Animals have thick skins or fur to protect them from the extreme cold. Reindeer, polar bear, arctic fox, wolf, musk ox, walrus and whale are a few animals of this region.
Human activities have led to changing the forested landscape completely. This has led to depletion of forest and wildlife. It is important that deforestation and clearance of grasslands is stopped.

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
