Probability
Category : 9th Class
Probability
An experiment in which all possible outcomes are known and the exact outcome cannot be predicted in advance is called a random experiment.
e.g. (1) Tossing a coin. (2) Rolling an unbiased die.
The set S of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the sample space.
e.g., (1) In tossing a coin, sample space (S) = {H, T}
(2) In rolling a die, sample space (S) = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
Probability is a concept which numerically measures the degree of certainty of the occurrence of events.
In a random experiment, let S be the sample space and let E be the event. Then probability of occurence of E
\[=P\left( E \right)=\frac{n\left( E \right)}{n\left( S \right)}\]
, where n (E) is the number of elements favourable in E, and n(S) is the number of distinct elements in S.
Note: (1) 0
\[\le\]
P (E)
\[\le\]
1
(2) If P (E) =1, then the event E is called a certain event and if P(E)=0 then the event E is called an impossible event .
Important points:
(a) A coin has 2 sides - one side is head (H) and the other side is tail (T).
(b) A die is a cube with 6 faces - with numbers (or dots) 1 to 6 on each face.
(c) Description of a normal pack (or deck) of cards (52):
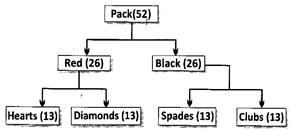
The cards in each suit are Ace(A), King(K), Queen(Q), Jack(J), 10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3 and 2. The cards A, J, Q and K are called honours and the cards 2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 and 10 are called numbered cards. The cards J, Q and K are called face cards.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
