Important Terms and Concepts - Physical Features of India
Category : 9th Class
IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS
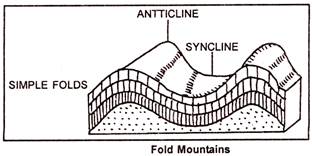
10. Fold mountains. Mountains formed due to the folding of the earth's crust, e.g., Himalayas.
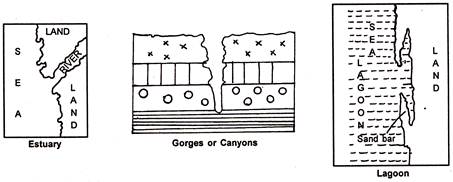
11. Estuary. A funnel shaped mouth of the river. The river joins the sea directly without depositing silt. It does not form delta, e.g., Tapi and Narmada rivers.
12. Lagoons. Shallow salt water lakes almost cut off from the sea by a line of rocks (sand bars) sub-merged in the sea.
13. Gorge/canyon. Formed due to erosional activity of a river. It is an I-shaped valley having steep vertical walls on either side of the river.
14. Convectional currents in the mantle. Heat from within the earth makes the molten rock in the mantle rise, forming convectional currents. Rising currents tear the crust apart, dividing it into large fragments called tectonic plates.
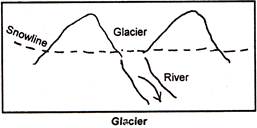
15. Glacier. A slow moving river of snow and ice formed above the snowline.
16. Basin. An area drained by river and its tributaries.
17. Catchment Area. The region which drains all the rain-water into a river or tributary.
18. Delta. An area of low, flat land-shaped like a triangle, where a river splits and forms several distributaries before entering the sea. This area contains large deposit of silt-alluvial soil.
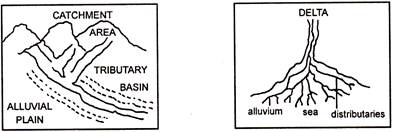
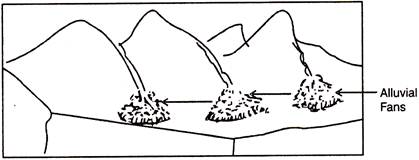
19. Alluvial fans. Himalayan rivers, flowing down the slopes of the mountains, reach the plains and form triangular-shaped alluvial deposits, with their base towards the plain called' alluvial fans.
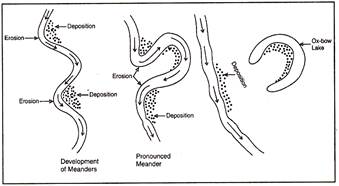
20. Meanders. The side to side wandering of a river channel, best developed in river deposits on the flood plains.
21. Ox-bow lake. The development of river meanders into large loops. Eventually the 'neck' between a looped meander is cut and the river straightens its course, leaving a cut-off loop or an ox-bow lake.
22. Atoll. A circular, or horse shoe-shaped coral reef.
23. Bhabar. A divison of northern plains, along the foothills of Shiwaliks from river Indus to Tista. It has porous bed and contains pebbles.
24. Tarai. It is a part of Northern plains along the foot hills of the Himalayas. It is generally a marshy area with thick growth of forest and wildlife.
25. Bhangar. The older alluvium of the northern plains. It forms alluvial flat uplands above the level of the flood plains and contains Kankar.
26. Khadar. The younger alluvium of the flood plains has fertile soil but is subject to floods.
27. Sedimentary rock. A rock formed by consolidation of sediments derived from erosion of the land. As these rocks have distinct layers, they are also known as stratified rocks, e.g., limestone, sandstone.
28. Metamorphic rocks. A rock resulting from the sedimentary and igneous rocks changing their original characteristics and appearance as a result of extreme heat, pressure and chemical action inside the earth's crust, e.g., marble, quartzite.
29. Greater Himalayas. The northernmost range of the Himalayas also known as Himadri range.
It is the highest mountain range of the Himalayas with an average height of 6100 metres above the sea level. It has the tallest peaks in the world, e.g.. Mount Everest, Kanchenjunga.
30. Middle range of the Himalayas. It is also known as the lesser Himalayas or Himachal range.
It lies between the Himadri range in the north and the Shiwalik range in the south. Its height varies from 3500 to 5050 metres above the sea level.
31. Shiwaliks. It is the southern most range of the Himalayas and runs parallel to the first two ranges.
This range has been formed by the depositional work of the rivers rising from the Himalayas.
The rock material in this range is still unconsolidated.
32. Tributaries. Small streams or rivers, which join the main river are called tributaries, e.g., Yamuna, Gomti are tributaries of Ganga river. Tributaries add more water and silt into the main river.
33. Distributaries. When the main river breaks up into small channels at its mouth, distributaries are formed. Distributaries distribute the water of the main river into small channels. Distributaries are formed in the deltas.
34. Pass. A narrow gap or opening between high mountains, through which communication takes place is known as gap. Himalayas have passes like Shipkila pass, Nathula pass, Bomdila pass.
35. Landslides. In the hilly regions, due to heavy rainfall, the unconsolidated material from the hills falls apart, this is called landslide. Landslides mostly occur in Shiwaliks.
36. Igneous rocks. They are formed by cooling and solidification of magma. They are crystalline, e.g.. Granite, Basalt.
37. Duns. Small hill-like structures formed by rivers depositing unconsolidated material in heaps. Shiwaliks contain duns.
38. Doab. The land between two rivers is locally known as Doab (in Punjab : do means two and ab means water)
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
