Modern Aspects of Banking
Category : Banking
Modern Aspects of Banking
Technology has transformed the global world of banking and financial services beyond recognition. No other industry offers more complex challenges and more exciting opportunities than banking. Computerization of the business of banks has been receiving great importance. The banking institutions have already crossed 70% level of computerization of their businesses.
AUTOMATED TELLER MACHINE
Automated Teller Machine is a computerized machine that provides the customers of banks the facility of accessing their account for dispensing cash and to carry out other financial and non-financial transactions without the need to actually visit their bank branch.
Types of ATMs
Free transactions at ATMs: With effect from November 01, 2014, a bank must offer to its savings bank account holders a minimum number of free transactions at ATMs. However, it is not applicable to Basic Savings Bank Deposit Accounts (BSBDA) as withdrawals from BSBDA are subject to the conditions associated with such accounts.
Transactions at any other bank's ATMs at Metro locations: In case of ATMs located in six metro locations, viz Mumbai, New Delhi/ Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru and Hyderabad, banks must Offer their savings account holders a three-time free transactions (Including financial and transactions) in a month.
Failed ATM transaction:
The customer should file a complaint with the card issuing bank at the earliest. This is applicable even if it was carried out at another bank's/non-bank's ATM.
Banks have been mandated to resolve Customer complaints by re-crediting the customer's account within 7 working days from the date of complaint. However, if the complaint raised by the customer is not resolved, banks have to pay Rs. 100 a day for delays in re-crediting the amount within 7 working days from the date of receipt of complaint.
The compensation has to be credited to the account of the customer without any Claim being made by the customer. If the complaint is not lodged within 30 days of transaction, the customer is not entitled for any compensation for delay in resolving his/ her complaint.
Credit Card
A credit card is a Plastic card issued by Banks to enable the cardholder to pay a merchant for goods and services, based on the cardholder's promise to the card issuer to pay them for the amounts so paid plus other agreed charges. Central Bank of India was the first public bank to introduce Credit card.
Debit Cards
Debit Cards, on the other hand, do not allow credit. The account usually debited immediately or on the same day when the card has been used to draw money or make purchases. No credit period is allowed.
Prepaid cards
A prepaid card works a bit like a gift card - you top it up with money, and you can only spend up to that amount. Often it is used by travellers to carry holiday money and by anyone without a normal bank account - generally kids, teens and people with poor credit ratings.
Smart card
It contains an electronic chip which is used to store cash. This is most useful when you have to pay for small purchases. For example bus fares and coffee bills. No identification, signature or payment authorisation is required for using this card. The exact amount of purchase is deducted from the Smart card during payment and is collected by smart card reading machines. No change is given.
Co-branded cards
They are credit cards issued by card companies that have tied up with a popular brand for the purpose of offering certain exclusive benefits to the consumer. For example, the Citi-Times card gives you all the benefits of a Citibank credit card along with a special discount on Times Music cassettes, free entry to Times Music events, etc.
RuPay Card
Kisan Credit Card
The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) introduced by the NDA Government in August 1998 has emerged as an innovative credit delivery mechanism to meet the production credit requirements of the farmers in a timely and hassle-free manner. The card is valid for five years and subject to annual renewals.
This KCC card offering Credit to the farmers in two types viz.
The scheme is under implementation in the entire country by the vast institutional credit framework involving Commercial Banks, RRBs and Cooperatives and has received wide acceptability amongst bankers and farmers. It was first proposed in the Budget 1998- 99 by then Finance Minister Yashwant Sinha. In the subsequent years, NABARD prepared a Model Kisan Credit Card Scheme in consultation with the major Banks on the recommendations of R V Gupta Committee.
Repayment:
Cash Credit: Crop loans as well as working capital for agriculture and allied activities to be provided as revolving cash credit limit repayable in 12 months
Term Loan: Repayable within a maximum period of 5 years, depending on the type of activity/ investment and repayment capacity Point of Sale Machine
A point-of-sale (POS) terminal is a computerized replacement for a cash register which can process credit and debit cards. A customer needs to enter a card PIN to complete the transaction using the POS terminal.
Merchant Discount Rate (MDR)
MDR is capped for debit cards but not for credit cards. Effective July 1, 2012, RBI capped the MDR for debit cards at 0.75 per cent of the transaction amount for value up to Rs. 2000 and 1 per cent for a transaction amount for value above Rs. 2,000. For credit cards, the MDR varies between 1.5 per cent to 2.5 per cent.
Electronic Funds Transfer at Point of Sale- (EFTPOS)
EFTPOS is an electronic payment system involving electronic funds Transfers based on the use of payment cards, such as debit or credit cards, at payment terminals located at points of sale.
MICR (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition)
It is a technology which allows machines to read and process cheques enabling thousands of cheque transactions in a short time. MICR code is usually a nine digit code. First three digits: Represent the city code that is the city in which the bank branch is located. Next three digits: Bank code; Last three digits: Bank branch code; for example, if you have an account with Axis Bank, New Delhi (Defence Colony) then its nine digit - MICR code will be 110211004 where:
110, the first three digits representing the city code for New Delhi.
211, the next three digits representing the bank code for Axis bank;
And 004, the last three digits representing the bank branch code for Defence Colony.
IFSC (Indian Financial System Code)
The Payment Systems such as National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) & Centralized Funds Management System (CFMS) used IFS Codes. IFSC is developed by the Reserve Bank of India.
The code consists of 11 Characters:
First 4 characters represent the entity Fifth position has been defaulted with a 0 (Zero) for future use
Last 6 characters denotes the branch identity e.g. ICIC0000438
SWIFT Code
It is a unique identification code for both financial and non-financial institutions approved by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). SWIFT Standards, a division of the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), handles the registration of these codes.
Electronic Clearing Service (ECS)
The Reserve Bank of India offers the Electronic Clearing System (ECS) for faster payments and collections.
Two variants:
ECS Credit: ECS Credit is for making bulk payment of amounts. Under this scheme, a single account is debited and then multiple accounts are credited. Example: A company has 50 employees and at the start of month, it gives salary to all the employees; so, instead of crediting each account separately, the company can use the ECS Credit Scheme.
ECS Debit: ECS Debit is for bulk collection of amounts. Under this scheme, multiple accounts are debited and then a single account is credited. Example: Many people go for insurance policies and they have allowed the payment of their premiums from their account. Now, it is possible that on a single day, many customer accounts are to be debited to have the premium from them. Here ECS Debit scheme can be used.
Mobile Banking
Mobile phone banking takes one step ahead of internet and telebanking. The customer can do a banking activity, without even making a phone call. The most obvious advantage of mobile phone banking over telebanking and internet banking is that it is truly "Any Time Any Where Banking". There are broadly two types of services that a customer could avail through mobile phone.
(a) Alert Services - Alert services help a customer keep a track of the activity on his accounts and;
Internet banking
Bank on the Net Internet banking has become a necessity in today's busy lifestyles. Using this mode to transact saves precious time and effort. From across the seven seas, as long as the customer has an access to the internet, he can have an access to his bank. Internet banking allows a customer to conduct a plethora of banking activities using the net. The best part about internet banking is the convenience offered along with total confidentiality and safety. The virtual ease with which a customer can bank today is reassuring.
Fund Transfers
Fund Transfers Internet banking or online banking allows a customer to transfer funds from one account to another, across branches and cities. Some banking institutions have gone one step ahead by offering the customers the facility to transfer money from his account to that of any person with an account at the same bank or any bank, any time and from anywhere. All the customer has to do is submit a signed declaration stating that he wants to access this facility.
RTGS, NEFT an IMPS
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) is based on the gross settlement where the transaction is settled on an instruction by instruction basis. In RTGS, the minimum amount should be above Rs. 2 lakh and maximum amount is Rs. 10 Lakh. National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) is an electronic fund transfer system that operates on a Deferred Net Settlement (DNS) basis which settles transactions in batches. NEFT has no limit either minimum or maximum - on the amount of funds that could be transferred.
|
(National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) |
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) |
|
NEFT and RTGS and settlement systems by RBI while IMPS is settlement mechanism introduced by National Payment Corporation in 2010. |
|
|
There is no limit - either minimum or maximum - on the amount of funds that could be transferred using NEFT. However, maximum amount per transaction is limited to Rs. 50,000/- for cash-based remittances within India and also for remittances to Nepal under the indo-Nepal Remittance Facility Scheme. |
(RBI has not fixed the maximum amount. It has given liberty to the bank to decide the maximum amount.) The minimum amount to be remitted through RTGS is Rs. 2 lakh. There is no upper ceiling for RTGS transactions. |
|
NEFT operates in hourly batches - there are twelve settlements from 8 am to 7 pm on week days (Monday through Friday) and six settlement from 8 and to 1 pm on Saturdays. |
The RTGS service window for customer's transaction is available to banks from 9.00 hours to 16.30 hours on week days and from 9.00 hours to 14:00 hours on Saturdays for settlement at the RBI end. |
|
(a) Inward transaction - Free no charge to be levied. (b) Outward transactions at originating bank branches - charges applicable for the remitter - For transactions up to Rs. 10,000 - Rs. 2.50 (+ Service Tax) - For transactions above Rs. 10, 000 up to 1 lakh: not exceeding Rs. 5 (+ Service Tax) - For transaction above Rs. 1 lakh and up to Rs. 2 lakhs not exceeding Rs. 15 (+ Service Tax) - For transactions above Rs. 2 lakhs: not exceeding Rs. 25 (+ Service Tax) |
(a) Inward transaction – Free, no charge to be levied. (b) Outward transaction - Rs. 2 lakh to Rs. 5 lakh - not exceeding Rs. 30,00 per transaction. Above Rs. 5 lakh - not exceeding Rs. 55.00 per transaction. |
Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) basically involves a transfer mechanism using the mobile phone. Many banks allow the transfer through this mechanism including the reputed banks like State Bank of India, ICICI Bank and Axis Bank. Here is the limit set by the bank.
For example. State Bank of India permits only one beneficiary in a calendar day which means one cannot send money through IMPS for more than one beneficiary in a day.
Pay Utility Bills
The customers can now even pay telephone, mobile and electricity bills over the net. However, some banks limit the facilities like these and creation of new fixed deposits and demand drafts requests to regular banking hours. In case, the customer puts in the request after banking hours, the bank promptly executes it on the next working day. So it is definitely better than standing in queues at utility offices or banking premises on a working day.
National Automated Clearing House (NACH) NPCI has implemented "National Automated Clearing House (NACH)" with an aim to consolidate multiple ECS systems running across India and provides a framework for the harmonization of standard & practices.
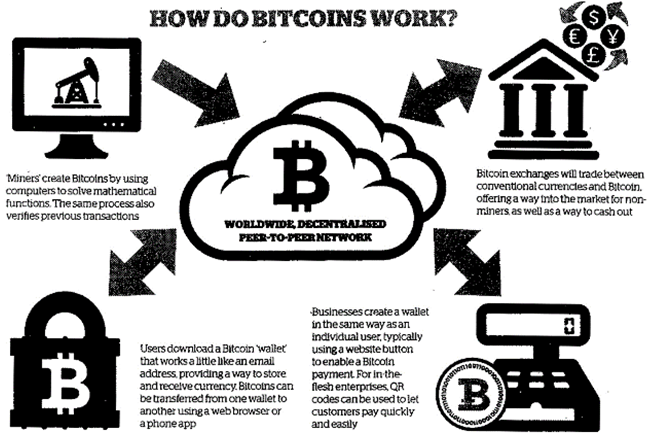
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency payment system invented by an unidentified programmer or group of programmers, under the name of Satoshi Nakamoto. The system is peer-to- peer and transactions take place between users directly, without an intermediary. It is the first decentralized peer-to-peer payment network that is powered by its users with no central authority or middlemen. Bitcoin was the first practical implementation and is currently the most prominent triple entry bookkeeping system in existence.
Block Chain Technology
ICICI Bank is the first bank in the country and among the first few globally to exchange and authenticate remittance transaction messages as well as original international trade documents related to purchase order, invoice, shipping & insurance, among others, electronically on block chain in real time.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
